GUIDE
Unlocking the Power of the CIS Critical Security Controls®
The Complete Guide

Introduction
In an era where cybersecurity threats loom larger than ever, organizations face a pressing need to fortify their defenses against cyberattacks. Amidst this challenging landscape, the CIS Critical Security Controls® (CIS Controls®) offer a comprehensive framework to safeguard digital assets and critical information for enterprises.
Developed by the Center for Internet Security, Inc. (CIS®), these Controls have evolved into a global standard, providing a practical roadmap to address the most critical and common cyber threats. In this guide, we’ll unpack the CIS critical security controls in plain language so you can see how they apply to your own environment. But how do the CIS Controls® align with various cybersecurity standards and frameworks, and how can they be tailored to meet your specific security requirements?
Let’s delve into the key principles and guidelines of the CIS Controls®, how to categorize and prioritize CIS Controls®, how the Controls are updated to address emerging threats, and benefits experienced by organizations across industries. We’ll also cover resources, tools, and case studies to help organizations effectively implement the CIS Controls®.
For a CIS controls MSP, the biggest win is having a repeatable, measurable baseline you can deploy across customers without rebuilding the program from scratch each time.

What are the CIS Critical Security Controls®?
The story of the CIS Controls® begins with a simple, yet compelling mission: to empower organizations to defend against the most critical and prevalent cyber threats. Developing the CIS Controls® emerged as a grassroots effort to identify real-world attacks that continually plague enterprises; translate that knowledge into positive, constructive actions for defenders; and share that information with a wider audience.
The original goals were modest: to help people and enterprises focus their attention and get started on the most important steps to defend themselves from attacks that really matter.
The 4 goals of the CIS Controls®
The CIS Controls® reflect the combined knowledge of experts from every part of the business ecosystem, from entire companies and governments to individuals. This community spans many sectors, like government, power, defense, finance, transportation, academia, consulting, security, and IT. These community members have banded together to create, adopt, and support the CIS Controls®, working toward four common goals:
1. To identify and share insights
The journey of the CIS Controls® commences with the identification of the most common and impactful cyber threats that organizations face daily. This keen understanding forms the foundation for developing controls that directly address these threats. The first goal is to share insights into attacks and attackers, identify the root causes of these attacks, and translate this knowledge into classes of defensive action.
2. Create and share tools
Knowledge alone isn’t enough. The CIS Controls® take the insights gained from understanding attacks and transform them into actionable defense strategies. These Controls bridge the gap between awareness and implementation, providing organizations with practical steps to protect themselves.
3. Map the CIS Controls® to other regulatory compliance frameworks
The CIS Controls® are not isolated; they are carefully mapped to regulatory and compliance frameworks. This not only enhances their applicability but also provides a collective sense of priority and focus.
4. Identify common challenges
The last goal is to identify common barriers and challenges, like initial assessments and implementation roadmaps, so the community can come together to solve those challenges. The community shares insights, creates tools, and solves these common problems to strengthen the Controls and ensure they remain relevant.
The power of the CIS Controls® lies in their collective wisdom, representing the combined knowledge of experts across various domains, roles, and sectors. Whether you’re a threat responder, technologist, auditor, or policy maker, the CIS Controls® encompass insights and strategies to bolster your organization’s cyber defense. This inclusive approach to cybersecurity has propelled the CIS Controls® into a global standard that organizations can rely on to safeguard their digital assets.
The CIS Controls® are more than a mere list of best practices; they are an organized and prioritized framework that empowers organizations to enhance their cybersecurity posture effectively. These Controls are structured to address the most critical threats first and are categorized to guide organizations on their journey to robust security.
The structure of the CIS Controls®
The CIS Controls® are organized into 18 top-level Controls. These Controls represent overarching measures that help strengthen an organization’s cybersecurity posture. Each of the Controls focuses on critical security aspects, providing a comprehensive framework for defense. As a prescriptive CIS Controls framework, this structure makes it easier to translate high-level security goals into concrete, testable safeguards.
