A Deep Dive into the EU Cybersecurity Certification Scheme on Common Criteria (EUCC)

As cyber threats evolve, the European Union has taken significant steps to bolster cybersecurity across its member states. Central to this effort is the European Cybersecurity Certification Scheme on Common Criteria (EUCC), spearheaded by the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA).
Released in early 2024, the EUCC aims to create a unified security benchmark for ICT (information communications technology) products and services. All this is part of a larger initiative to foster a secure and trustworthy digital ecosystem within the EU.
This article will explore the logic behind the EUCC and what’s inside the certification scheme. You’ll also learn how to get up to speed with EUCC compliance faster. And since you might be grabbing your head thinking, “Not another compliance framework,” we’ll discuss whether it’s worth seeking EUCC certification or not.
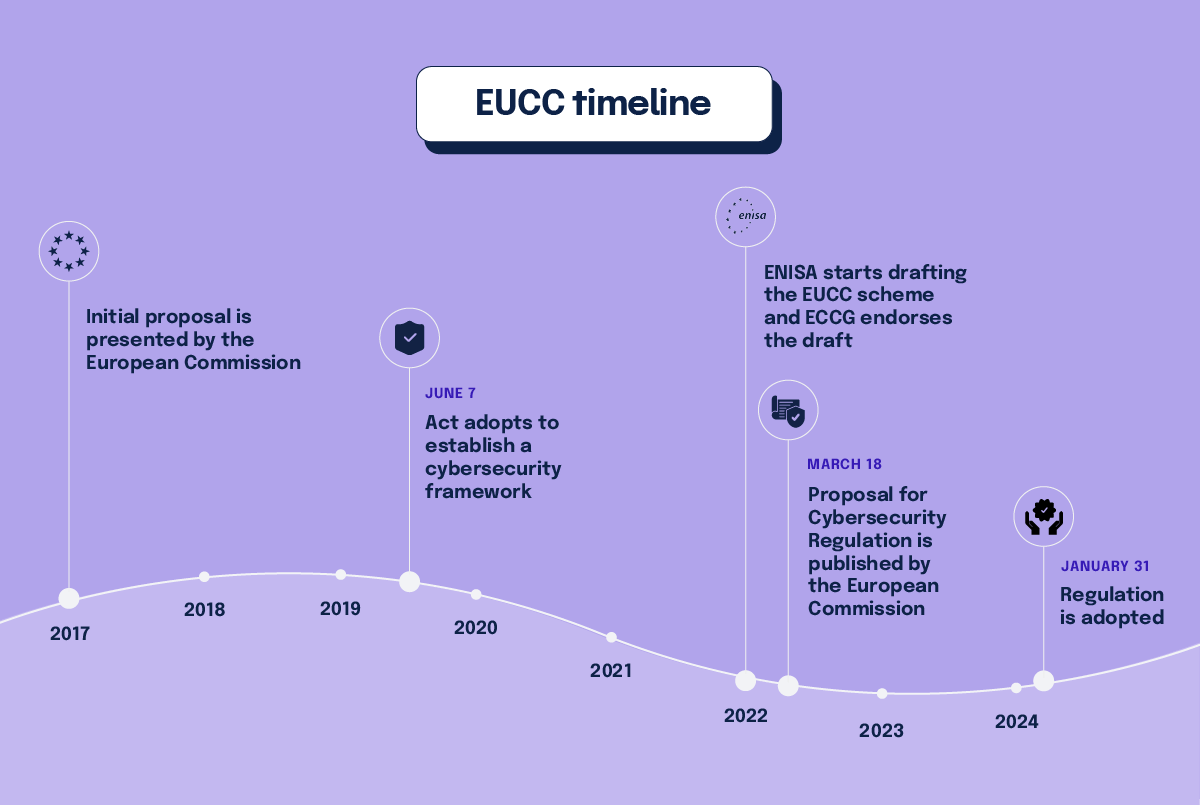
The launch of the EUCC
As the first scheme released under the ENISA framework, the EUCC targets ICT products like hardware, software, and components. Launched on January 31, 2024, this scheme establishes a structured and transparent assessment process for ICT suppliers to certify their products’ cybersecurity features. Some features might include user authentication, encryption, network security, software security, and access control.
