Key Elements of an Effective Compliance Audit: A Complete Checklist
Navigating compliance is not just about ticking boxes — it’s about ensuring your organization can thrive in an environment where trust and accountability are paramount. An effective compliance audit doesn’t merely mitigate risks; it empowers you to confidently meet standards, improve stakeholder trust, and avoid penalties that can damage your reputation or bottom line. To make your compliance audit process seamless and impactful, you need a comprehensive plan. This compliance audit checklist will walk you through every essential element — and if you also need a checklist for IT audit, use it as a practical baseline (checklist it audit, audit it checklist) before you start evidence gathering.
1. Assemble your compliance team
The first step you should take during your audit process is assembling your compliance team. An effective audit requires collaboration from a well-rounded team with diverse expertise. Carefully selecting your team ensures a smooth audit process. Key roles include:
Audit coordinator
This individual oversees the audit, ensuring timelines, resources, and goals are managed effectively.
Departmental representatives
These team members provide insights into the specific operations, controls, and challenges of their respective areas.
Compliance specialists
Legal or regulatory experts help interpret requirements and verify compliance with specific standards.
Internal auditors
Provide an independent assessment of internal controls, risk management, and compliance processes, ensuring that the organization adheres to its policies and regulatory requirements.
External auditors (if applicable)
Engage impartial auditors who bring objectivity and credibility to the process.
Ensure that the team is not only knowledgeable but also has access to the resources needed to succeed, such as software tools for tracking progress or regulatory guidance documents.
2. Define the scope of your audit
Next, define the scope of your audit. Defining clear audit objectives starts with aligning your goals with both regulatory requirements and business priorities. Are you assessing internal controls, verifying compliance, or ensuring financial accuracy? Pinpoint your focus early. Bring in key stakeholders — compliance, IT, finance, and leadership — to align expectations and avoid blind spots. Also, use risk assessments, past audit findings, and regulatory mandates to shape your scope.
With your objectives in place, set a clear plan for execution. Whether you’re validating controls, uncovering vulnerabilities, or preparing for certification, defining expected outcomes keeps the process on track. Assign responsibilities, establish remediation timelines, and ensure accountability at every step. A well-planned audit doesn’t just check boxes — it strengthens your compliance posture and drives real improvements.

Every compliance audit begins with a clear understanding of its scope. This means identifying what you need to audit and why it matters. Start by:
Understanding the regulatory environment
Assess the requirements and guidelines specific to your chosen compliance framework. Identify key areas the framework emphasizes, such as risk management, access control, or incident response. Your audit should align with the framework’s objectives, address gaps, and demonstrate adherence to standards. Tailor your approach to reflect the framework’s priorities while supporting your organization’s compliance goals.
Prioritizing audit objectives
Define how the audit aligns with your business goals. For example:
Preparing for certification
A tech company aiming for ISO 27001 certification conducts an audit to evaluate its security controls, policies, and training programs. The goal is to build customer trust, meet contractual demands, and enhance marketability.
Managing risk identified by internal stakeholders
An e-commerce company facing increased fraud conducts an audit to assess payment processing and fraud detection controls. Aligning with PCI DSS, the audit focuses on encryption and incident response, identifying gaps and strengthening defenses to protect revenue and customer trust.
Responding to a past compliance issue
A manufacturing company fined for environmental non-compliance audits its waste management and reporting processes to prevent recurrence. By addressing gaps in documentation and supplier compliance, the audit ensures adherence to regulations and safeguards the company’s reputation.
Evaluating risks to refine audit processes
A well-defined audit scope starts with a risk assessment to determine potential compliance gaps, operational vulnerabilities, and security threats. By analyzing factors such as data sensitivity, regulatory obligations, and past audit findings, organizations can prioritize critical areas. For example, a financial institution evaluating risks under SOC 2 may focus on data encryption, while a healthcare provider aligning with HIPAA may emphasize patient data access controls. By assessing the likelihood and impact of risks, organizations can ensure the audit concentrates on areas that pose the highest compliance and security concerns.
Mapping internal processes
Outline the departments, systems, and processes within the audit’s purview. For example, when auditing data privacy, your scope might include IT systems, employee training records, and vendor management policies. By setting clear parameters, you reduce ambiguity and ensure your audit targets what’s truly important.
Defining audit boundaries
Clearly outlining what is included and excluded from the audit prevents scope creep and ensures alignment with business priorities. Organizations should define scope limitations based on factors such as legal jurisdiction, business functions, and system dependencies. For instance, an audit focused on GDPR compliance may include EU customer data but exclude non-EU operations unless explicitly required. Establishing these boundaries in advance helps manage expectations and prevents unnecessary resource allocation.
Allocating necessary resources
A successful audit requires dedicated personnel, sufficient time, and appropriate technology. Organizations should assign key roles, such as compliance officers, IT security teams, and internal auditors while setting aside time for interviews, testing, and documentation reviews. Investing in compliance software, automated control monitoring, and audit management tools can streamline processes and improve accuracy. Leadership should also ensure cross-functional collaboration by allocating subject matter experts from different departments as needed.