The 18 CIS Critical Security Controls®
Done well, CIS controls support not just checkbox compliance, but a living, adaptive security program that can evolve alongside new threats, technologies, and business priorities.
1. Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets
Catalog all “enterprise assets” attached to your enterprise (physically and virtually) to have a complete understanding of what needs to be monitored and to identify potentially harmful unauthorized or unmanaged devices.
2. Inventory and Control of Software Assets
Track all software on your network to prevent others from installing software that hasn’t been reviewed or authorized by your enterprise.
3. Data Protection
Securely manage and monitor data by creating detailed data protection processes and controls.
4. Secure Configuration of Enterprise Assets and Software
Develop comprehensive processes to ensure that your enterprise’s assets and software are configured securely.
5. Account Management
Track user credentials for all accounts. Whether an account is tied to confidential data or is purely administrative, no account should be discounted or overlooked as a potential security risk.
6. Access Control Management
Create detailed processes to track and manage who has credentials or access to what assets and software — the process of revoking user access should be just as carefully monitored as assigning access.
7. Continuous Vulnerability Management
Build processes that regularly track and monitor vulnerabilities in order to identify potential risks and better prevent security incidents.
8. Audit Log Management
Create an audit log where your team can track and manage events tied to security incidents. This log can be used to understand why incidents occur and as a means to help prevent future attacks.
9. Email and Web Browser Protections
Identify potential email and web browser threats, then develop new protections or improve existing protections against those threats.
10. Malware Defenses
Build processes focused on defending against the installation or spread of malware on your enterprise’s physical and virtual assets.
11. Data Recovery
Develop robust practices to ensure that your enterprise’s assets can recover from, and potentially be restored after, any security incidents.
12. Network Infrastructure Management
Protect vulnerable network services and access points by carefully tracking and monitoring your enterprise’s devices (physical and virtual).
13. Network Monitoring and Defense
Utilize tools and processes to monitor and defend against potential security threats to your network.
14. Security Awareness and Skills Training
Increase employee knowledge and awareness of potential security issues via a security awareness program that includes regular cross-departmental training sessions.
15. Service Provider Management
Thoroughly evaluate service providers who have access to your enterprise’s sensitive data to ensure that they are managing data securely and appropriately.
16. Application Software Security
Assess software that is developed, housed, or acquired by your company for security weaknesses, then protect and monitor those weaknesses to prevent potential incidents.
17. Incident Response Management
Create a detailed incident response plan that will detect and analyze security incidents when they occur and then trigger the appropriate actions needed to mitigate such incidents.
18. Penetration Testing
Identify and test weaknesses of enterprise assets in order to better understand how effective your controls are.
Taken together, these 18 measures give organizations a pragmatic CIS computer security baseline they can build on as their programs mature.
Each of these 18 top-level Controls is further broken down into specific Safeguards (formerly referred to as Sub-Controls). These Safeguards are individual and unique actions that guide the logic of the top-level CIS Controls®. They define precise measurements as part of the implementation process, ensuring that they require minimal interpretation to put into practice. This level of detail and specificity ensures that organizations have clear guidance for implementing security measures.

How do I get started with adopting the CIS Controls®?
Adopting the CIS Controls® is typically done in three phases, called Implementation Groups (IGs). IGs are self-assessed categories based on an organization’s risk profile and access to resources. Each IG identifies a set of Safeguards that businesses need to implement based on their business maturity and needs.
Your business will need to self-assess based on your risk profile and business maturity to see which of the IGs you fall into. From there, you can get started with implementing the suggested Safeguards.
Implementation Groups
To further guide organizations in prioritizing the implementation efforts, the CIS Controls® are grouped into three IGs, which we will explore in more detail below. There are a total of 153 Safeguards in CIS Controls® v8. The IGs offer organizations flexibility in how they approach the CIS Controls® based on their specific needs and maturity levels.
