Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) Compliance Guide

Financial institutions are increasingly more dependent than ever on Information and Communication Technology (ICT). This dependency offers numerous benefits, like increased efficiency and the ability to provide innovative services, but also exposes financial institutions to a wide array of risks, like cyber attacks and ICT disruptions.
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is a regulatory framework introduced by the European Union (EU) to address these challenges. DORA is designed to enhance the resilience of financial institutions against cyber attacks and ICT disruptions by requiring robust risk management and cybersecurity measures, helping to mitigate risks and support operational continuity. This explains why the scope of DORA is so wide and why its rules are so strict for most financial institutions, although there are exemptions for smaller or less critical entities and service providers.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand key aspects of DORA, its significance, and the requirements financial institutions must meet under the framework. We’ll also explore how to get your DORA compliance up to speed faster and how to stay compliant for the long term.
What is DORA?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is part of the EU’s Digital Finance Package, introduced to bolster the resilience of financial entities against ICT-related risks. DORA aims to ensure that financial institutions can withstand, respond to, and recover from all types of ICT-related disruptions and threats. This regulation applies to a broad range of financial entities, including banks, insurance companies, investment firms, payment service providers, and other financial intermediaries.
The significance of DORA
DORA is significant for four main reasons:
1. Enhanced security
By imposing stringent requirements on ICT risk management, DORA aims to strengthen the operational resilience of the financial sector.
2. Consumer confidence
By ensuring that financial institutions are better prepared to handle ICT disruptions, DORA aims to enhance consumer confidence in the financial system.
3. Harmonization
DORA seeks to harmonize ICT risk management practices across the EU, providing a unified regulatory framework that ensures consistency and comparability.
4. Operational resilience
DORA emphasizes the importance of operational resilience, ensuring that financial institutions can continue to operate and deliver critical services despite severe disruptions.
How to meet DORA requirements