The EUCC is voluntary and based on the SOG-IS Common Criteria evaluation framework, already used by 17 EU Member States. The EUCC is part of the greater Cyber Resilience Act, which focuses on securing the collection, storage, and transfer of data across the EU. The Cyber Resilience Act will eventually include other components like cloud computing (EUCS) and 5G mobile networks (EU5G). The EUCC is the first ENISA initiative, and it’s meant to help secure devices that have built in security components, like medical devices.
How ENISA develops certification schemes
ENISA plays a pivotal role in developing draft certification schemes upon request from the European Commission or EU Member States. The Agency collaborates closely with the Commission, member states, and relevant stakeholders to ensure that the schemes are robust and widely accepted.
To build effective cybersecurity certification schemes, ENISA relies on Ad-Hoc Working Groups (AHWGs) and other stakeholders who provide valuable insights and recommendations. The Cybersecurity Resilience Act encourages various key players to pull together to strengthen cybersecurity standards across the EU.
ENISA’s pivotal role in developing and implementing the EUCC reflects a broader commitment to enhancing cybersecurity across Europe. Beyond certification schemes, ENISA also develops guidelines, coordinates cybersecurity exercises, and supports member states in managing security incidents like ransomware.
Why the EUCC matters to markets
Currently, the ICT marketplace is a complex maze of highly variable security claims and labels which can confuse consumers and developers. Developers and service providers wishing to enter new markets might need to comply with many different security frameworks. This lack of harmonization leads to high compliance costs, which then trickle down to customers.
The EU Cybersecurity Certification seeks to address these challenges by providing a unified certification recognized across the EU. The goal is to simplify market access, reduce costs, and enable developers and service providers to reach a broader audience with a single certification.