Engaging stakeholders for alignment
Proactive stakeholder engagement ensures that leadership, compliance teams, and operational departments understand and support the audit’s scope. Regular meetings, briefing sessions, and documented expectations help align priorities and address concerns before the audit begins. For example, involving finance and HR teams in a SOC 1 audit ensures that internal controls over financial reporting are accurately assessed. By maintaining open communication, organizations can reduce resistance and enhance audit preparedness.
Documenting the audit scope
A well-documented audit scope serves as a reference point for the audit team and stakeholders. Organizations should create a formal scope document outlining objectives, boundaries, key controls, and resources required. This document should be shared with relevant teams to ensure clarity and alignment. Additionally, maintaining an audit trail in compliance management platforms can provide historical context and facilitate future audits. Hyperproof simplifies scope definition by enabling you to map controls to multiple frameworks so you can understand your current compliance posture and gaps your auditor will likely flag.
3. Conduct a pre-audit assessment
A pre-audit assessment is your opportunity to identify weak points before the formal audit begins. This step functions as a low-pressure rehearsal that can highlight gaps in documentation, processes, or controls. During this phase:
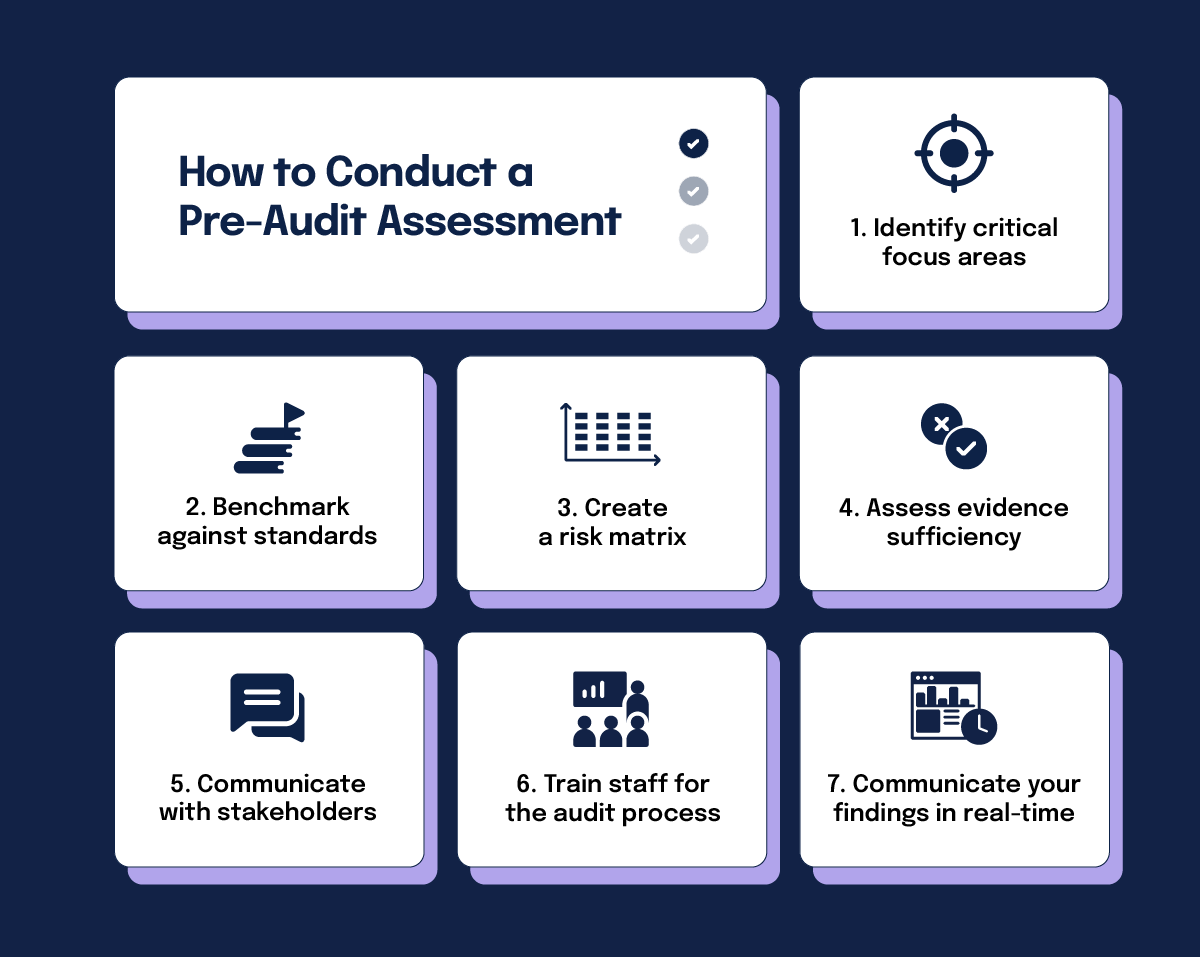
Identify critical focus areas
Analyze past audit findings, industry trends, and regulatory updates to pinpoint areas likely to receive the most scrutiny. For example, if previous audits flagged data privacy concerns, focus on access controls and encryption practices. Reviewing enforcement actions against similar organizations can also highlight key risk areas.
Perform spot checks
Test a sample of controls, processes, or records to identify immediate gaps.
Create a risk matrix
Develop a visual representation of risks, categorizing them by likelihood and impact.