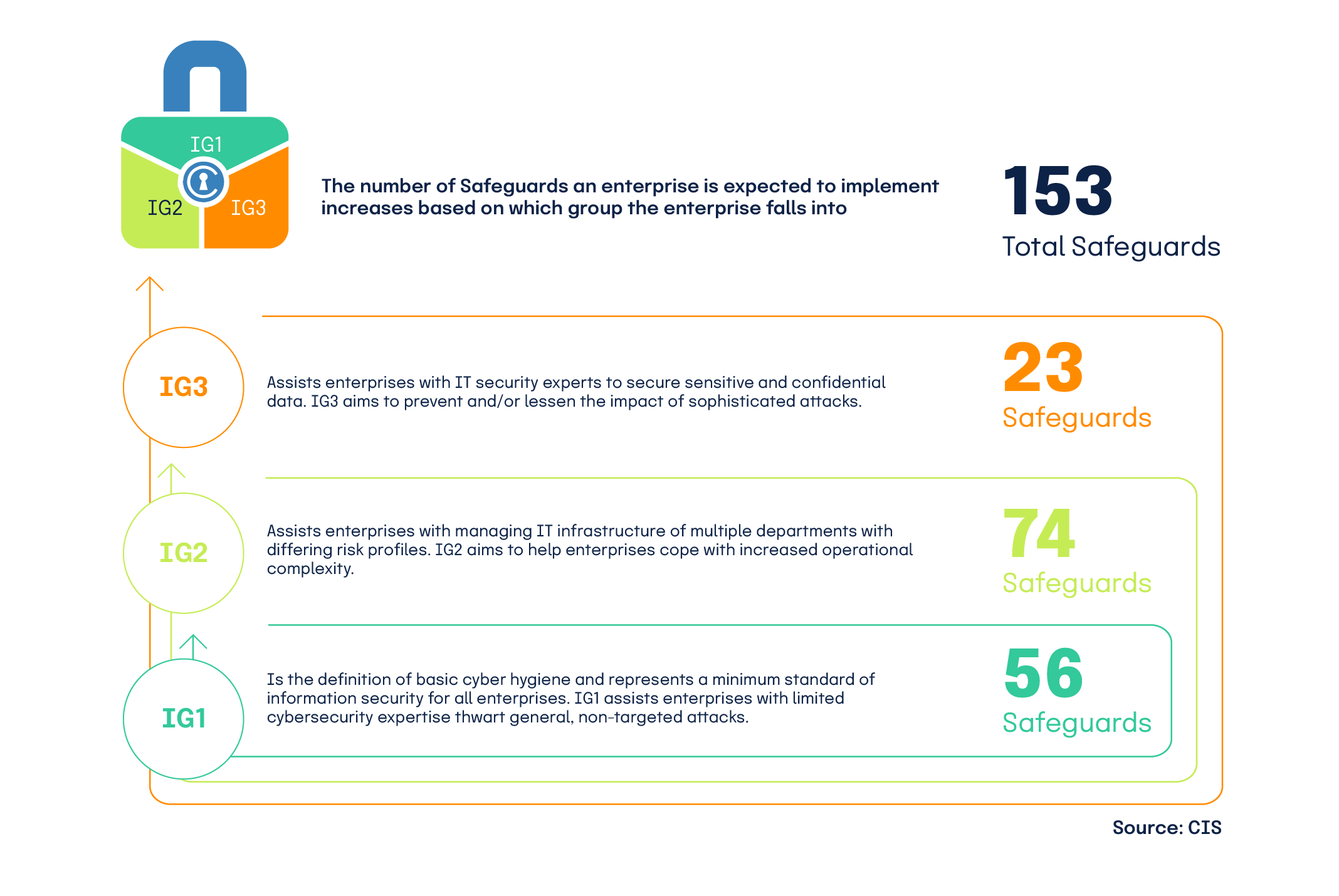
Implementation Group 1 (IG1)
Every enterprise should start with IG1, as it is defined as essential cyber hygiene — the foundational set of cyber defense Safeguards that every enterprise should apply to guard against the most common attacks. It’s a foundational set of 56 Safeguards against the most common attacks and constitute baseline protection for enterprises. IG1 is an ideal starting point for organizations looking to establish a solid security foundation — it’s essentially the onramp to the CIS Controls®.