The main components of DORA include risk management, incident reporting, resilience testing, third-party risk management, and governance. Here’s how you can meet these requirements.
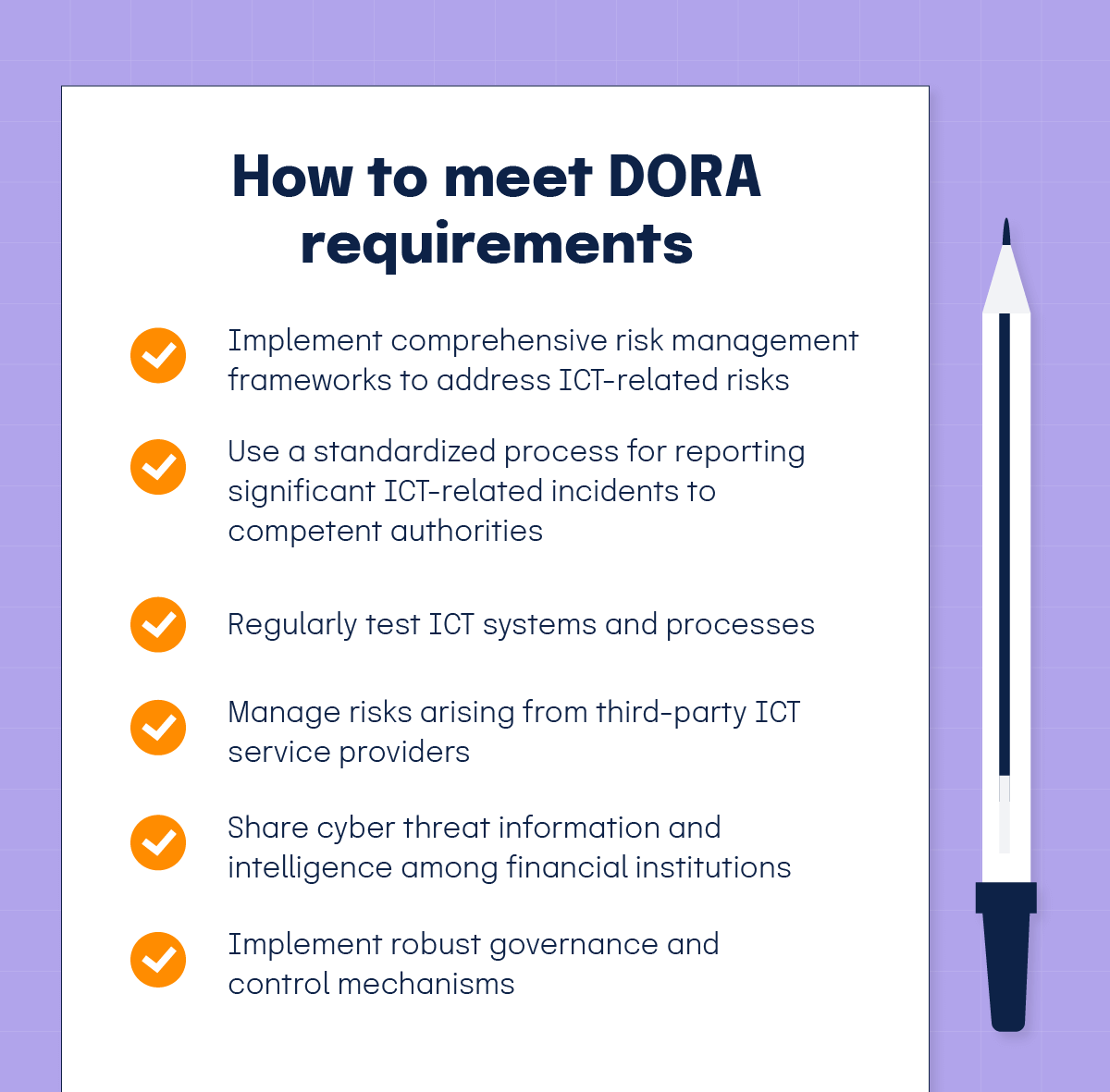
1. ICT risk management requirements
DORA mandates that financial entities implement comprehensive risk management frameworks to address ICT-related risks. To comply, you’ll need adequate:
Risk identification
Financial institutions must identify and assess ICT risks that could impact their operations. This means assessing your risks arising from internal systems, processes, and external threats.
Risk protection
Implement the right controls to protect your ICT systems and data from identified risks. This includes measures such as encryption, access controls, and network security.
Risk detection
Continuous monitoring and detection mechanisms must be in place to identify potential ICT incidents and vulnerabilities in real-time.
Risk response
Develop and implement detailed response plans to address ICT incidents promptly and effectively.
Risk recovery
If a significant disruption occurs, establish robust recovery plans to ensure the continuity of critical services.
2. ICT incident reporting
DORA introduces a standardized process for reporting significant ICT-related incidents to competent authorities. This ensures timely and effective communication and mitigation of incidents. Key aspects of incident reporting include:
Incident classification
Financial institutions must classify ICT incidents based on their severity and impact on operations. Classification criteria can include the number of users affected, data losses, geographical spread, economic impact, and incident duration.
Reporting timelines
DORA specifies strict timelines for reporting incidents, ensuring that authorities are informed promptly. If you experience an incident, you must notify authorities within four hours of determining the incident is major, but in any case, no later than 24 hours from the moment you became aware of the ICT-related incident. This is followed by intermediate reports at the latest within 72 hours from the submission of the initial notification, even where the status or handling of the incident has not changed, followed by a final report no later than one month after either the submission of the intermediate report or after the latest updated intermediate report. If an incident is not initially classified as major within 24 hours but is later reclassified as major, the initial notification must be submitted within four hours from the reclassification.
Incident details
Following an incident, you must provide detailed information including its nature, impact, and measures taken to mitigate it.