Assess evidence sufficiency
Ensure that documentation and audit trails meet regulatory and auditor expectations. Verify that logs, reports, and approvals provide clear proof of compliance. If evidence is lacking or inconsistent, supplement it with additional documentation or process refinements. If you need a concrete starting point, use an audit readiness checklist to confirm owners, evidence sources, and timelines before the formal audit begins.
An audit risk assessment checklist is especially useful here because it forces alignment on risk ratings, evidence sources, and who owns each mitigation before auditors begin testing.
Communicate with stakeholders
Notify key teams about the audit timeline, expectations, and their specific responsibilities. Regular status updates and pre-audit meetings can align efforts, clarify concerns, and prevent last-minute scrambling. Involving leadership early can also help secure necessary resources and reinforce audit readiness as a priority.
Train staff for the audit process
Equip employees with the knowledge they need to respond to auditor inquiries confidently. Training should cover compliance policies, documentation practices, and how to provide accurate and concise responses. Conducting mock audit interviews can help staff feel more prepared and reduce the risk of miscommunication during the actual audit.
Treat the pre-audit as a constructive exercise rather than a critique. It allows you to address deficiencies proactively, reducing surprises during the formal audit. Think of it as a dress rehearsal that prepares you for the real thing. The benefits of pre-audit readiness check work show up quickly — fewer last-minute evidence scrambles, clearer remediation priorities, and smoother auditor interactions.
Communicate your findings in real-time
At this point, it might be smart to establish a structured reporting timeline that includes preliminary findings, stakeholder briefings, and final report distribution.
Train staff for the audit process
Equip employees with the knowledge they need to respond to auditor inquiries confidently. Training should cover compliance policies, documentation practices, and how to provide accurate and concise responses. Conducting mock audit interviews can help staff feel more prepared and reduce the risk of miscommunication during the actual audit.
Treat the pre-audit as a constructive exercise rather than a critique. It allows you to address deficiencies proactively, reducing surprises during the formal audit. Think of it as a dress rehearsal that prepares you for the real thing.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof enables pre-audit readiness to conduct gap analyses with ease. Automated assessments and customizable templates ensure that your organization is well-prepared for the formal audit.
4. Evaluate risk management practices
Without a structured approach to identifying and mitigating risks, your organization is vulnerable to breaches, fines, and reputational damage. If risk management practices are in-scope of the audit (not all internal audits test this), a strong risk management program includes:
Dynamic risk assessment tools
Implement tools that allow you to update risk assessments in real time as threats evolve.
Cross-functional input
Engage stakeholders across departments to identify risks that might otherwise be overlooked. For instance, cybersecurity risks may involve IT, HR, and compliance teams working together.
Scenario testing
Simulate potential scenarios, such as data breaches or regulatory audits, to evaluate the effectiveness of your controls.
Monitoring and managing risks effectively
An in-scope audit of risk management practices requires evidence of structured risk monitoring. Organizations should establish defined metrics, conduct periodic reviews, and maintain audit trails of risk mitigation activities. Dashboards and reporting tools can help track key risk indicators (KRIs) and ensure timely responses to emerging threats.
Prioritizing risks with clear criteria
Establishing a risk prioritization framework ensures that high-impact threats receive immediate attention. Organizations should categorize risks based on likelihood, severity, and regulatory significance. For example, a financial institution may rank fraud risks higher due to potential monetary losses and compliance violations, while a healthcare provider may prioritize data privacy risks under HIPAA requirements.
Integrating risk management into strategic planning
Risk management should not operate in isolation but instead, inform key business decisions. Organizations can embed risk assessments into budgeting, project planning, and operational strategies. For instance, before expanding to a new market, a company should assess compliance risks tied to regional regulations and data sovereignty laws.
Defining clear roles and responsibilities
A well-structured risk management program assigns accountability at all levels. Organizations should establish risk owners, define escalation paths, and create a governance framework to oversee risk mitigation efforts. Regular training and documented policies help ensure consistency in risk management execution across departments.
Ensuring consistency across all functions
Standardized risk management processes prevent gaps in compliance and security. Organizations should implement uniform risk assessment methodologies, enforce enterprise-wide policies, and conduct periodic cross-departmental reviews to validate adherence. This ensures that risk management practices are applied uniformly, regardless of department or function.
Regularly revisiting and enhancing your risk management practices ensures that you stay ahead of potential threats.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s dynamic risk management allows you to update risk assessments in real time and align mitigation strategies with audit findings. Built-in analytics help prioritize risks effectively.
