Data Protection Strategies for 2026
Your organization’s 2026 data protection strategies require clear alignment with new AI and privacy rules, active control of AI-enabled threats, and practical engineering choices that work across cloud, edge, and on-premises systems. Start with data discovery, extending zero trust, backup discipline, and compliance automation, then layer in post-quantum encryption and AI-assisted monitoring. The outcome will be lower breach risk, audit-ready evidence, and faster recovery when incidents occur.
What changes define 2026 data protection strategies?
Next year’s regulatory environment links privacy, AI transparency, and cross-border data rules, so your controls must document data use and model logic:
Sector rules for children’s privacy, employment-related AI fairness, and pricing-algorithm transparency sit on top of these laws.
Modern threats now blend AI tooling, quantum-related risks, supply-chain compromise, and insider abuse. Phishing and ransomware campaigns use large language models to write convincing lures and to automate vulnerability discovery. Progress in quantum computing puts current encryption at risk, which drives planning for post-quantum algorithms. Third-party software remains a common entry point. Insider threats use AI to evade detection. You can raise detection rates by wiring real-time threat-intelligence feeds into machine-learning correlation.
Blended compute models further influence where data protection happens. Edge devices and Internet of Things nodes store and process sensitive data, so discovery, labeling, and encryption must start at the source. Serverless functions are short-lived and opaque, which requires policy enforcement that follows the data, not the server.
Failures can carry both direct and indirect costs. Fines can reach up to 10% of global turnover in GDPR-style regimes, while U.S. state AI laws impose tiered damages by affected individual counts. Operational downtime can extend to weeks, driving multimillion-dollar recovery costs, and missed retention or notice timelines can trigger injunctions that disrupt business continuity.
Strong 2026 data protection strategies match legal requirements with controls that detect advanced threats and keep data secure across every compute model.
Which regulations most affect 2026 data protection strategies?
Authorities expect documented AI transparency, clear cross-border data controls, and timely notices. Align your evidence to these expectations, then map each rule to a control.
| Jurisdiction | Regulation (effective date) | Core obligations | Recommended technical controls | Penalty range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European Union | EU AI Act (mid‑2025) / EU Data Act (12 Sep 2025) | • AI transparency and model‑logic docs • Pre‑contractual data‑use disclosures • Cross‑border transfer safeguards | • Discovery and classification • Zero‑trust architecture • Audit‑ready logging • Post‑quantum encryption | Up to 10% of global turnover |
| United States (TX, CA, IL, CO) | State AI statutes (Jan – Jun 2026) | • Training‑data source disclosures • Algorithmic‑logic explanations • Employment‑fairness provisions | • Model‑provenance tagging • Real‑time threat‑intel feeds • Adaptive authentication | Per‑record damages; tiered by affected individuals |
| China | PIPL amendment (2026) | • Extraterritorial duties • Higher penalties for cross‑border breaches • Strict consent and data‑locality rules | • Immutable storage for audit logs • Post‑quantum key‑management • Continuous data‑flow monitoring | Up to 5 % of turnover |
Which threat vectors matter most for 2026?
Expect more AI-written phishing, ransomware, supply-chain backdoors, quantum-risk planning, and insider misuse. Pair threat feeds with machine-learning correlation to surface patterns quickly.
How do edge, IoT, and serverless change data protection work?
Every node can now hold sensitive data. Extend discovery, classification, and encryption to endpoints, functions, and devices, then enforce policy at the point of processing.
What business impacts follow a failure in 2026?
Penalties, brand damage, downtime, and injunctions amplify costs. The fastest way to reduce exposure is better discovery, least-privilege access, and tested recovery.
How should risk assessment evolve for 2026 data protection strategies?
To be effective, risk decisions must start with full data discovery, then quantify loss in dollars. You can justify spend by translating scenarios into Annual Loss Expectancy and showing Return On Security Investment improvement after measuring each control’s effectiveness.