3. Digital operational resilience testing
Regular testing of ICT systems and processes is a cornerstone of DORA. Financial institutions are required to conduct various types of tests to ensure adequate resilience against potential disruptions. These tests include:
Penetration testing
Threat-led penetration testing (TLPT) uses simulated cyber-attacks to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in ICT systems, following the TIBER-EU framework methodology for qualifying institutions.
Disaster recovery drills and scenario-based testing
Mandatory exercises to test the institution’s ability to recover from ICT disruptions and validate recovery procedures and testing based on hypothetical scenarios that assess your institution’s preparedness and response capabilities for different types of ICT incidents and disruptions.
Tabletop exercises
Discussion-based exercises that evaluate the effectiveness of your incident response and recovery plans through structured scenario walkthroughs without actual system testing.
4. Third-party risk management
DORA also places significant emphasis on managing risks arising from third-party ICT service providers. Financial institutions must comply with:
Due diligence
Financial institutions must conduct thorough due diligence on third-party service providers to assess their risk profiles and resilience capabilities, as third-party risks directly impact the institution’s operational resilience.
Contractual agreements
Contracts with third-party providers must include comprehensive provisions covering ICT risk management, incident classification and reporting procedures, digital operational resilience testing requirements, and information sharing obligations.
Ongoing monitoring
Continuously monitor the performance and security of third-party providers through integration into the overall ICT risk framework, including regular reviews of third-party risk strategy and maintenance of a contractual arrangements register to ensure ongoing compliance with DORA requirements.
5. Information sharing
DORA establishes requirements for the sharing of cyber threat information and intelligence among financial institutions. This collaborative approach aims to enhance collective resilience against cyber threats. Key aspects include:
Information sharing
Financial institutions must exchange threat intelligence and best practices as part of DORA’s information-sharing requirements. The information you exchange may include cyber threat information and intelligence, including indicators of compromise, tactics, techniques, and procedures, cyber security alerts, and configuration tools.
Anonymity and confidentiality
Financial institutions must implement measures that ensure the anonymity and confidentiality of shared information.
6. Governance and control
Robust governance and control mechanisms are essential for effective ICT risk management. DORA mandates that financial institutions:
Organizational structure
Establish appropriate organizational structures and governance frameworks that support effective ICT risk management, including clear lines of accountability and decision-making authority.
Establish clear roles and responsibilities
Clearly define roles and responsibilities for managing ICT risk within your organization, with the management body maintaining ultimate responsibility for ICT risk management and ensuring appropriate oversight mechanisms are in place.
Senior management involvement
Ensure that senior management maintains ultimate responsibility for ICT risk management, approves ICT risk strategies and policies, and oversees their implementation and effectiveness.
Regular reporting
Provide regular reports on ICT risk management activities, including risk assessments, incident reports, testing results, and third-party risk management to senior management and the board of directors, ensuring appropriate escalation procedures are in place.
The broader implications of DORA
While DORA primarily focuses on enhancing the cyber resilience of financial institutions, its comprehensive approach to ICT risk management within this sector establishes rigorous standards that may influence best practices in other industries. By setting a high standard for ICT risk management, DORA serves as a benchmark for other industries that are increasingly reliant on digital technologies.
The principles and practices outlined in DORA are specifically tailored for financial institutions and their ICT service providers, though other sectors may review these financial sector standards when developing their own operational resilience frameworks. The goal is to improve overall operational resilience and security postures, specifically within the financial sector and its supporting ICT infrastructure.
Impact on financial stability
DORA contributes to financial system stability by enhancing the operational resilience of financial institutions against ICT-related disruptions. Financial institutions play a crucial role in the economy, and ICT-related disruptions to their operations can have significant consequences for service continuity and operational resilience. By strengthening institutions’ ability to withstand and recover from ICT disruptions, DORA supports the overall operational resilience of the financial system. This operational resilience helps maintain continuity of financial services, supporting confidence in the financial sector’s ability to manage ICT-related risks.
