Everything You Need to Know About the FFIEC

It’s no secret that the financial sector is one of the most highly regulated industries in the United States. Given the wide range of regulatory agencies that exist, who makes the rules? The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC), that’s who.
The FFIEC plays a crucial role in the oversight and regulation of U.S. financial institutions. It’s essential for banks, credit unions, trusts, and mortgage lenders to understand what the council has to say. The FFIEC’s guidelines and standards play a central role in how financial institutions manage compliance and risk.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the FFIEC, its functions, and how institutions can align faster with FFIEC requirements.
What is the FFIEC?
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) is a U.S. interagency council that develops uniform standards, examination procedures, and guidance for federal and state regulators that supervise financial institutions. Rather than enforcing laws directly, the FFIEC sets shared expectations for how banks, credit unions, and other institutions are examined for safety, soundness, and regulatory compliance.
The FFIEC’s origins and purpose
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) is a U.S. interagency council, established by the Financial Institutions Regulatory and Interest Rate Control Act of 1978, that promotes uniform, consistent supervision of financial institutions.
The FFIEC doesn’t directly enforce any regulations. Instead, it develops examination standards, guidelines, and procedures that federal regulatory agencies use to evaluate financial institutions’ compliance with applicable laws.
FFIEC member agencies
The FFIEC is composed of representatives from five federal regulatory agencies: the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (FRB), the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB).

1. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (FRB)
The Board of Governors of the FRB supervises and regulates bank holding companies, state-chartered banks that are members of the Federal Reserve System and other financial institutions.
2. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
The FDIC oversees state-chartered banks that are not members of the Federal Reserve System, providing deposit insurance and examining these institutions for safety and soundness.
3. The National Credit Union Administration (NCUA)
The NCUA regulates and supervises federal credit unions.