What is Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE)?
ALE multiplies the probability of a breach by the expected financial impact to produce an annualized loss figure you can compare across scenarios.
What is Return On Security Investment (ROSI)?
ROSI compares the cost of a control with the reduction in annual loss expectancy to show whether the spend delivers positive value.
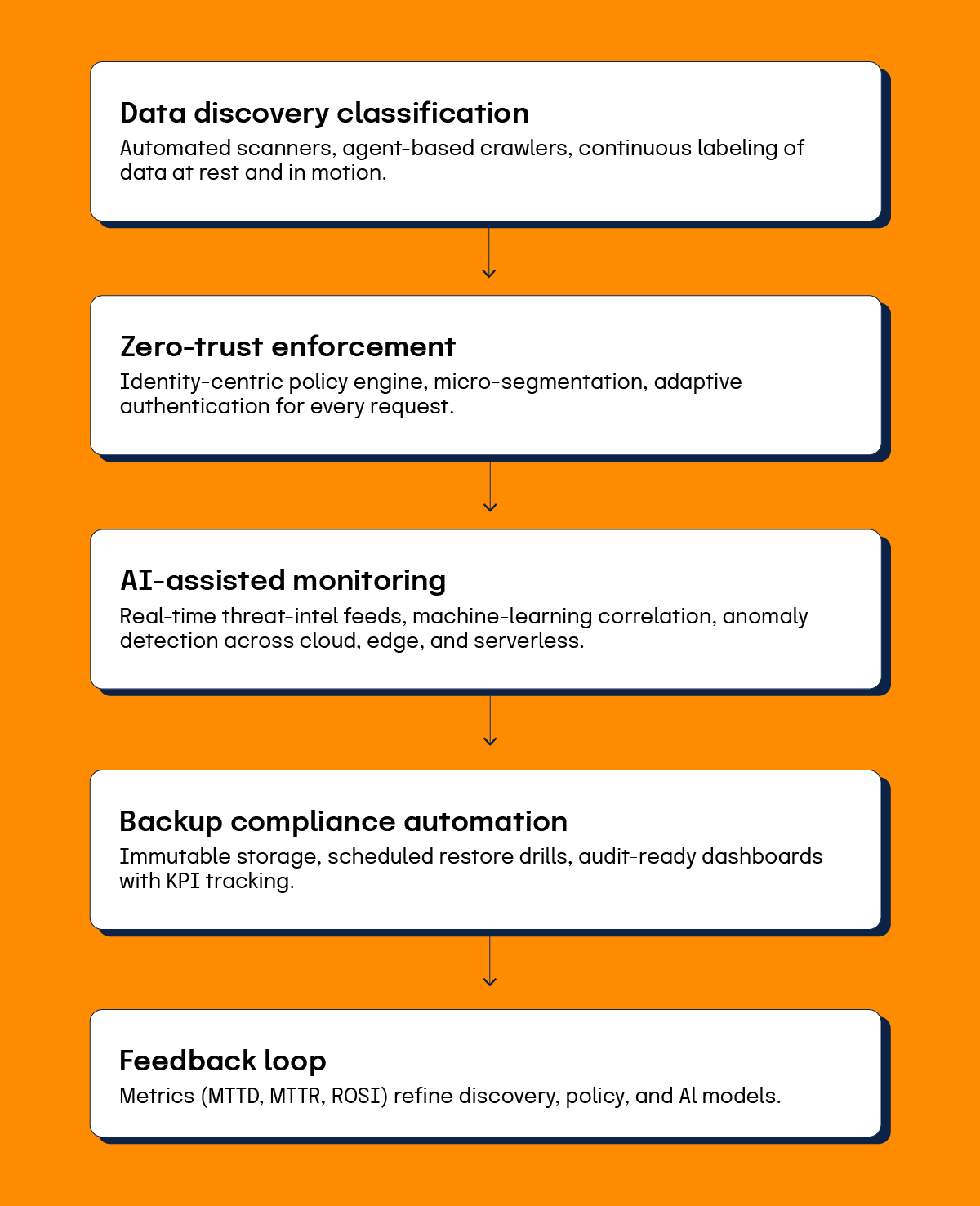
How can you discover and classify data at scale?