5. Test internal controls
Internal controls are your safety net. For example, access controls, encryption protocols, and segregation of duties should be tested to ensure they operate seamlessly. They ensure your policies and procedures are not only well-designed but also consistently applied. During this phase:
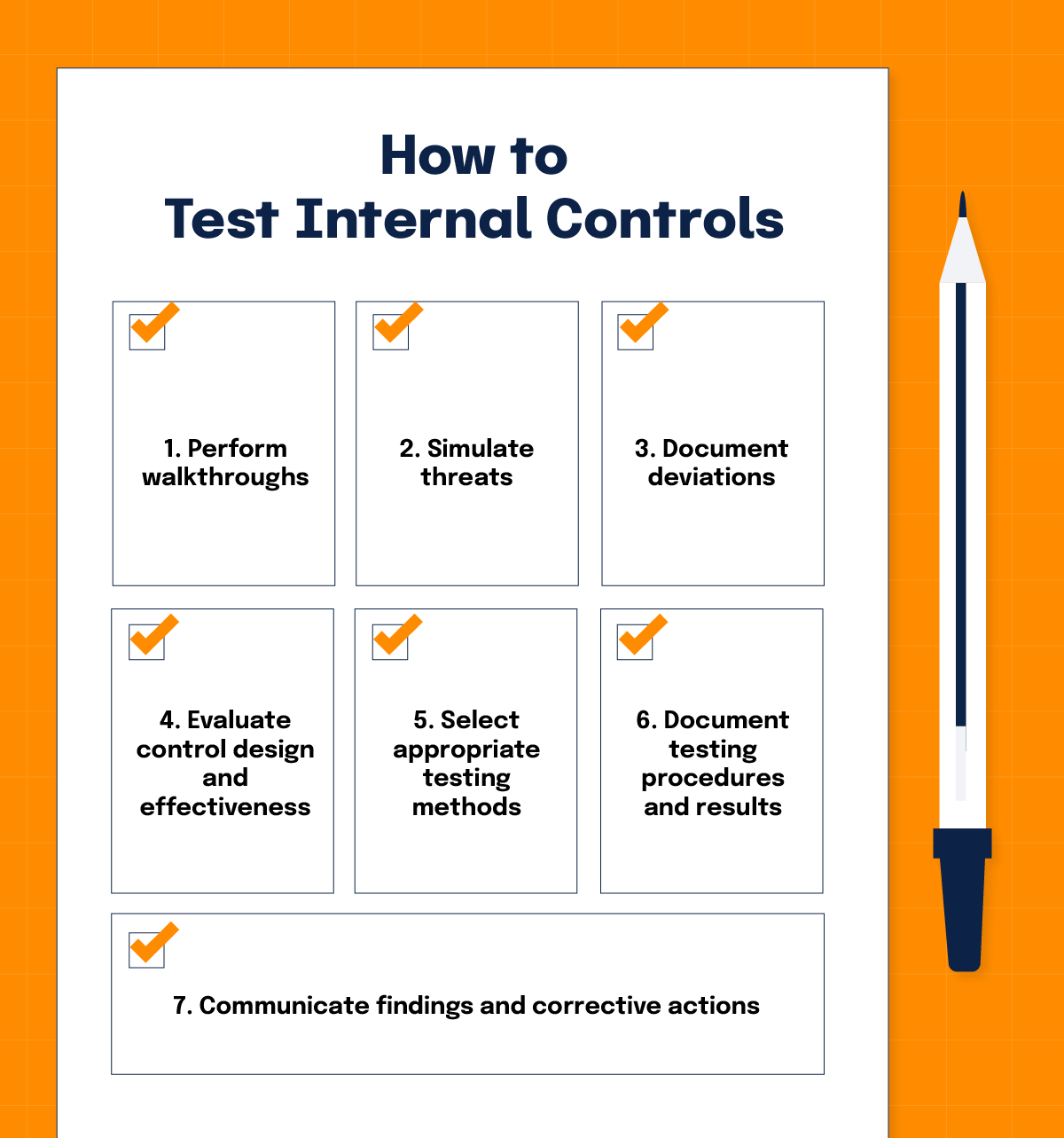
Perform walkthroughs
Observe processes in action to ensure employees follow documented procedures.
Simulate threats
Test the robustness of controls by simulating scenarios like unauthorized access attempts or phishing attacks.
Document deviations
Keep a record of any inconsistencies or failures, along with recommendations for improvement.
Evaluate control design and effectiveness
Assess whether controls are appropriately designed to mitigate identified risks and align with organizational objectives. This involves mapping controls to specific risk factors and regulatory requirements. For instance, if a company is mitigating financial fraud risks, segregation of duties and transaction approval workflows should be tested to confirm they function as intended. Organizations should also analyze historical data to determine whether existing controls have effectively prevented past incidents.
Select appropriate testing methods
Different controls require different testing approaches. Organizations should use a mix of:
Inquiry: Interview employees to confirm their understanding of policies and procedures.
Observation: Watch processes in real time to ensure adherence to documented controls.
Inspection: Review documentation, such as access logs, audit trails, and policy updates, to verify compliance.
Reperformance: Manually re-execute control activities, such as reprocessing a sample transaction, to ensure consistent results.
Document testing procedures and results
Maintain a structured record of control testing activities, including test objectives, methodologies, findings, and any deficiencies noted. Documentation should include timestamps, personnel involved, and supporting evidence such as screenshots, logs, or process checklists. A standardized template for control testing can help ensure consistency across different functions.
Communicate findings and corrective actions
Stakeholders must be informed of test results, especially when control weaknesses are identified. A formalized reporting structure should be in place to escalate critical deficiencies to senior leadership while ensuring operational teams receive actionable recommendations. Organizations should also establish a timeline for corrective actions and track remediation efforts to ensure accountability.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s control testing workflows allow you to automate evidence collection, simulate scenarios, and document results — all in one intuitive platform.