EUCC implementation and recognition
Once in force, each EU country will have the authority to perform and issue cybersecurity certifications under the EUCC. The certificates will be recognized uniformly across the Union. The result will be a much simpler regulatory environment for manufacturers. The EUCC aims to ensure that ICT products and services meet consistent security standards with the ultimate goal of protecting critical infrastructures and sensitive information.
In addition to the certification schemes for cloud services and 5G, the Agency has also conducted a feasibility study on EUCC requirements for artificial intelligence (AI). These efforts reflect a broader strategy to cover various technological domains and address emerging cybersecurity challenges.
What is the EUCC framework based on?
The EUCC framework is derived from the SOG-IS Common Criteria which in turn is based on the ISO/IEC 15408-1 Common Criteria standard for Information Technology Security Evaluation. However, the SOG-IS adds an additional layer of mutual recognition among European countries. This means that a product evaluated and certified in one member state under SOG-IS is recognized by other member states, reducing the need for multiple evaluations.
ISO/IEC 15408-1 and SOG-IS are closely related to several other ISO standards within the broader context of information security management and evaluation. Related standards might include:
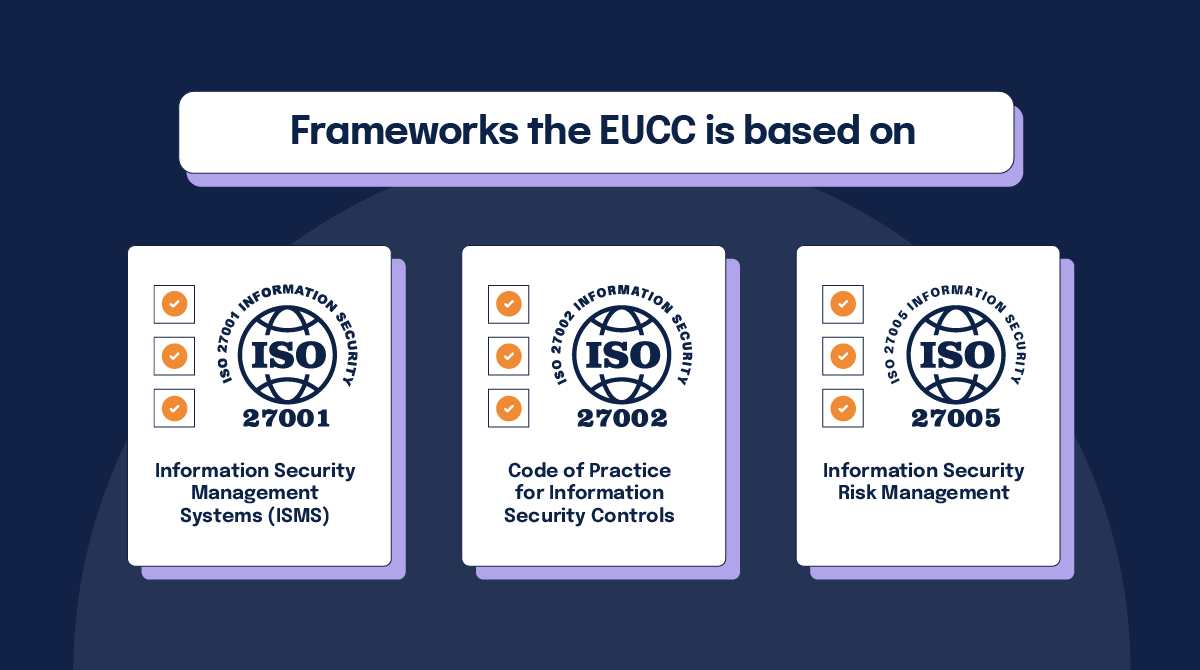
- ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS)
- ISO/IEC 27002: Code of Practice for Information Security Controls
- ISO/IEC 27005: Information Security Risk Management
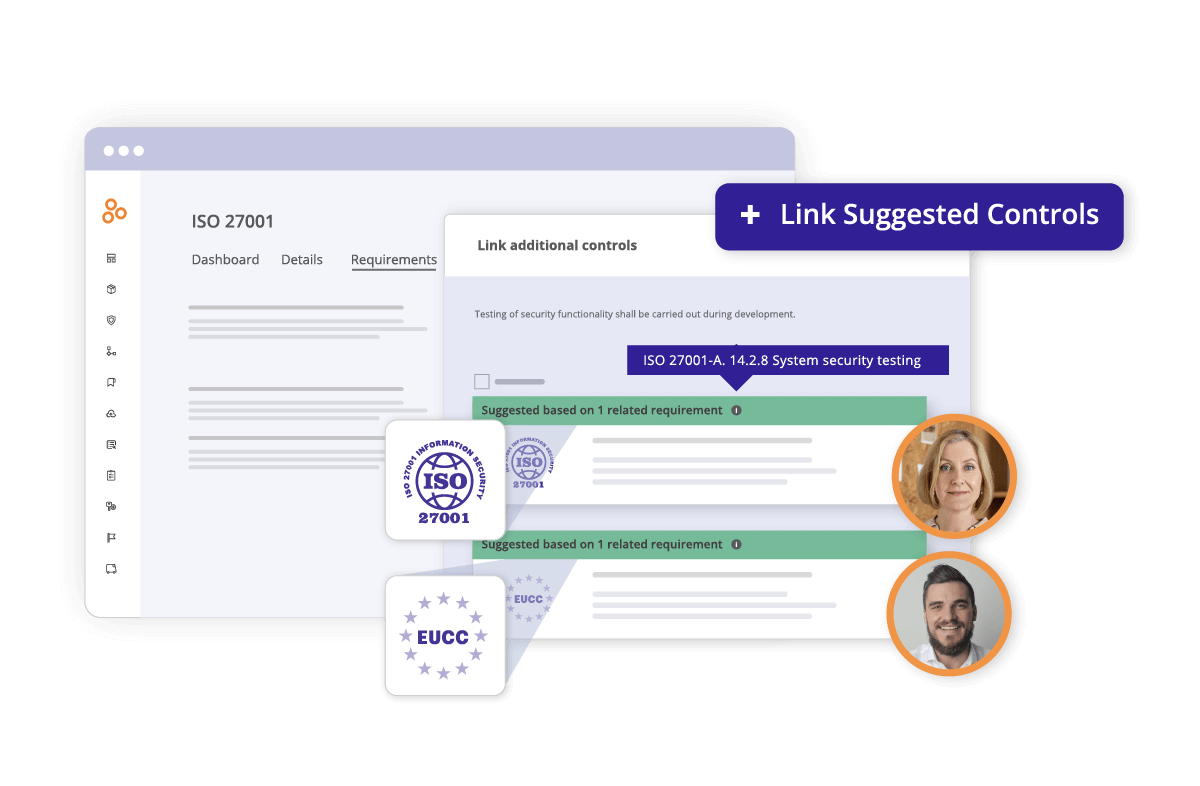
If your organization is currently certified by other ICT frameworks, you may already be in compliance with a significant percentage of EUCC requirements. The Hyperproof platform crosswalks controls between frameworks, which enables you to reuse the controls from an existing framework like ISO 27001 and apply them to EUCC.
