A Guide to IAM Compliance: Set Your Organization Up for Success

When it comes to successfully securing your organization today, the three most important words may be who, what, and how. Who can access your network, what company assets will they have access to, and how are the access privileges used?
Identity access management (IAM), or the practice of monitoring and regulating the who, what, and how of cyber network access, has become a popular topic in modern security circles–and with good cause. Almost two-thirds (61%) of all breaches today involve credentials, or the lack of the correct ones, when attempting access. Correctly identifying, authenticating, and authorizing all who receive access to your company’s network is a critical component of security and compliance today. Failing to create and maintain effective identity access management policies and practices can jeopardize your most sensitive data and leave your organization at risk of compliance violations.
This article will explore IAM and IAM compliance, why it’s important, and why it needs to be a core component of your security and compliance program. We’ll also discuss specific requirements for the cloud and how your organization can prepare to demonstrate proof of IAM compliance for auditors.
What is IAM?

Identity access management is the practice — including all organizational tools, processes, and policies — of managing user identities and controlling user access to an organization’s network systems. Users can be employees, partners, vendors, or applications. Access refers to the type of contact or action allowed and the degree or level of that contact.
IAM frameworks provide a critical gatekeeping security function, regulating all access to the most sensitive and valuable assets within a business. IAM frameworks typically include a user identity repository and numerous tools for user identity provisioning. They also maintain a login and authentication system with access history, password account management, and an audit function.
IAM policies and procedures are a critical component of every organization’s security and compliance policy. They’re designed to ensure only approved entities gain access to IT resources through three essential steps: identification, authentication, and authorization.
Identification is the ability to recognize the user as present in the system, usually by a title or user name. Authentication is the ability to prove true identity through knowledge (password), a possession (smartcard, token), or an inherent trait (fingerprint, eye scan). Authorization is the granting of permission after identifying and authenticating a user, and it’s usually based on one’s role in an organization.
Most IAM programs deploy robust access controls with predetermined access privileges based solely on job roles and the duties required for the position. Multi-factor authentication requires two means of identity validation, and adaptive authentication challenges system users with multiple login steps based on risk profiles. Previously authenticated and authorized users can enjoy the convenience of a single-sign-on function, allowing access to numerous applications through one initiation.
Why is IAM important?

Who gains access to your network and what they can do when inside has massive security and compliance implications. Protecting sensitive data, complying with privacy regulations, and your business’s future may depend on how your team manages network access.
One cannot overstate the importance of establishing an effective IAM policy as a core component of your security policy. IAM policies lay the foundation for establishing an access control system, tracking all network activity, minimizing breaches, and reducing risk. A robust IAM program is also essential for maintaining compliance, as virtually all security compliance frameworks (from SOC 2 to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to CIS Security Controls to PCI DSS) have requirements and guidelines around IAM.
Effective IAM eases the IT workload (e.g., through fewer access-related password reset tickets) while reducing the time and resources required to monitor network access. It also streamlines productivity, allowing faster access for partners and vendors without slowing workflow. As smartcards and biometrics replace traditional passwords, employees will enjoy a faster, more convenient user experience.
IAM in the cloud
With many organizations switching to storing data in cloud environments such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Azure Cloud, it’s important to use fine-grained access controls when employing IAM in the cloud. Fine-grained access permissions allow precise access guidelines that specify the exact individual granted privilege, the accessed resources, and the specific conditions under which access is granted.
The security implications are significant for off-premise cloud environments requiring strict access regulations. Access is automatically denied by default and only granted by specific permissions, usually for employees with AWS SSO or workloads with IAM roles. Fine-grained access controls are highly effective for helping enforce the least-privilege access policies required for securing cloud environments. These specific, detailed guidelines help provide stricter security control and optimize cloud security posture.
Attribute-based access controls (ABAC) allow the automatic scaling of fine-grained permissions. These authorization controls are based on attributes like job level, position, and team affiliation and assist in reducing the number of individual permissions needed for a fine-grained control framework.
Understanding IAM compliance