6. Employee training and awareness
A key component of compliance training is preparing employees for interactions with auditors. Organizations should provide guidance on how to answer questions accurately, concisely, and confidently. Best practices include:
Encouraging honesty and clarity
Employees should provide direct answers based on documented policies and procedures rather than speculation or assumptions.
Understanding roles and responsibilities
Employees must know what aspects of compliance apply to their roles and be able to describe relevant processes when asked.
Practicing mock audit interviews
Conducting role-playing exercises with sample auditor questions can help employees feel more comfortable and reduce anxiety.
Emphasizing documentation
Employees should know where to find relevant policies, logs, and records to support their responses.
Training key personnel as audit liaisons
Designating specific employees to interact with auditors can ensure consistency in responses and prevent unnecessary disclosures. Employees play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance. No matter how robust your policies are, they’re only as strong as the people implementing them. These methods assess training effectiveness:
- Audit training content: Verify that training materials are updated regularly to reflect changes in regulations or organizational policies.
- Evaluate participation rates: Confirm that all relevant employees — especially new hires — have completed the required training.
- Measure behavioral impact: Use surveys, quizzes, or incident rates to assess whether training has improved employee compliance behaviors.
Investing in ongoing education programs not only boosts compliance but also fosters a culture of accountability and awareness.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof helps you to establish continuous compliance to ensure alignment with compliance requirements at all times.
7. Review third-party relationships
Your compliance doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Compliance status extends to the vendors, contractors, and partners who interact with your organization. However, third-party relationships aren’t always within the scope of every audit. Assessing third-party relationships involves:
Contractual reviews
Ensure that your contracts clearly outline compliance expectations, such as adhering to data privacy laws or ethical sourcing standards.
Performance metrics
Establish measurable KPIs for vendors that include compliance-related indicators.
Audit rights
Maintain the right to audit vendor practices, and exercise this right when needed to ensure they meet your standards.
To ensure third-party partners adhere to contractual obligations and regulatory requirements, organizations should implement a structured vendor compliance program. This includes conducting periodic compliance assessments, requiring vendors to complete self-assessments or attestations, and integrating automated monitoring tools to track adherence in real time. Clear escalation procedures should be in place for addressing non-compliance, with predefined corrective action plans or contract termination clauses if necessary.
Neglecting third-party compliance could expose your organization to risks that are beyond your direct control.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof enables vendor risk assessments and tracks third-party compliance metrics. You can centralize vendor documentation and streamline audits with built-in tools for performance monitoring.
8. Check data security and privacy measures
If required as part of your compliance audit, few areas are as critical as data security and privacy. With growing regulatory scrutiny, you must ensure robust protections for sensitive data. When the scope of your audit includes data security and/or privacy, remember to focus on:
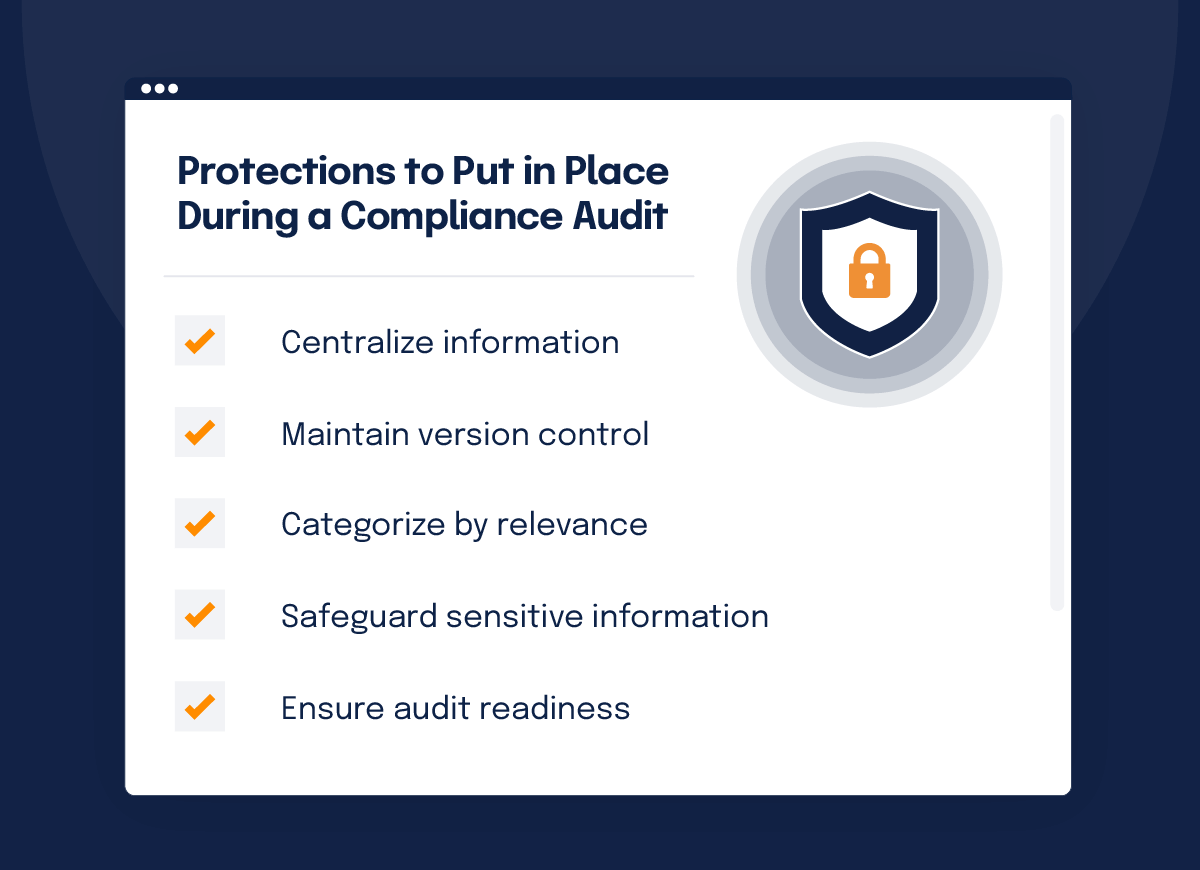
Audit your access management systems
Regularly audit user access privileges to ensure only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data.