Enhancing customer protection
DORA’s emphasis on ICT risk management and incident reporting supports operational resilience, which indirectly contributes to maintaining service continuity for customers. In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, ensuring the continuity and security of ICT systems that support financial services is paramount. By mandating stringent security measures and timely incident reporting, DORA strengthens operational resilience, which supports service continuity for customers. This focus on operational resilience is particularly important as more financial services rely on digital infrastructure.
Promoting innovation and digital transformation
While DORA’s primary focus is on enhancing operational resilience through stringent ICT risk management requirements, its clear regulatory framework may provide greater certainty for financial institutions. By providing a clear regulatory framework for managing ICT risks, DORA may provide greater regulatory certainty and foster a more predictable environment for financial institutions to pursue digital initiatives. This regulatory clarity may support the development of new and innovative financial products and services that leverage digital technologies while maintaining robust risk management standards.
Fostering a culture of cyber resilience
A culture of cyber resilience not only implements technical controls and procedures but also promotes a mindset that prioritizes security and resilience. Financial institutions must ensure that staff members have appropriate competencies and understanding of their roles and responsibilities in managing ICT risks as part of DORA compliance requirements. Effective implementation of DORA’s ICT risk management requirements necessitates that organizations develop appropriate staff competencies and awareness of security and resilience responsibilities.
Challenges of implementing DORA
While DORA provides a comprehensive framework for enhancing ICT resilience, its implementation poses several challenges for financial institutions. These challenges include:
Complexity of ICT systems
Financial institutions often operate complex and interconnected ICT systems that span multiple geographies and business functions. Implementing DORA’s requirements across these systems requires comprehensive planning and systematic execution. To comply with DORA, you should conduct thorough assessments of your ICT infrastructure, identify vulnerabilities, and implement appropriate controls as mandated by the regulation.
Resource constraints
Implementing DORA may require significant investments in technology, personnel, and/or processes. Financial institutions, especially smaller ones, may face resource constraints that hinder their ability to comply with DORA requirements. Allocating your resources to enhance ICT resilience while balancing other business priorities can be challenging.
Third-party dependencies
Managing risks arising from third-party ICT service providers is a critical aspect of DORA. Financial institutions often rely on a wide range of third-party providers, each with its own risk profile and resilience capabilities. Ensuring that all third-party relationships comply with DORA’s requirements requires robust due diligence processes and continuous monitoring, including maintaining registers of ICT third-party providers’ contractual arrangements that must be available for competent authorities, which can be resource-intensive.
Evolving threat landscape
The cyber threat landscape is constantly changing, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. To stay ahead of these threats, you should continuously update your risk management practices and security controls. This requires ongoing investment in threat intelligence, advanced security technologies, and skilled cybersecurity personnel.