4. The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
The OCC supervises and regulates national banks and federal savings associations.
5. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
The CFPB focuses on consumer protection in the financial sector and enforces federal consumer financial laws.
In addition, the State Liaison Committee (SLC) represents state regulatory agencies. This cohesive structure ensures a comprehensive and coordinated approach to financial institution supervision.
Key functions of the FFIEC
The FFIEC performs several critical functions to achieve its mission:
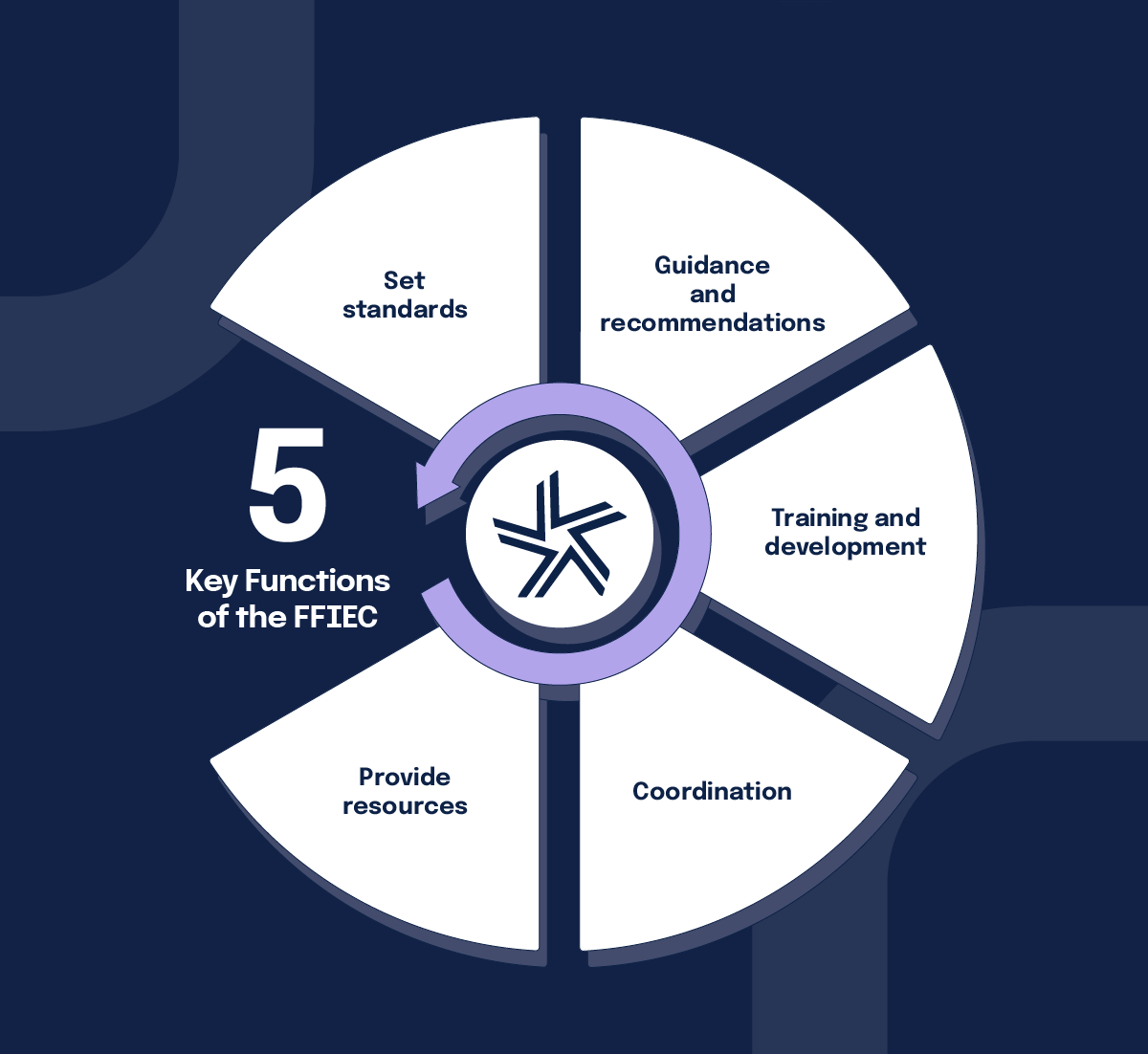
1. Set standards
The council develops uniform principles, standards, and report forms for the examination of financial institutions. These standards help ensure consistency in the regulatory processes across different agencies.
2. Provide guidance and recommendations
The FFIEC issues guidelines, advisories, and recommendations to its member agencies. These documents provide a framework for regulatory practices and help address emerging risks and issues within the financial sector.
3. Offer training and development
The council provides training programs for examiners from member agencies to ensure they are well-equipped to conduct thorough and effective examinations.
4. Coordination
By facilitating communication and cooperation among member agencies, the FFIEC enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of regulatory activities.
5. Provide resources
The council publishes various reports, manuals, and bulletins to keep financial institutions informed about regulatory trends and emerging risks. In fact, they have an online portal called the FFIEC IT Handbook InfoBase that hosts a wealth of FFIEC resources. The FFIEC also develops tools, such as the Cybersecurity Assessment Tool, which financial institutions can use to assess their risk management practices and preparedness for various threats.
FFIEC-based recommendations
The examination of financial institutions is a critical regulatory function aimed at safeguarding the financial system and protecting consumers. These examinations ensure that financial institutions operate in a safe, sound, and compliant manner.
Examinations are conducted by member FFIEC regulatory agencies such as the Federal Reserve System (FRB), the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA). These agencies use standardized examination procedures and guidelines developed by the FFIEC to ensure a consistent and thorough review process.