The EUCC certification process
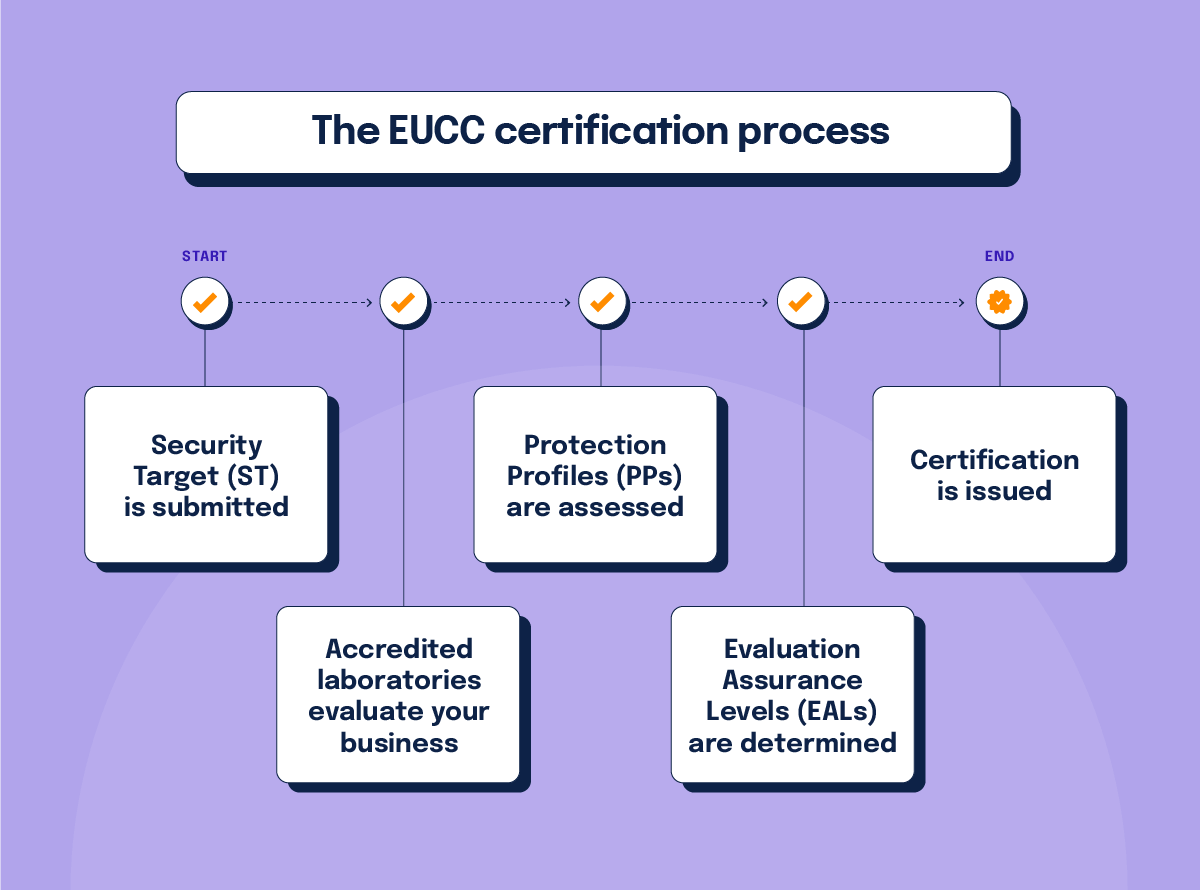
EUCC certification starts with vendors submitting a detailed Security Target (ST) description. The ST description outlines the product’s security attributes and alignment with relevant assessment components. Accredited laboratories then conduct a thorough product evaluation to determine the product’s adherence to defined security specifications.