Implementation Group 2 (IG2)
Building on the foundation laid by IG1, IG2 introduces 74 additional Safeguards that offer enhanced protection against more sophisticated attacks. While IG1 is about essential cyber hygiene, IG2 elevates an organization’s security posture.
Implementation Group 3 (IG3)
IG3 implements 23 additional Safeguards, meaning all 153 Safeguards are implemented for your business. This extends your security measures to defend critical systems and protect against advanced, targeted attacks, like ransomware, malware, web application hacking, insider and privilege misuse, and targeted intrusion. IG3 is suitable for organizations that face complex and high-stakes threats.
Who typically uses the CIS Controls®?

The CIS Controls® offer a universal approach to cybersecurity applicable across all industries. Regardless of your sector or domain, the principles and strategies encapsulated within the CIS Controls® provide a robust defense against a wide spectrum of cyber threats.
From government and power to defense, finance, transportation, academia, consulting, security, IT, and more, organizations have adopted the CIS Controls® across a wide range of industries. The Controls are designed to address common cybersecurity challenges that transcend specific sectors.
Which frameworks do the CIS Controls® map to?
The CIS Controls® map to most major compliance frameworks. Currently, the Controls map to 25 frameworks:
These mappings offer a starting point for action, simplifying the process of compliance alignment. Organizations can leverage the structure and guidance provided by the CIS Controls® to meet the specific requirements of their industry and region.
In addition to mappings that match the cybersecurity best practices of the CIS Controls® to various industry-specific frameworks, CIS also offers numerous resources and guides for specific use cases, such as the following:
How customizable are the CIS Controls®?

The CIS Controls® are prescriptive. However, because organizations can select their own IGs, they can tailor their approach to meet their specific security requirements, industry regulations, and risk profiles. For instance, organizations of any size should begin with IG1 for essential cyber hygiene and can advance to IGs 2 and 3 when they feel ready since each subsequent IG group is designed to incorporate a more complex threat landscape. By customizing the CIS Controls® to address their unique challenges, organizations can create a cybersecurity strategy that aligns with their goals and resources.
Common challenges to avoid when adopting the CIS Controls®
While implementing the CIS Controls® is highly beneficial for organizations, there are a few common challenges to avoid:
1. Not knowing where to start
For many organizations, the biggest challenge is knowing where to begin. The CIS Controls® provide a structured framework, but selecting the right starting point can be daunting. This is where the Implementation Groups (IGs) come into play, helping organizations choose an appropriate level of security maturity to begin with.
2. Budgetary constraints
Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures can be resource-intensive. Smaller organizations often face budget constraints when implementing the CIS Controls®. However, selecting the right IG and implementing a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) tool can help balance security requirements with available resources.
3. Resource availability
Many organizations may lack the in-house expertise required to implement the CIS Controls® effectively. Acquiring the necessary skills and resources can pose a challenge. In such cases, organizations can consider outsourcing or seeking external assistance.
4. Manually mapping the CIS Controls® to other frameworks
Organizations operating in heavily regulated industries may find it challenging to align the CIS Controls® with specific regulatory requirements. However, the mappings provided by CIS via their Controls Navigator and a GRC tool that automates these mappings can simplify the process and save hours of time.
5. Overly ambitious goals
Organizations may be tempted to implement all CIS Controls® simultaneously. This can lead to inefficiencies and resource allocation issues. Avoid the trap of trying to do too much at once and focus on what’s most critical.
6. Inadequate measurement
Some organizations may not establish effective metrics for measuring the impact of Control implementation. Measuring the effectiveness of each Control is crucial for ensuring that security improvements are realized.
7. Inconsistent interpretation
The CIS Controls® are designed to be specific and practical. However, organizations may interpret them differently. It’s important to avoid inconsistent interpretations by clearly defining implementation standards.
8. Threshold misunderstanding
Some Controls may have specific thresholds that organizations must meet. Understanding these thresholds and ensuring they are met is essential to control effectiveness.
Navigating these challenges and avoiding common pitfalls is essential to achieving the maximum benefit from implementing the CIS Controls®. By doing so, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity defenses and reduce the risk of security breaches.