The examinations focus on five key areas:
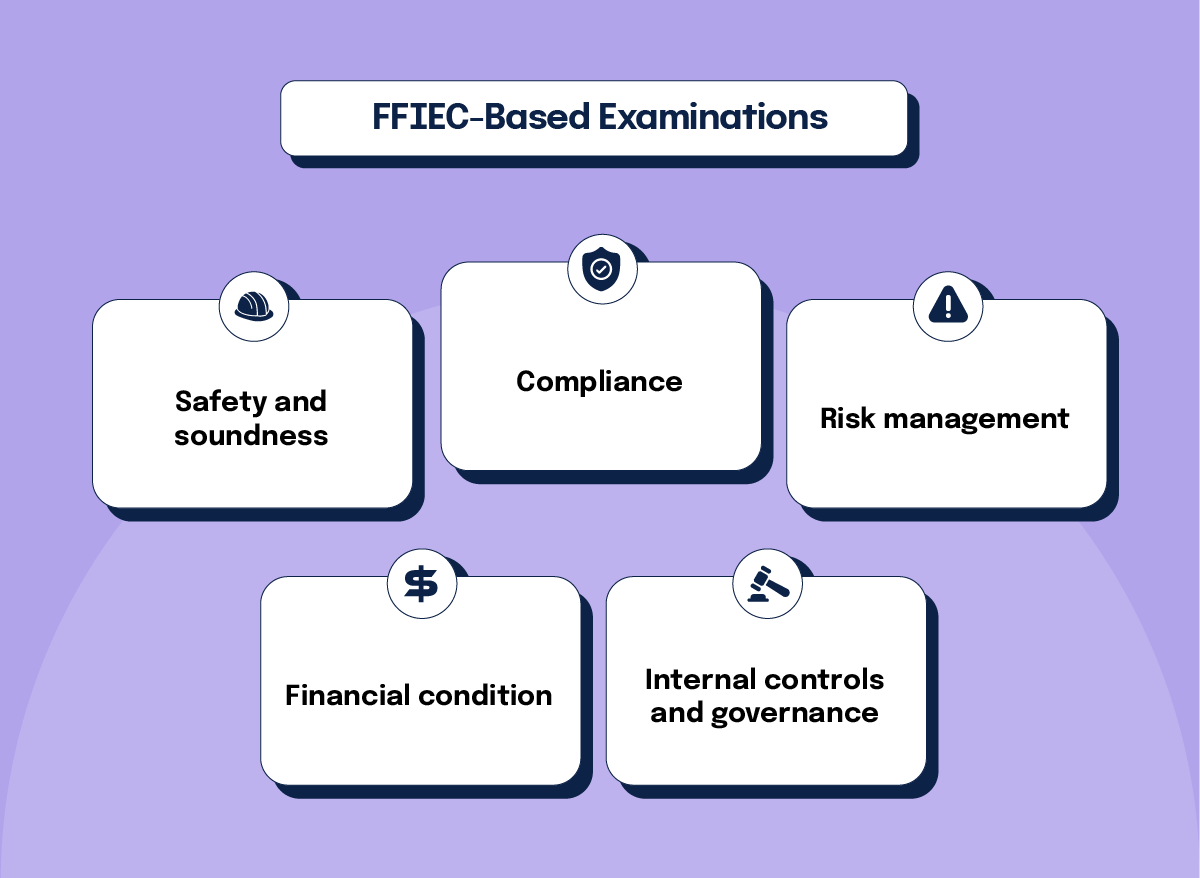
1. Safety and soundness
Ensure that financial institutions operate in a safe and sound manner, maintaining sufficient capital, liquidity, and risk management practices to withstand economic fluctuations and financial stress.
2. Compliance
Verify that financial institutions comply with applicable laws and regulations, including consumer protection laws, anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and other regulatory requirements.
3. Risk management
Assess the effectiveness of a financial institution’s risk management practices, including how it identifies, measures, monitors, and controls various risks (credit risk, market risk, operational risk, etc.).
4. Financial condition
Evaluate the overall financial health of the institution, including its capital adequacy, asset quality, earnings, and liquidity.
5. Internal controls and governance
Review the institution’s internal controls, corporate governance, and audit functions to ensure they are effective and appropriate for the size and complexity of the institution.