The framework’s two key assessment components include Protection Profiles (PPs) and Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs):
1. Protection Profiles (PPs)
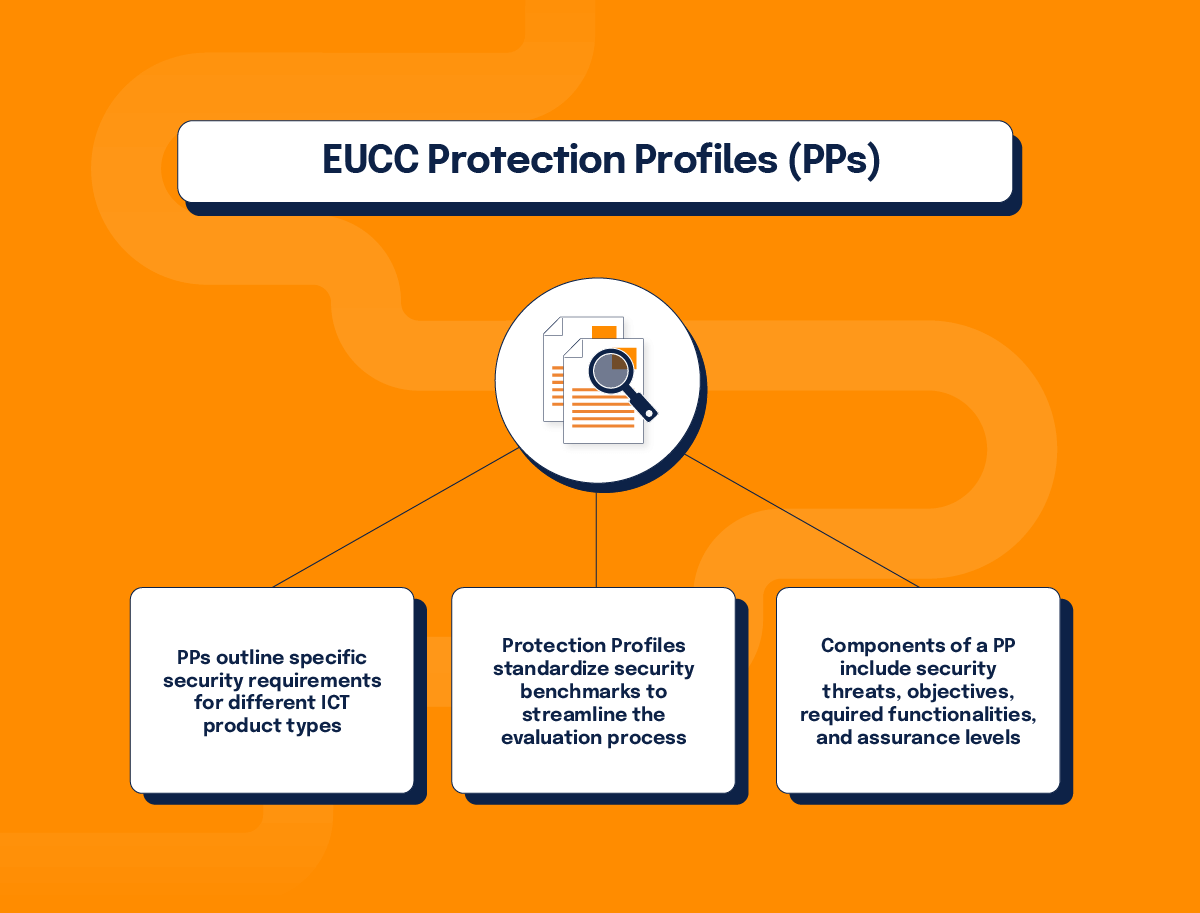
- PPs outline specific security requirements for different ICT product types.
- Protection Profiles standardize security benchmarks to streamline the evaluation process.
- Components of a PP include security threats, objectives, required functionalities, and assurance levels.
2. Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs)
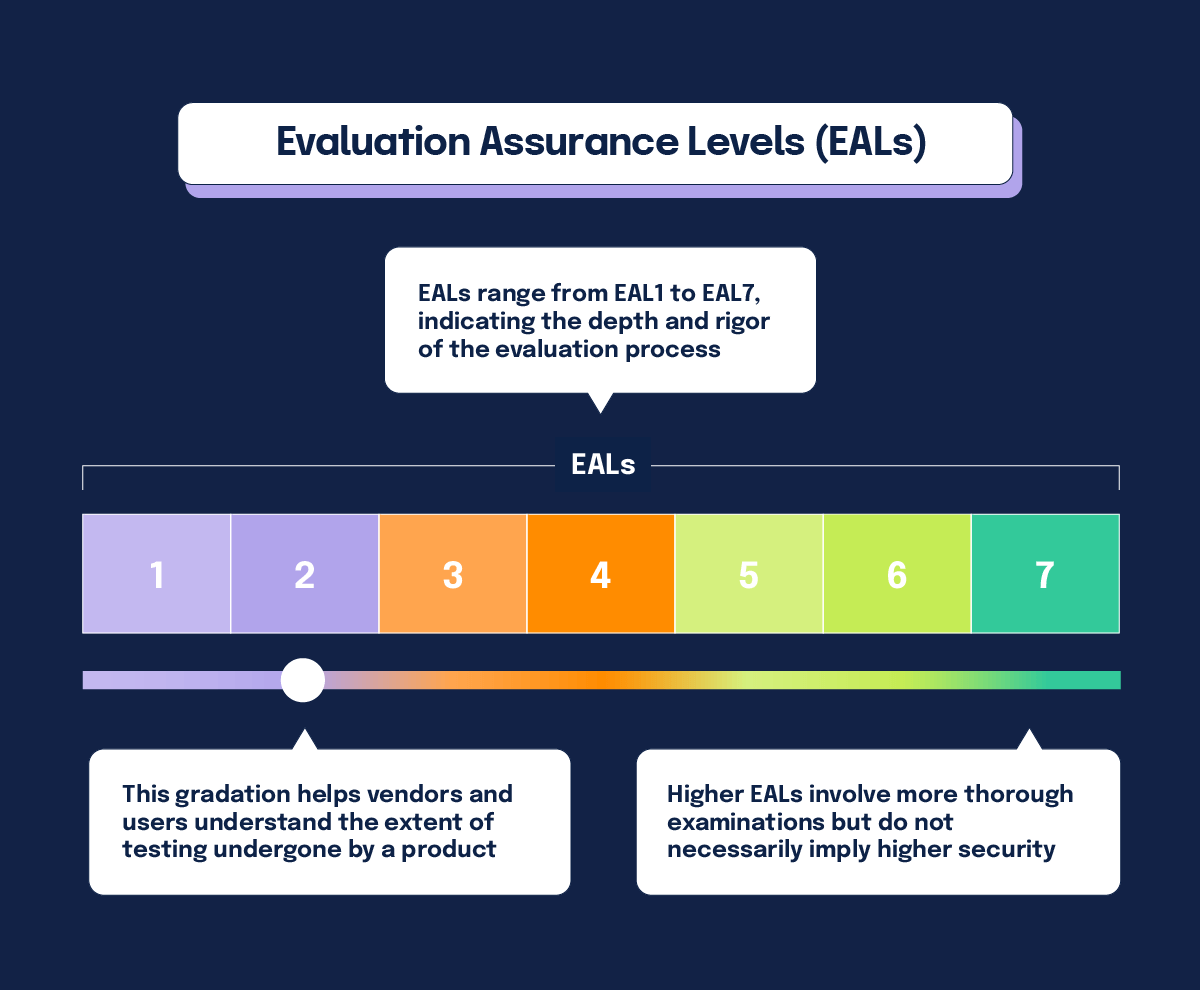
- EALs range from EAL1 to EAL7, indicating the depth and rigor of the evaluation process.
- Higher EALs involve more thorough examinations but do not necessarily imply higher security.
- This gradation helps vendors and users understand the extent of testing undergone by a product.