Protecting customer data privacy is a priority for today’s lawmakers, and governing access privileges plays a significant role in this equation. Today, many data privacy regulations like PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2, and NIST SP 800-53 require strict IAM policies restricting user access, enforcing access controls, conducting reviews to certify processes, and performing audits that require documented proof of access governance. PCI DSS provides a simple example–to comply with this standard mandated by credit card brands, a vendor must provide evidence of existing IAM policies and processes restricting access to environments where any cardholder data presides.
Maintaining IAM compliance is a five-step process that originates with granting or removing individual access privileges. IAM policies must define user identities, establish authentication and authorization methods, and outline what type of activity corresponds to access privileges at resource locations. Following the permission phase, IAM controls must be enforced across all SaaS applications, both on-premise and in the cloud. Regular reviews and system certification support policy and procedure enforcement–this step requires establishing the guidelines for proof of access governance and regulatory compliance. Finally, your team will need to collect evidence to document the successful functioning of the IAM program and prepare for an audit.
Documenting the success of your IAM program in meeting compliance regulations is becoming more challenging than ever. As companies add more SaaS applications for business convenience, reduced visibility is often the price. With the explosion of mobile access points, the battle to identify and regulate network entry becomes nearly impossible, especially as cloud and hybrid infrastructures struggle to mesh with legacy IAM tools.
Fortunately, one needn’t look hard for the solution. Automation significantly evens the playing field by expediting the IAM identification, authentication, and authorization processes while simplifying the steps and activities required for compliance verification. Below are some benefits automation can bring to IAM:
- Creation of a single, comprehensive identity repository, allowing the use of a standardized identity model
- Streamlining the access review process using risk-based rule guides and the development of attribute-based access controls
- Simplifying all provisioning necessary to keep your identity access model current and agile
- Boosting control enforcement when teamed with analytics such as triggering alerts and quickly processing access request escalations
- Simplifying evidence collection, proving compliance for audits, and scaling all IAM activities to meet the growing needs of a modern organization
Preparing for an IAM audit