Enhancing DORA compliance with Hyperproof
For organizations striving to meet these standards, Hyperproof offers you an integrated, automated solution to simplify and enhance compliance efforts. Here’s how Hyperproof can help your organization to achieve DORA compliance:
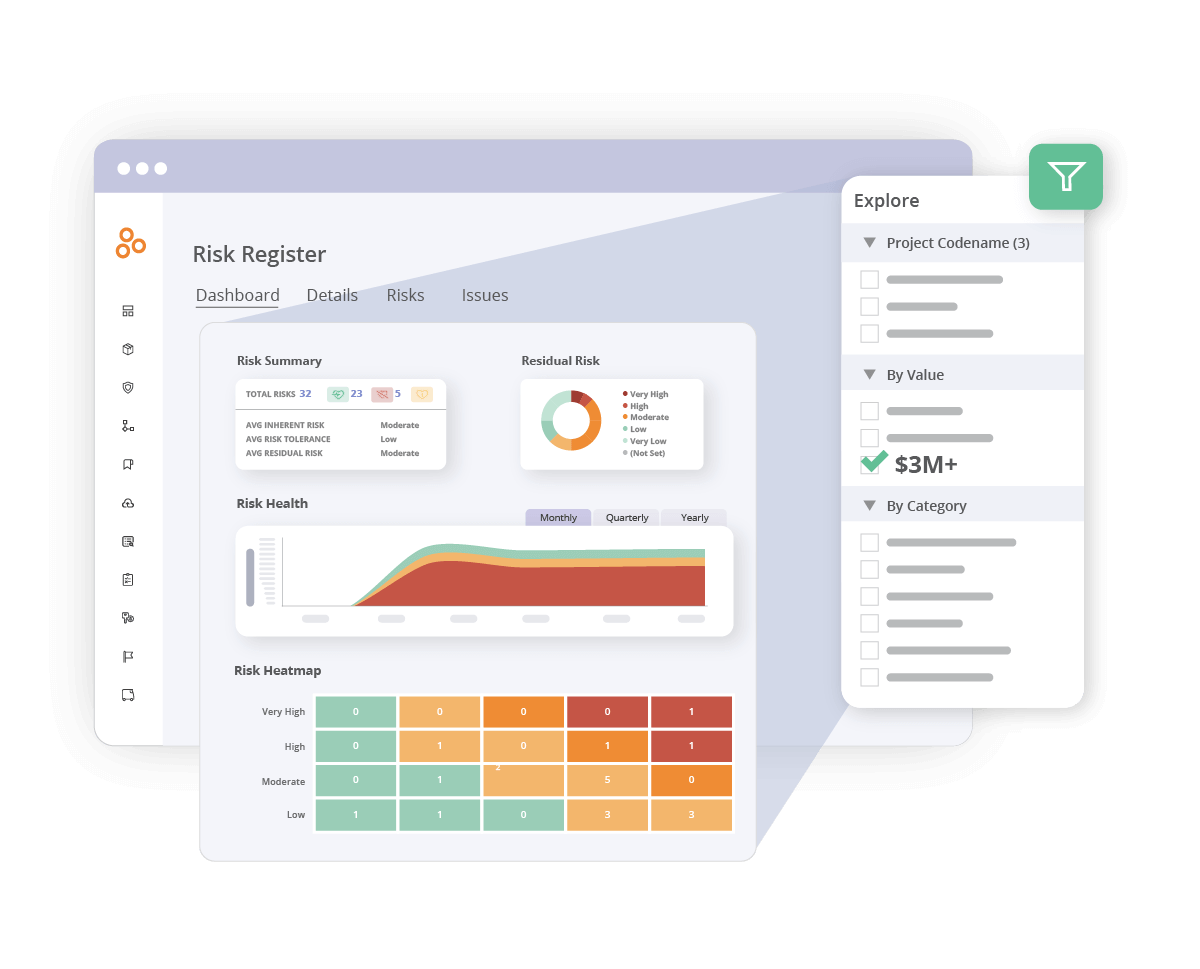
1. Centralized risk management
DORA emphasizes comprehensive risk management strategies to protect against ICT-related risks. Hyperproof’s powerful risk management capabilities can help you achieve DORA compliance:
Risk register
Hyperproof’s risk register allows you to collect, track, and manage all identified risks in one place, ensuring no risk is overlooked.
Risk evaluation and prioritization
Organizations can evaluate risks based on various criteria, like tolerance, inherent risk, likelihood, and impact. This helps you prioritize and mitigate critical risks effectively.
Real-time tracking
Our platform provides real-time visibility into risk posture, enabling continuous monitoring and adjustments as needed.
2. Automated evidence collection
DORA requires institutions to maintain detailed records and evidence of compliance:
Hypersyncs that automate evidence collection
Hyperproof uses Hypersyncs to automate the collection of compliance evidence. This means your documentation is always current and audit-ready when you need it.
Integration with existing tools
By integrating with tools like Jira, Asana, and ServiceNow, Hyperproof allows seamless evidence collection from various workflows, reducing your team’s manual workload and errors.