Automated scanners should index on-premise, cloud, and edge stores, then tag that content against categories like personal data, health data, and AI-training sets. Real-time classifiers must recheck new or modified records to keep labels accurate.
What updates strengthen privacy impact assessments for AI?
Traditional PIAs looked at collection and storage. PIAs in 2026 must examine training-data provenance, feature selection, explainability, and cross-border flows where consent regimes differ.
How do you evaluate your third-party risks continuously?
Move from static questionnaires to API-based attestations and telemetry that show posture, patch cadence, and data-handling logs. Contracts should bind vendors to the same AI-law standards that apply to you.
How can quantitative models justify protection investments?
Use Annual Loss Expectancy and Return On Security Investment to express risk reduction in dollars.
You can direct budgets to controls with the highest dollar benefits by starting with discovery and by ensuring that your controls are quantifiable using standard metrics.
Which technical controls anchor 2026 data protection strategies?
Identity-driven access, encryption that’s ready for quantum risks, modern DLP, and disciplined backup are table stakes for protection in 2026. Plan to deploy these based on risk and threat assessments to deliver immediate coverage for existing risks while you pilot advanced methods.
How does zero trust protect data?
Zero trust treats every request as untrusted until verified. For data, this means identity checks, least-privilege access, and continuous authentication for every read and write.
To get started, map your organization’s data flows, define policy baselines for high-value data, pilot micro-segments in one business unit, monitor performance, then scale across the organization while integrating with your existing SIEM and DLP solutions.
Is there a reasonable encryption and key-management roadmap?
Plan for quantum-resistant algorithms, privacy-preserving computation, and centralized key control. Here’s a timeline to help you get started:
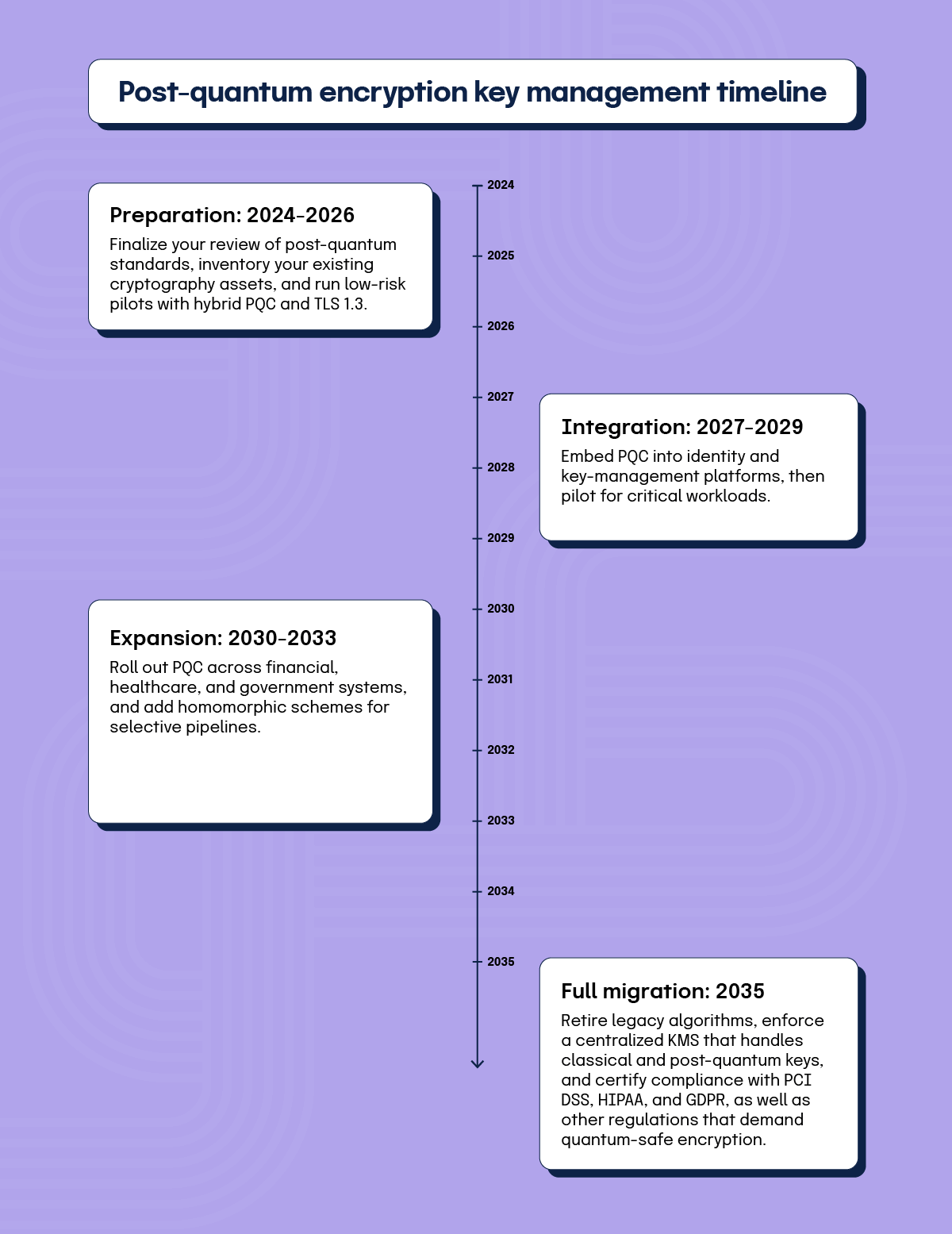
Preparation: 2024-2026