Understand where sensitive data resides
Understand where sensitive data resides, how it flows through your systems, and how it’s protected at every stage. Verify data is encrypted both at rest and in transit.
Conduct tabletop exercises
Are incidents tracked, analyzed, and resolved promptly to prevent recurrence? Conduct tabletop exercises to test your team’s readiness to respond to data breaches or cyberattacks.
Ensure compliance with data protection laws
Organizations must align their security policies with frameworks like GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA by implementing regulatory-specific controls. This includes maintaining detailed records of processing activities (ROPA), ensuring lawful data collection practices, and defining data retention policies. Regular internal audits and compliance gap assessments help verify adherence to evolving legal requirements.
Train employees on data security responsibilities
Organizations should conduct regular training on topics such as secure data handling, phishing prevention, and incident reporting procedures. Interactive training modules, simulated phishing tests, and role-specific guidance ensure that employees understand their responsibilities in maintaining data security and privacy.
Maintain organized documentation for audits
Comprehensive records of data security practices should be maintained in a structured manner for easy retrieval during audits. Documentation should include access control policies, encryption standards, incident logs, risk assessments, and evidence of regulatory compliance. A centralized document management system ensures that security policies, data protection impact assessments (DPIAs), and breach response plans are always up to date and audit-ready.
Strong data security measures not only protect you during audits but also prevent costly breaches that could erode stakeholder trust.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s data mapping capabilities and automated monitoring tools allow you to track sensitive data flows, manage access controls, and maintain robust incident response readiness.
9. Gather and organize documentation
Documentation is the lifeblood of any compliance audit – and strong compliance audit documentation makes it easier to prove controls, track evidence, and avoid last-minute scrambling. Auditors need clear, accessible records to verify compliance, and disorganized documentation can derail even the best-prepared audit. To streamline this process:
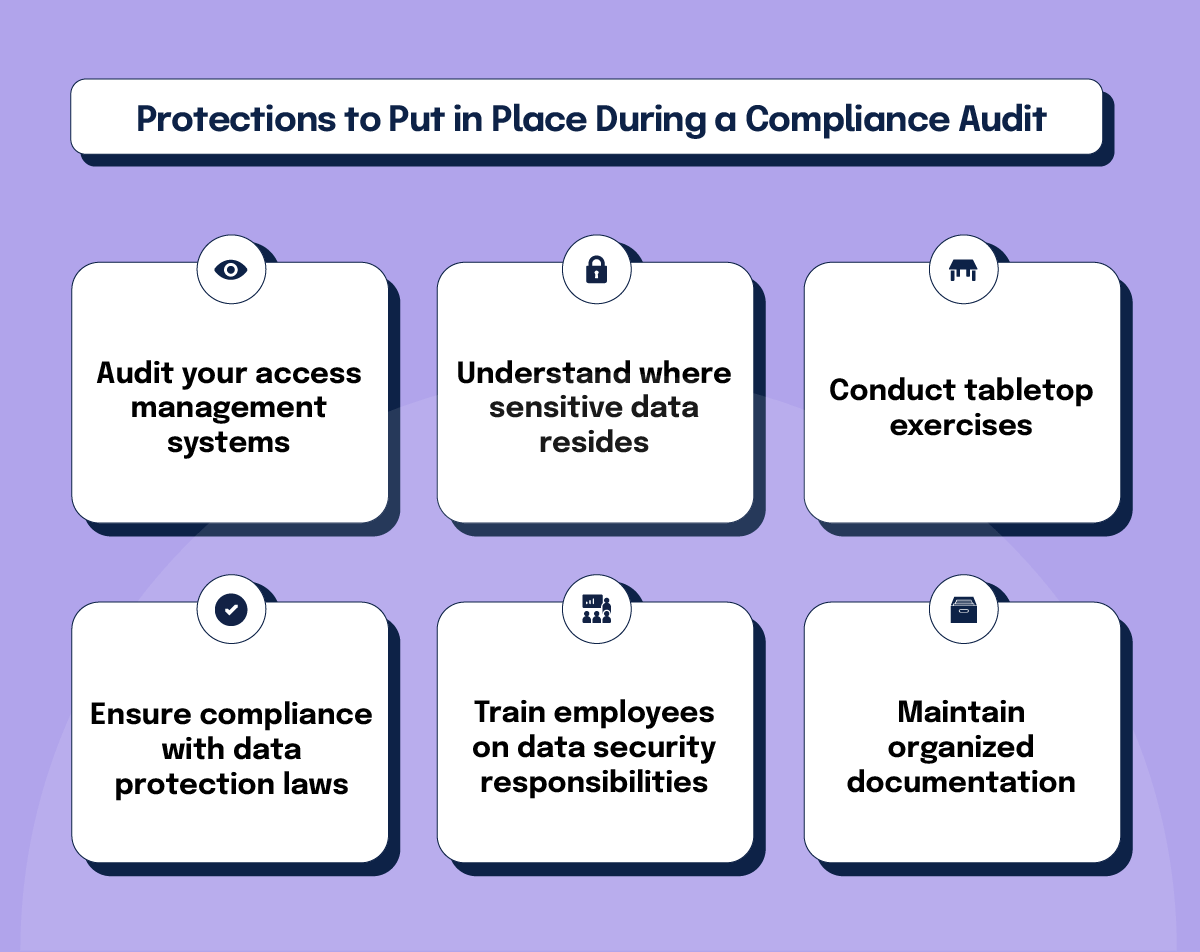
Centralize information
Use a digital platform or document management system to store all relevant records in one place. This reduces the risk of losing critical documents in fragmented filing systems.