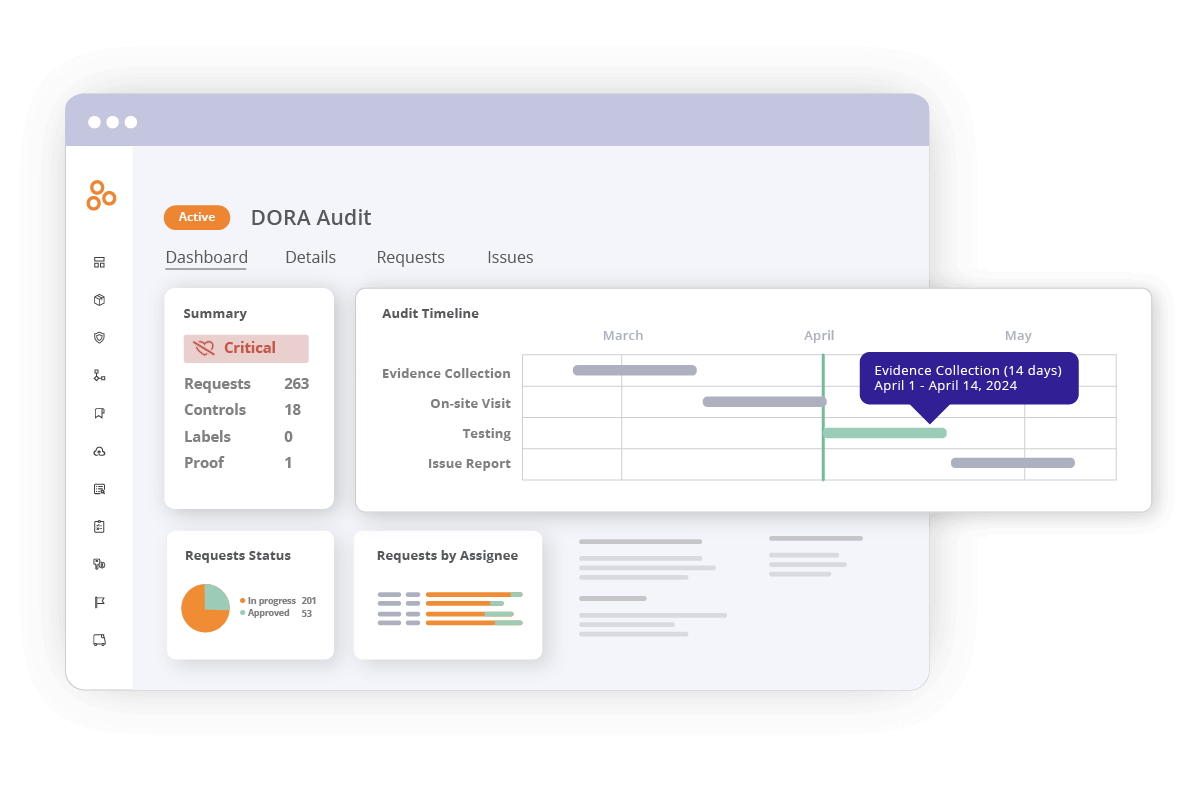
3. Comprehensive audit management
DORA mandates regular audits to ensure compliance with ICT risk management standards, which you can streamline with Hyperproof:
Centralized audit management tools
Hyperproof centralizes all your audit-related activities, linking audit requests directly to controls and their associated evidence. This streamlines the audit process and reduces preparation time.
Collaboration with auditors in one place
Organizations can invite auditors to a dedicated audit space within Hyperproof, making it easier to share information and communicate efficiently while maintaining control over access permissions.
4. Customizable frameworks and reports
To adapt to DORA’s evolving requirements, organizations need flexible compliance tools, such as:
Custom framework capabilities
Hyperproof enables you to upload custom frameworks so you can align your compliance efforts with DORA’s specific requirements.