Finalize your review of post-quantum standards, inventory your existing cryptography assets, and run low-risk pilots with hybrid PQC and TLS 1.3.
Integration: 2027-2029
Embed PQC into identity and key-management platforms, then pilot for critical workloads.
Expansion: 2030-2033
Roll out PQC across financial, healthcare, and government systems, and add homomorphic schemes for selective pipelines.
Full migration: 2035
Retire legacy algorithms, enforce a centralized KMS that handles classical and post-quantum keys, and certify compliance with PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, as well as other regulations that demand quantum-safe encryption.
Expect larger key sizes and added latency. Use hybrid deployments to limit disruption while you gather benchmarks.
How should you select and deploy next-generation DLP?
Modern DLP uses machine learning, behavioral analytics, and real-time response to reduce false positives and improve user experience. Here are some steps to get you started:
How do you optimize backup and recovery systems for compliance?
Regulators expect defined retention, immutable storage, and tested restoration.
Technical controls pay off when they enforce least privilege, stop data loss, and recover fast without breaking audit commitments.
How should governance and policy work in 2026?
A cross-functional committee aligns controls with business goals and keeps decisions moving. The chair is a senior leader, usually the CIO or CRO, with IT, security, legal, compliance, risk, and business unit representation. The group approves classification schemas, reviews high-impact incidents, and guides investment. Meetings occur monthly, with ad-hoc sessions for breaches.
What process produces sustainable policies?
How can training programs raise maturity?
At the executive level, focus on risk appetite, ROI of security investments, and regulatory exposure. For technical teams, provide hands-on labs for zero-trust configuration, DLP tuning, and post-quantum migration testing. At the user level, continue running phishing simulations, add in safe data-handling practices, and privacy-by-design basics. Measure your results with assessments, lower policy-violation rates, and better behavior in simulations.
Should we update our incident response playbook?