Examination process
The FFIEC regulatory agency examinations provide in-depth evaluations of financial institutions. The process follows these steps:
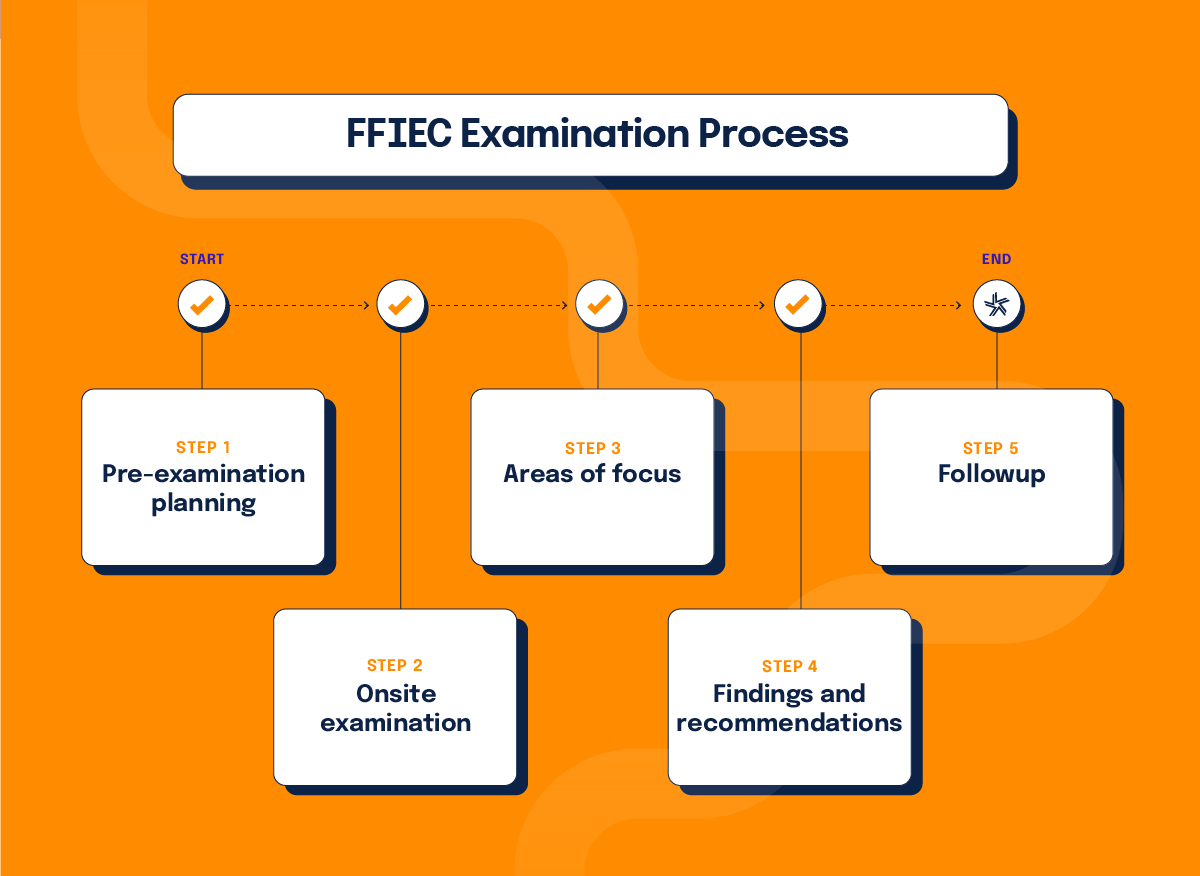
Step 1: Pre-examination planning
Examiners gather information about the institution, including its financial condition, business activities, and any previous examination findings. They may also review off-site surveillance data, regulatory reports, and public information.
Step 2: Onsite examination
Examiners visit the financial institution to conduct a detailed review of its operations. They interview management and staff, review policies and procedures, examine financial records, and test internal controls.
Step 3: Areas of focus
During this phase, examiners review the following:
Areas of focus
Capital adequacy
Examiners assess the institution’s capital levels relative to its risk profile.
Asset quality
Examiners evaluate the quality of the institution’s loan portfolio and other assets, including the adequacy of loan loss reserves.
Management
Examiners review the effectiveness of the institution’s management and board of directors.
Earnings
Examiners analyze the institution’s profitability and sustainability of earnings.
Liquidity
Examiners assess the institution’s liquidity position and ability to meet short-term obligations.
Sensitivity to market risk
Examiners evaluate the institution’s exposure to market risks, such as interest rate risk and foreign exchange risk.
Compliance and consumer protection
Examiners ensure adherence to consumer protection laws and regulations, including fair lending practices and disclosure requirements.
IT and cybersecurity
Examiners review the institution’s IT infrastructure and cybersecurity measures to protect against threats and vulnerabilities.
Step 4: Findings and recommendations
After the examination, examiners compile their findings and provide recommendations for corrective actions, if any. They may issue a report of examination (ROE) detailing the institution’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas requiring improvement.
Step 5: Followup
Regulatory agencies monitor the institution’s progress in addressing any identified issues and may conduct follow-up examinations to ensure compliance with recommendations.
How often do FFIEC exams occur?
The frequency of FFIEC examinations varies based on the size, complexity, and risk profile of the institution. Large, complex institutions are typically examined annually, while smaller, well-managed institutions may be examined every 18 months.