CIS Controls® key principles and guidelines
The effectiveness of the CIS Controls® lies not only in their goals but also in the key principles and guidelines that underpin them. These design principles guide the selection, prioritization, and implementation of the Controls, ensuring that they are not just a theoretical framework but a practical strategy to defend against cyber threats.
Here are the essential principles that drive the CIS Controls®:
1. Offense informs defense
At the core of the CIS Controls® is the principle that offense informs defense. These Controls are not arbitrarily selected but are chosen and prioritized based on real-world data and a deep understanding of attacker behavior. The Controls are not theoretical; they are born out of practical knowledge about how to stop cyber attacks effectively.
2. Focus
In the complex landscape of cybersecurity, it’s easy to become overwhelmed with the sheer number of potential threats and security measures. The CIS Controls® alleviate this complexity by helping defenders identify the most critical actions to take to protect against the most significant attacks. The key is to focus on what matters most and avoid the temptation to address every security problem.
3. Feasibility
All individual recommendations within the CIS Controls®, known as Safeguards, are designed to be specific and practical to implement. This means that they should not be overly abstract or challenging for organizations to put into practice. Practicality is key to ensuring that organizations of various sizes and resources can benefit from these Controls.
4. Measurability
Measuring the effectiveness of security controls is vital. The CIS Controls®, particularly for IG1, emphasize measurability. This focus on measurement ensures that organizations can assess their progress in implementing these Controls effectively. Clear metrics and measurement criteria are integral to the implementation process.
5. Alignment
The world of cybersecurity is multifaceted, with various governance, regulatory, and process management schemes, frameworks, and structures. The CIS Controls® aim to create a sense of “peaceful co-existence” with these existing standards, like the National Institute of Standards and Technology® (NIST®), Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), Software Assurance Forum for Excellence in Code (SAFECode), ATT&CK, and Open Web Application Security Project® (OWASP®). They cooperate with and point to independent standards and security recommendations wherever possible, ensuring that organizations can align their efforts with well-established industry best practices.
By adhering to these principles, the CIS Controls® ensure that they are not just a set of theoretical concepts but a practical roadmap to bolster an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
The benefits of adopting the CIS Controls®
Adopting the CIS Controls® can help your organization:
Enhance your security
The CIS Controls® provide a practical roadmap to bolster an organization’s defenses. By adhering to these Controls, organizations can reduce vulnerabilities and strengthen their security posture.
Align compliance across your organization
Many industries have their own compliance and regulatory requirements. The CIS Controls® are thoughtfully mapped to most major compliance frameworks, ensuring that organizations can align their cybersecurity efforts with regulatory requirements.
Mitigate risks
Effective implementation of the CIS Controls® helps organizations mitigate risks associated with cyber threats. By addressing critical security aspects, organizations reduce the likelihood of security breaches and their associated costs.
Improve operational efficiency
By following a structured framework, organizations can streamline security practices, reduce complexities, and optimize resource allocation.
Build multiple layers of defense
The CIS Controls® ensure that organizations have multiple layers of defense against cyber attacks, which enhances their resilience against both common and sophisticated attacks. Because the CIS cybersecurity controls are prioritized, you can focus on the highest-impact safeguards first and demonstrate measurable risk reduction quickly.
Establish cybersecurity best practices
By adopting the CIS Controls®, organizations tap into a repository of global best practices and benefit from insights and strategies collaboratively developed by experts from various sectors and backgrounds.
How are the CIS Controls® updated?
In the dynamic world of cybersecurity, staying ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities is paramount. The CIS Controls® aren’t static; they adapt and evolve to address the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape. Regular updates ensure that these Controls remain effective and relevant, providing organizations with a robust defense against the latest threats.
The update process
The CIS Controls® are updated and reviewed through an informal community process. Practitioners from government, industry, academia, and various technical backgrounds come together with deep technical understanding from different viewpoints, such as vulnerability, threat analysis, defensive technology, tool vendors, enterprise management, and more. These efforts are guided by senior-level cybersecurity engineers at CIS that lead the technical research from a tactical perspective. These experts from CIS are also skilled technical writers who ensure the content provided is both relevant to the industry and digestible to C-Suites and external practitioners who might not be as familiar with the industry.