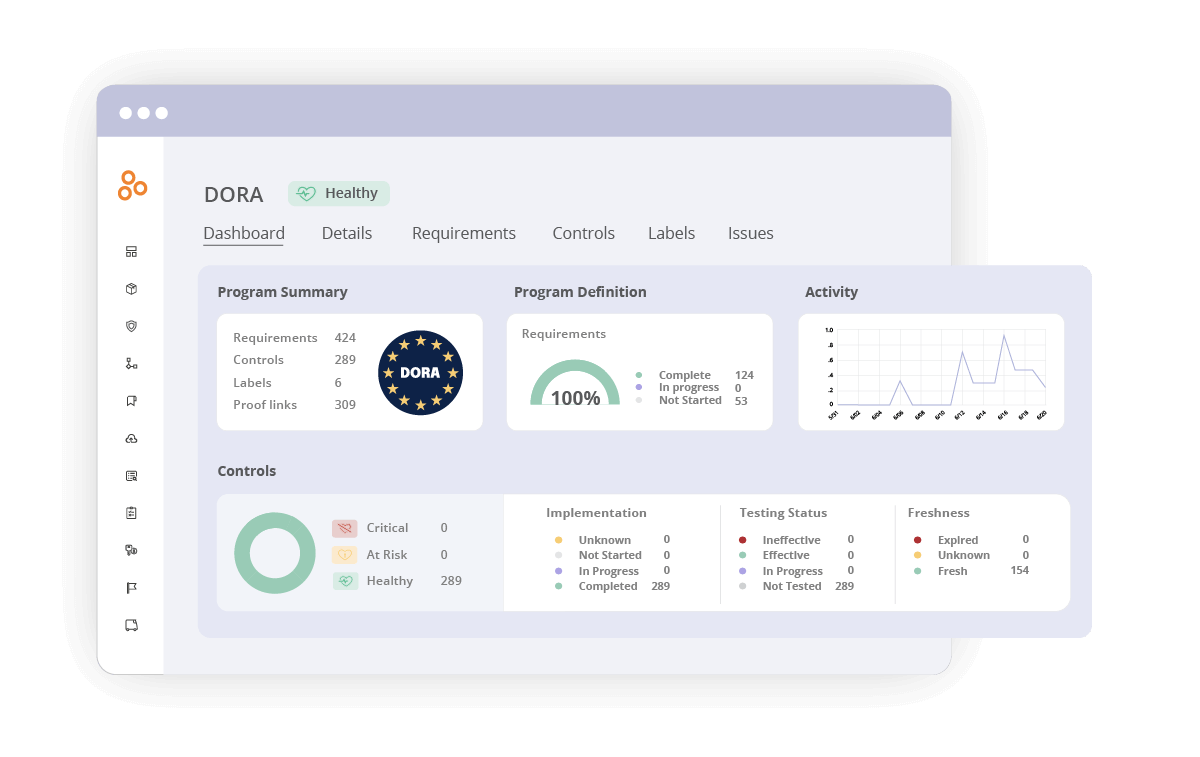
Dashboards and real-time reporting
Our dashboards and customizable reports provide real-time insights into compliance status, helping organizations demonstrate adherence to DORA to stakeholders and regulators.
DORA: A step forward against ICT-related risks
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) represents a significant step forward in enhancing the resilience of the financial sector against ICT-related risks. DORA mandates comprehensive risk management frameworks, regular resilience testing, robust third-party risk management, and information sharing. The goal is for financial institutions to be ready to withstand, respond to, and recover from ICT disruptions and threats.
Ultimately, DORA’s significance lies in strengthening the financial sector’s operational resilience, establishing comprehensive standards for ICT risk management within this sector. In an era of increasing digitalization and cyber threats, DORA is a crucial step toward building more operationally resilient financial institutions capable of withstanding ICT-related disruptions.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?