Risk-based examination approach
Regulators often use a risk-based approach to determine the frequency of examinations. Factors that influence this approach include:
Financial condition
Institutions in poor financial health or with declining performance may be examined more frequently.
Risk profile
Institutions with higher risk activities, such as complex financial products or significant exposure to market or credit risk, may require more frequent examinations.
Compliance history
Institutions with a history of compliance issues or regulatory violations are likely to be examined more frequently.
Size and complexity
Larger, more complex institutions generally require more frequent examinations due to the complexity of their operations and the potential impact on the financial system.
Supervisory programs
Regulatory agencies may also implement ongoing supervisory programs for certain institutions, particularly large and complex ones. These programs involve continuous monitoring and periodic on-site examinations. This ensures that regulators maintain a current understanding of the institution’s risk profile and condition.
Cybersecurity Assessment Tool (CAT)
The FFIEC Cybersecurity Assessment Tool (CAT) is designed to help financial institutions identify their cybersecurity risks and assess cyber-preparedness. Launched in June 2015, the tool provides a structured approach to evaluate an institution’s risk profile and corresponding cybersecurity maturity. The CAT has two main components:
CAT’s two components:
1. Inherent risk profile
Assesses the institution’s inherent risk based on technologies and connection types, delivery channels, online/mobile products and technology services, organizational characteristics, and external threats.
2. Cybersecurity maturity
Measures the institution’s cybersecurity maturity across domains such as Cyber Risk Management and Oversight, Threat Intelligence and Collaboration, Cybersecurity Controls, External Dependency Management, and Cyber Incident Management and Resilience.
The CAT does not directly influence regulation but serves as a guideline for financial institutions to evaluate their cybersecurity risks and preparedness. It helps institutions understand their risk profile and cybersecurity maturity, aligning their practices with regulatory expectations.
Regulatory agencies may reference the CAT during examinations to assess an institution’s cybersecurity posture, but the tool itself is not a regulatory requirement. It provides a structured framework for institutions to enhance their cybersecurity measures in line with regulatory standards.
How to align faster with the FFIEC’s regulations
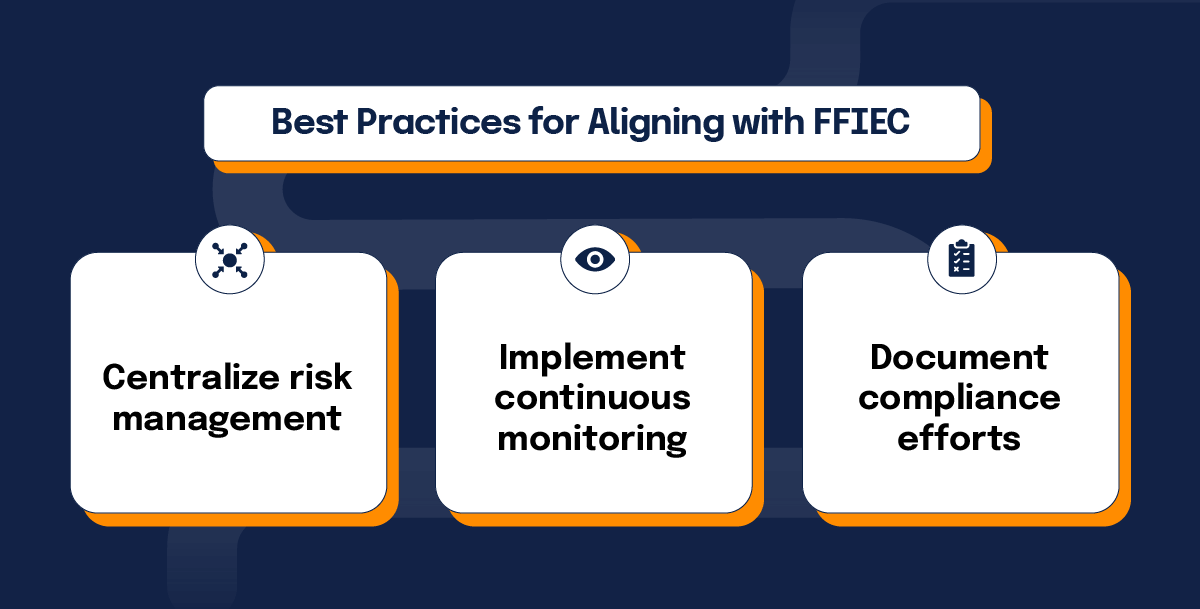
Hyperproof’s platform can be instrumental in implementing and maintaining FFIEC compliance standards. Here are a few ways Hyperproof can help you align with the FFIEC’s regulations:
1. Centralize risk management
Hyperproof allows institutions to centralize their risk management processes, making it easier to assess and monitor cybersecurity risks.