Is your team prepared to collect the evidence needed to document required access reviews and prove the effectiveness and compliance of your IAM program?
Compliance audits provide an opportunity for a checkup of your IAM program and overall security health. These periodic assessments can prove beneficial, allowing the removal of all old users, groups, partners, policies, and practices. Audits ensure that your network users have proper identification and authorization for their degree of access and that your IAM program meets current security, compliance, and business needs.
IAM teams should conduct regular (at least quarterly) identity access reviews, checking that all users have role-appropriate privileges while disabling and deleting all unnecessary accounts, keeping the system current and functioning at optimum efficiency. Remember that external auditors will request evidence proving regular access reviews, so be sure to document all evidence and make it easily accessible come audit time.
Below is a list of eight audit preparation tips your team should follow internally to ensure the effectiveness of your IAM system and help prepare for your next audit:
- Create and maintain IAM policy: Make sure all IAM framework policies are clearly defined and understood. Remember that your IAM policies should be a core component of your overall security policies.
- Establish and outline IAM procedures: Clearly outline all procedures and practices required to maintain IAM policies, including identifying all stakeholders, roles, and responsibilities.
- Strictly regulate privileges: Uphold the least privilege access control based on the necessity of job requirements. Limit the time someone has privileged accounts and monitor those accounts closely.
- Practice separation of duties: This effective risk-avoidance practice breaks up all responsibilities and tasks, keeping roles and processes separate so no one individual or department has too much access or control.
- Conduct regular access reviews: Employees leave, roles and responsibilities change, and jobs get eliminated, so schedule regular system access reviews to stay abreast of all identification, authentication, and authorization changes with your IAM system. Also, document these access reviews as evidence for compliance audits.
- Keep all accounts current: Keep your IAM systems clean and current by prioritizing the upkeep of all accounts. Don’t allow unused accounts or access to remain open; remove all unnecessary users, groups, functions, or processes as soon as possible.
- Monitor generic accounts: Generic accounts can get overlooked, so monitor them regularly. Avoid assigning admin rights or using generic passwords and instantly delete these accounts when they become idle.
- Maintain immaculate records: Keep flawless records of all IAM system policies, processes, and activities. This documentation will provide evidence proving compliance governance and help improve your IAM program’s effectiveness.
Utilize identity and access management software
IAM software solutions can streamline identity access management for today’s organizations. IAM teams need fast, centralized, and scalable software tools, allowing authorized users to access data with real-time convenience. IAM software can significantly expedite three critical functions: confirming user identity by rapidly cross-referencing database credentials, granting or denying authorization, and regulating each user’s necessary level of access.
When choosing an IAM software tool, look for one that:
- Helps answer the three essential questions of who (gains access), what (assets they can access and the degree), and how (access is used)
- Offers cross-application and cross-network authentication
- Seamlessly integrates with all systems, including legacy
- Reduces IT costs and workload
- Assists in maintaining compliance and simplifies the documentation process
- Simplifies and expedites the enforcement of all IAM policies
Okta, Auth0, and Ping Identity top the list of recommended IAM software providers in 2022. Hyperproof integrates with Okta, so IT can conduct access reviews in Hyperproof directly instead of logging into Okta separately. The access review documentation can be stored directly in Hyperproof.
Hyperproof helps you manage IAM compliance and audits
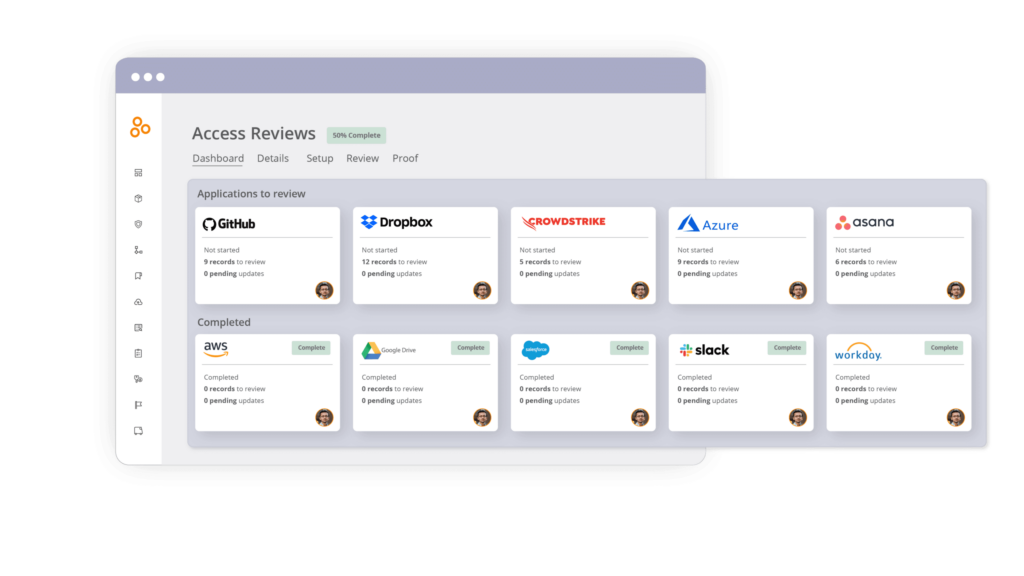
Hyperproof simplifies the often challenging processes of maintaining compliance and audit preparation. Hyperproof’s IAM software solution allows your team to:
- Automatically update your IAM policy using the LiveSync feature to pull the latest document version from G-Drive, SharePoint, Dropbox, or other cloud-based file storage systems.
- Describe your IAM controls while mapping them to multiple requirements, satisfying multiple compliance standards without duplicating evidence collection.
- Prove you’re following IAM policy and procedures while simplifying the process of regularly conducting user access reviews.
- Integrate your system with popular IAM software such as Okta, including valuable compliance data as part of regular access review procedures.
- Utilize Hypersync, our third-party connector to other cloud-based services, to automatically pull and update the required List of Groups, List of Users, and password policies from various cloud services (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, etc.).
Sign up for a customized demo to learn how Hyperproof can boost your compliance program for proactive risk reduction and increased security.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