This collective knowledge is pooled to identify the most effective technical security controls needed to counter the attacks observed in the real world. The update process ensures that the CIS Controls® reflect the latest insights and strategies to thwart emerging threats effectively.

Frequency of updates
CIS Controls® have historically been updated every 2-3 years, with minor updates in between as-needed. Typically, the organization releases an updated version of the CIS Controls® when warranted to keep pace with new and changing technology, practices, and attack patterns. This regular updating process keeps the Controls aligned with the rapidly evolving threat landscape and helps organizations to remain resilient in the face of new and sophisticated cyber threats.
The CIS Controls® Ecosystem: Resources and tools
CIS provides a range of resources to help companies achieve compliance with the CIS Controls®. These resources empower organizations to assess, implement, and prioritize the CIS Controls®, ultimately enhancing their cybersecurity posture.
CIS Controls® Self Assessment Tool
CIS CSAT is a proprietary tool that helps organizations assess, track, and prioritize their implementation of CIS Controls® versions 7.1 and 8. This tool empowers organizations to gauge their progress in implementing the CIS Controls® and identify areas that need improvement.
The Center for Internet Security Risk Assessment Method (CIS-RAM)
CIS-RAM is an information security risk assessment method designed to assist organizations in implementing and assessing their security posture against the CIS Controls®. The CIS-RAM Family of Documents provides instructions, examples, templates, and exercises for conducting a cyber risk assessment.
CIS Controls® Navigator
To further simplify the alignment process, CIS offers the CIS Controls® Navigator, a free interactive tool that provides detailed mapping information for both CIS Controls® version 7.1 and version 8. This tool makes it easy for organizations to explore how the CIS Controls® align with various standards and frameworks.
White papers and guides
CIS provides a collection of white papers and guides that cover various aspects of the CIS Controls®. These resources offer in-depth insights, explanations, and best practices for effective implementation.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof’s powerful compliance operations platform is designed to help you maintain security controls and continuous compliance in the most efficient way possible.
Reference the CIS Controls® and tailor them for your security program
Enterprises large and small, from a variety of industries, have incorporated the CIS Controls® into their environment to support a solid security posture, but many firms also need to implement controls recommended by other cybersecurity guidelines (e.g. NIST SP 800-53, NIST CSF, Cloud Security Alliance’s Cloud Controls Matrix) for a host of reasons.

In Hyperproof, it’s easy to reference the CIS Controls® and a host of other data protection control frameworks and add them to your control environment. By creating a single source of controls – or a common controls framework – within your enterprise, you’ll gain better visibility into your compliance posture, catch issues sooner, and improve the operational efficiency of your compliance program.
Implement the CIS Controls® to meet multiple compliance requirements
Use Hyperproof to cut down on the time it takes to comply with new regulatory regimes and standards. Hyperproof comes with the CIS Controls® (including IG1, IG2, and IG3) out-of-the box, making it easy to implement the CIS Controls® in your environment.
Hyperproof automatically maps the CIS Controls® to your other frameworks, standards, and regulatory regimes, like PCI DSS, SOC 2, ISO 27001, NIST SP 800-53, and more. Once a control is mapped to multiple compliance requirements, you’ll be able to collect evidence once and use that evidence to satisfy multiple auditors’ requests.
Continuously monitor your controls
While CIS provides native tools to conduct point-in-time tests of their controls, Hyperproof comes with an automation engine that enables you to set up a continuous controls monitoring system.
You can configure Hyperproof to automatically extract evidence of specific control procedures from source systems, define automated tests highlighting success or failure of each assertion, conduct tests at any frequency you need, and automate a workflow for managing the generated alarms, including communicating and investigating any failed assertion and ultimately correcting the control weakness.
The structured approach of the CIS Controls®, with their categorization, prioritization, and alignment with Implementation Groups, provides organizations with a clear roadmap for enhancing their cybersecurity defenses.
Download the PDF