2. Implement continuous controls monitoring
The Hyperproof platform supports continuous monitoring of cybersecurity controls, ensuring that institutions can maintain and improve their cybersecurity posture over time.
3. Document compliance efforts with automated evidence collection and label creation
Automate evidence collection and link evidence to requirements and controls. Generate labels, them to proof, and automatically refresh evidence in real-time or on a regular cadence.
By leveraging Hyperproof, financial institutions can enhance their ability to identify, assess, and mitigate compliance risks, ensuring robust adherence to FFIEC standards.
The BSA/AML Examination Manual
One of the key resources provided by the FFIEC is the Bank Secrecy Act/Anti-Money Laundering (BSA/AML) Examination Manual. This manual offers detailed guidelines for examiners to assess a financial institution’s compliance with BSA/AML regulations. The manual covers various topics, including customer due diligence, suspicious activity reporting, and currency transaction reporting.
The BSA/AML manual is several hundred pages long. Simply reading the manual and then implementing recommendations is a huge task. And from there, you have to make sure your organization remains compliant year after year.
Hyperproof can assist institutions in maintaining compliance with BSA/AML requirements by providing tools for managing customer information, monitoring transactions, and generating required reports. We help institutions meet the rigorous standards set forth in the FFIEC’s examination manual.
With continuous updates and monitoring, Hyperproof can help financial institutions remain compliant over time without big spikes in resource use when examination time arrives. This can be especially useful when an entity is under a supervisory program. Our platform is a perfect fit for organizations that require continuous monitoring and periodic on-site examinations.
Stay compliant with FFIEC requirements
For institutions seeking to align with FFIEC guidelines, Hyperproof’s products and services offer significant advantages:
1. Compliance management: Hyperproof provides tools for managing compliance with various regulatory frameworks, including those set by the FFIEC. This ensures that institutions can efficiently track and document their compliance efforts.
2. Risk assessment: Hyperproof’s platform allows institutions to conduct comprehensive risk assessments, identifying and mitigating potential risks that could impact their operations. Regular risk assessments increase productivity by guiding the information security team on where to allocate their time. This aligns with the FFIEC’s emphasis on effective risk management.
3. Audit management: Hyperproof helps institutions prepare for and manage audits by organizing documentation and streamlining audit processes. Centralizing audit information and facilitating automated workflows makes audits a lot less painful. This is particularly useful for meeting the rigorous examination standards set by the FFIEC.
4. Continuous monitoring: Hyperproof helps you continuous monitor your compliance and risk management activities, ensuring that institutions remain in alignment with FFIEC guidelines between examinations. The platform offers a single repository that documents and tracks controls, automatically collects evidence, and tests and monitors controls at scale.
Future challenges in the financial sector
As the financial landscape evolves, institutions will face new challenges, such as cybersecurity threats and advancements in financial technology. The FFIEC continuously updates its guidelines to address these emerging risks. Hyperproof’s adaptable platform is designed to help institutions stay ahead of these changes by providing flexible and scalable solutions for compliance and risk management.
For instance, in the realm of cybersecurity, Hyperproof can help institutions implement robust cybersecurity frameworks and continuously monitor their security posture. This aligns with the FFIEC’s emphasis on protecting financial institutions from cyber threats. And this emphasis will certainly grow in importance.
Align with FFIEC guidelines the right way
The FFIEC plays a vital role in ensuring the stability and integrity of the financial system through its examination and supervisory activities. For financial institutions, aligning with FFIEC guidelines is crucial for maintaining compliance and managing risk effectively.
By leveraging Hyperproof, financial institutions can streamline their compliance processes, enhance their risk management practices, and be well-prepared for FFIEC examinations. This not only helps in achieving regulatory compliance but also in building a strong foundation for long-term success.
What does FFIEC stand for?
FFIEC stands for the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council. It’s an interagency body that issues uniform examination standards, guidance, and tools federal and state regulators use to supervise banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