Yes. Planning for improvements to your data protection strategy includes reviewing and updating your IR playbook to include the following:
Clear roles, current policies, targeted training, and a tested playbook keep decisions fast and evidence audit-ready.
How can you automate compliance and monitoring?
Automation reduces manual effort and makes audit evidence easy to retrieve. A compliance platform should ingest logs from DLP, identity, and cloud services, then translate them into regulatory compliance dashboards.
What design principles guide continuous monitoring?
Attach user, device, and location context to every event. Build behavioral baselines with machine-learning models per role. Route high-severity incidents to incident handling teams with playbook links, and work to suppress low-confidence noise.
How should you prepare for audits?
First, build a control matrix mapping each requirement to a specific technical control. Then, store configs, scan reports, and policy versions in a searchable centralized solution. Next, run internal audits and tabletop exercises with cross-functional reviewers. Lastly, brief leadership on scope and resource commitments.
Which KPIs show data protection program effectiveness?
Measure your program’s effectiveness with quantifiable goals across detection and response times, policy adherence, audit readiness, and Return On Security Investment:
Automated evidence, clear KPIs, and tuned alerting prove compliance status and speed up investigations.
What new technologies should your 2026 data protection strategies plan for?
AI now assists with protection, so teams can classify data, detect anomalies, and predict risks earlier. Deep-learning models label unstructured content with high accuracy. Unsupervised models spot access deviations that rules miss. Bayesian networks estimate future breach likelihood from new threat intelligence. If you adopt these technologies, make sure that you can document explainability, conduct bias audits, and provide transparent notices to meet AI Act transparency provisions.
Quantum risk planning is active work. Inventory your organization’s RSA, ECC, and symmetric keys. Pilot hybrid cryptography that combines classical TLS 1.3 with post-quantum key exchange. Create a migration plan to replace high-value assets by 2030, aligned with NIST milestones. Keep dual-key capability to support legacy systems during the transition.