Maintain version control
Ensure that policies, contracts, and procedures are updated and tagged with revision histories to reflect their currency.
Categorize by relevance
Group documents into categories such as training records, incident reports, risk assessments, process maps, and access logs. This helps auditors navigate your records with ease.
Safeguard sensitive information
Classify documents based on sensitivity levels and apply appropriate security controls. For instance, use encryption for highly confidential data, limit access to authorized personnel, and implement audit logs to track document views and modifications. For compliance with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA, ensure that personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI) are stored securely and redacted when necessary.
Ensure audit readiness
Develop a checklist of required documents based on regulatory and auditor expectations. Conduct periodic internal reviews to verify that all necessary files are complete, current, and formatted correctly. Assign ownership to team members for maintaining specific categories of documentation to prevent last-minute scrambling.
Proactively filling gaps in your documentation ensures that you’re ready to provide proof for every claim of compliance.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof offers a centralized, secure platform for storing all compliance documentation. Its document management features ensure proper categorization, version control, and easy accessibility for auditors.
10. Conduct a gap analysis
A gap analysis bridges the space between your current state and the desired level of compliance. This exercise helps you prioritize improvements by:
Analyzing root causes: Determine whether deficiencies stem from resource shortages, unclear policies, or process inefficiencies.
Categorizing gaps: Group gaps by criticality — those that pose legal or operational risks should be addressed first.
Assigning ownership: Clearly identify who will be responsible for closing each gap and when. Create an actionable plan to close gaps and prevent future issues. A targeted remediation plan emerging from this analysis keeps your compliance efforts focused and efficient.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s gap analysis tools provide actionable insights by automating root cause identification and tracking remediation efforts, ensuring efficient and effective improvements.
11. Establish an audit trail
A transparent and detailed audit trail demonstrates accountability and compliance over time – and it supports any audit for compliance by showing how controls operated, who approved what, and when remediation happened. A strong audit trail also validates your compliance audit process by showing that your compliance audit procedures are executed consistently – not improvised when an auditor asks. Key components of a strong audit trail include:
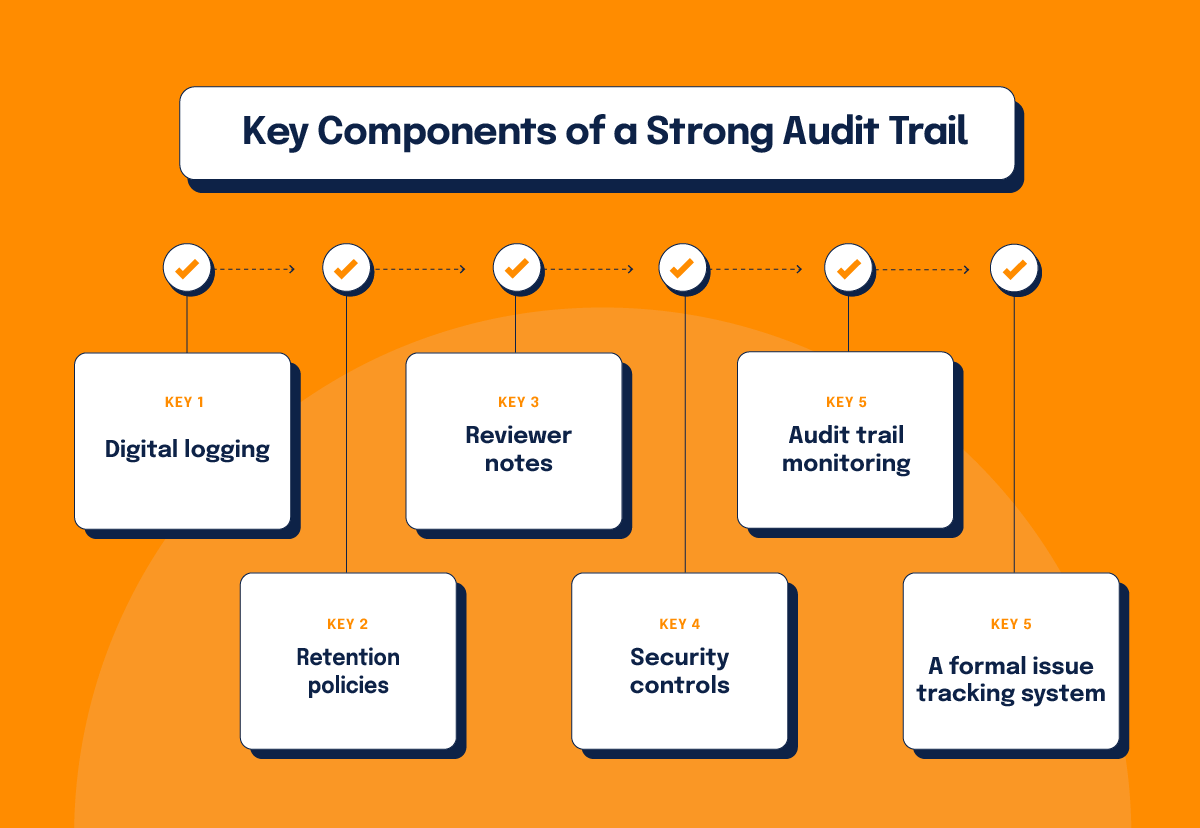
Digital logging
Use automated systems to track changes, approvals, and updates to policies and controls.