Plan for AI-assisted defense and quantum-safe cryptography so your design stays secure as technology shifts.
What’s a reasonable data protection roadmap?
Resource your rollout in phases so value shows up early and keeps compounding.
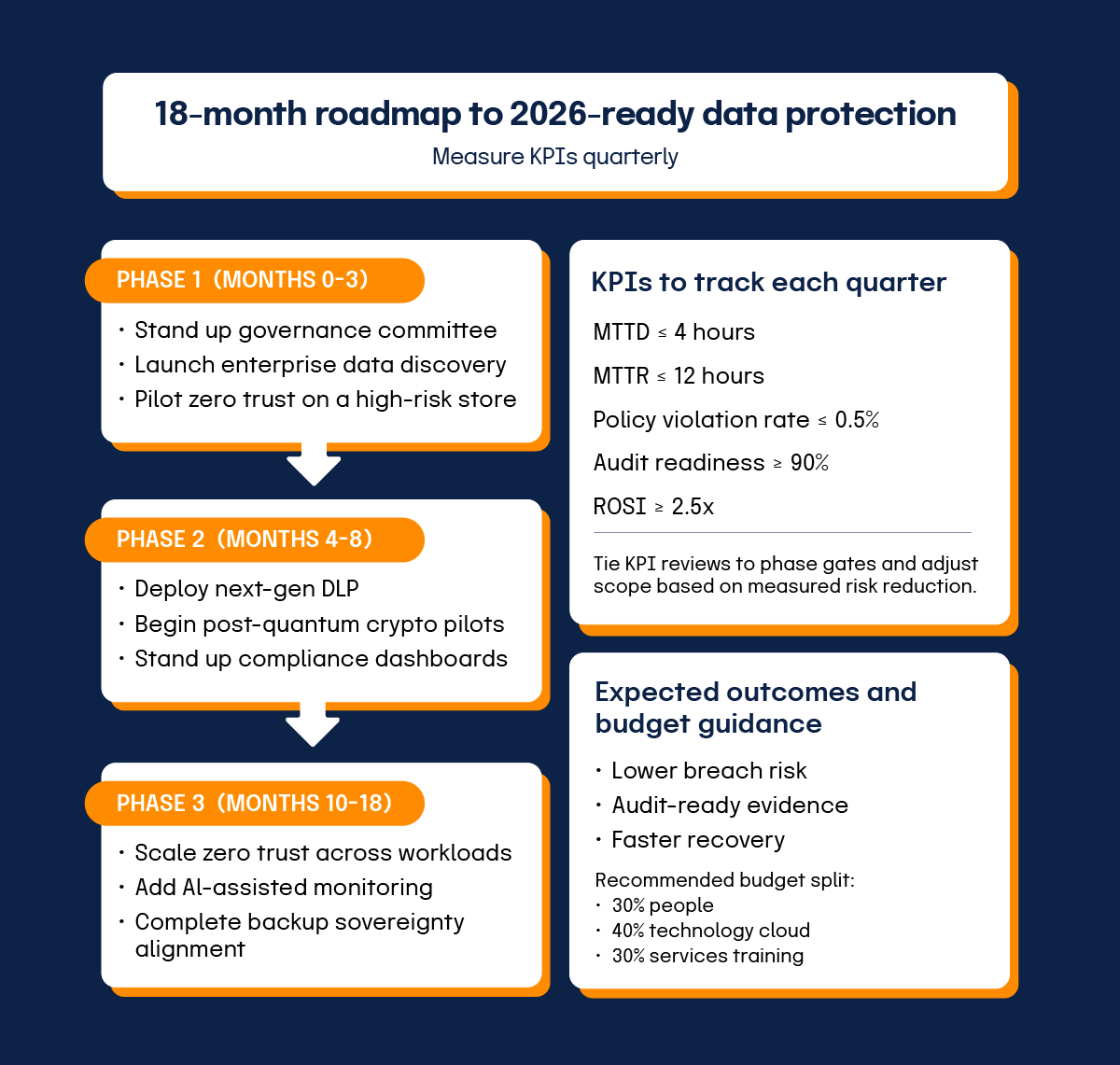
Phase 1, months 0-3
Stand up the governance committee, launch data discovery, and pilot zero trust on a high-risk data lake or similar asset.
Phase 2, months 4-9
Deploy next-gen DLP, begin post-quantum pilots, and automate compliance dashboards.
Phase 3, months 10-18
Scale zero trust across workloads, add AI-enhanced monitoring, and complete backup-compliance migration.
Your budget split should be approximately 30% personnel, 40% technology licenses and cloud services, and 30% for consulting, training, and contingency. Adoption improves when senior leaders connect the program to goals like entry speed and customer trust. Workshops with business-unit owners shape policy exceptions and workflow changes. Bi-weekly updates and an internal FAQ keep teams informed. Early-adopter champions, short post-training surveys, and manager incentives reduce resistance.
Quarterly reviews should track MTTD, MTTR, the policy-violation rate, audit-readiness score, and ROSI. Use trend analysis to adjust controls and refresh the scorecard for the committee and the board. Control your costs by consolidating vendors, preferring usage-based cloud security, choosing audited open-source cryptography where policy allows, and negotiating fees based on data volume. Regular ROI checks move spend to the controls that cut expected loss the most.
Phased delivery, clear metrics, and targeted change management produce measurable risk reduction at a predictable cost.
TL;DR: What are the final takeaways for 2026 data protection strategies?
2026 data protection strategies require combining regulatory insight, quantified risk, and technical execution. Build on your data discovery and classification, zero trust, AI-assisted monitoring, post-quantum planning, and compliance automation. With a cross-functional committee, a practical roadmap, and visible KPIs, your program can meet your company’s legal duties and block modern attacks while supporting growth and innovation.
A measured plan that starts now delivers lower risk, faster audits, and stronger customer trust.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