Retention policies
Adhere to regulatory requirements for how long specific records must be maintained.
Reviewer notes
Document decisions made during the audit, including the rationale for any corrective actions taken.
Security controls
To prevent unauthorized modifications, organizations should implement security controls such as access restrictions, cryptographic hashing, and immutable logging mechanisms. Audit logs should be stored in a secure, centralized repository with automated backup processes to protect against tampering or accidental deletion.
Audit trail monitoring
Regular reviews of logs help detect inconsistencies, unauthorized access, or process deviations. Organizations should establish periodic audit log reviews, leveraging automated tools to flag suspicious activities. Assigning dedicated personnel to monitor logs ensures prompt investigation and mitigation of anomalies.
A formal issue tracking system
When inconsistencies are identified in the audit trail, organizations must document findings, conduct root cause analyses, and implement corrective measures. A formalized issue-tracking system should be used to log discrepancies, assign remediation responsibilities, and verify resolution. If gaps indicate systemic issues, policy updates or process adjustments may be necessary to prevent recurrence. A comprehensive audit trail not only satisfies regulatory demands but also positions you for success in future audits.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof automatically logs all activities, including control changes, evidence collection, and approvals, providing a tamper-proof audit trail that ensures accountability and compliance.
12. Automate where possible
Automation reduces the burden of manual tasks while improving consistency and accuracy—and it’s a core part of effective audit and compliance management. Consider automating:
Policy updates: Use systems that automatically notify relevant stakeholders when regulations change.
Incident reporting: Deploy tools that enable employees to report compliance violations easily and anonymously.
Monitoring and alerts: Leverage real-time monitoring tools that flag non-compliance issues as they arise.
Investing in automation simplifies compliance management and frees up your team to focus on strategic initiatives.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof automates evidence collection, compliance tracking, and regulatory updates, enabling your team to focus on strategic initiatives while maintaining compliance seamlessly.
13. Communicate findings effectively
The value of an audit is in how the findings are communicated and acted upon. Schedule debrief meetings with relevant teams to discuss key takeaways before the official report is finalized, allowing for clarification and alignment on next steps. Your audit report should:
Highlight strengths
Showcase areas where your organization excels to reinforce stakeholder confidence.
Provide context
Offer background information that explains why certain deficiencies exist.
Deliver actionable insights
Outline clear, specific recommendations for addressing gaps and improving compliance.
Document communication and stakeholder feedback
Maintain a record of all communications related to audit findings, including reports, meeting minutes, and stakeholder responses. Feedback should be logged in a centralized system to track concerns, requested clarifications, and action items. This ensures transparency and provides a historical reference for future audits. Clear and honest communication ensures buy-in from leadership and other stakeholders.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s reporting and dashboard features make it easy to present findings visually, highlighting strengths and areas for improvement to key stakeholders.
14. Follow up and improve
The audit process doesn’t end with the report. Its true impact comes from the improvements you implement. Thorough follow-up means you:
Close critical gaps: Address high-risk issues first, ensuring your organization meets baseline compliance standards.
Track progress: Use project management tools to monitor the status of remediation efforts.
Reassess impact: Periodically evaluate whether implemented changes have effectively addressed the original deficiencies.
Your ability to learn and adapt from the audit process is what sets you apart as a resilient, forward-thinking organization. Continuous improvement transforms compliance from a periodic obligation to a competitive advantage.
How Hyperproof helps
Hyperproof’s project management integrations and continuous compliance monitoring keep your organization on track with remediation plans and improvement initiatives.
Your blueprint for compliance success
An effective compliance audit is a journey, not a destination. By following this detailed checklist and leveraging Hyperproof’s comprehensive compliance platform, you’ll ensure that your organization not only meets regulatory requirements but also builds a foundation for sustainable growth and trust. Start today, and make your next compliance audit a testament to your organization’s commitment to excellence.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