Comprehensive scoring methodology
The EUCC employs a comprehensive scoring methodology derived from Common Criteria’s vulnerability assessment components. This approach is designed to assure high confidence in certified product resilience against diverse cyber threats. Factors considered in the scoring include:
Elapsed time
How long does it take to identify and exploit vulnerabilities?
Specialist expertise
What level of expertise is required for vulnerability exploitation?
Knowledge of the Target of Evaluation (TOE)
What extent of understanding is needed about the product for effective exploitation?
Window of opportunity
What is the timeframe for vulnerability exploitation before mitigation?
Required equipment
How complex and accessible are the tools needed for vulnerability exploitation?
Two tiers of EUCC assurance
The EUCC offers two tiers of assurance: Substantial or High, depending on the risk associated with the product’s intended use.
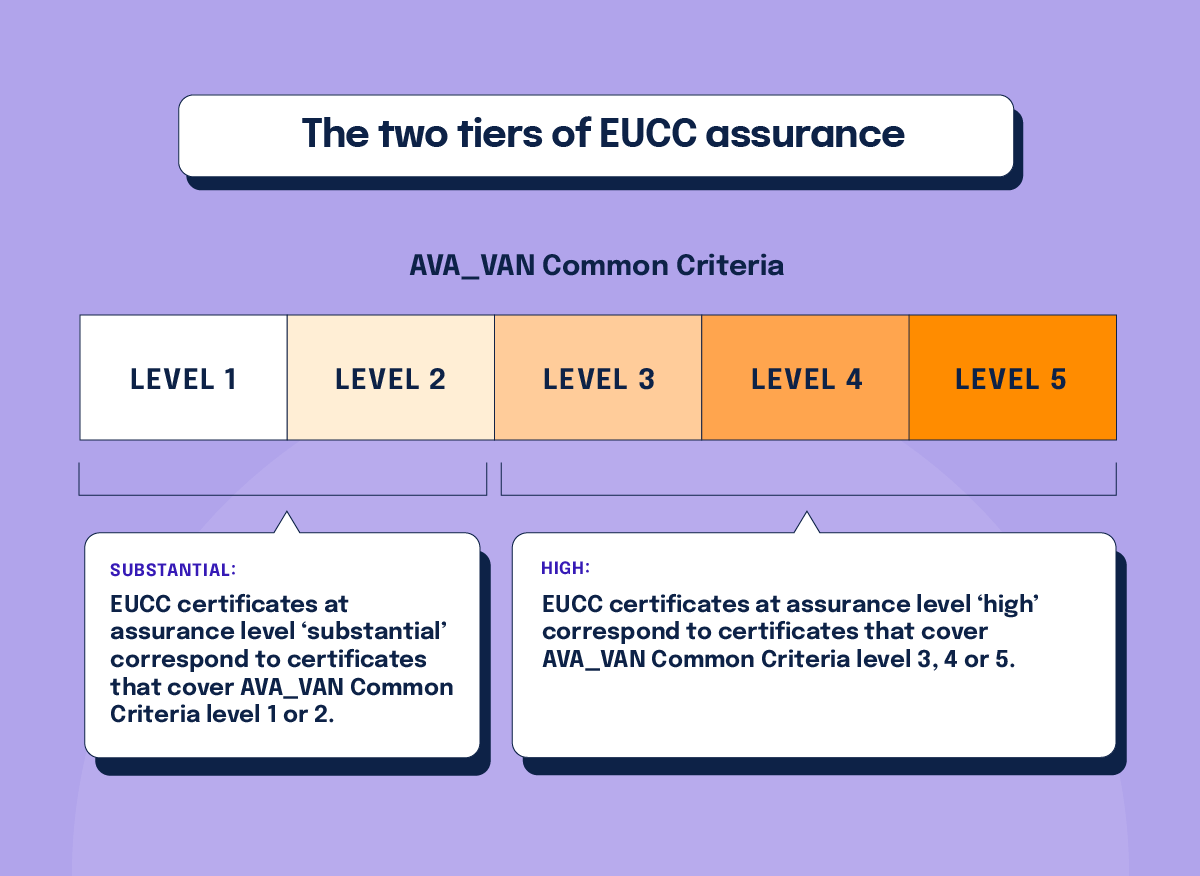
Substantial
EUCC certificates at assurance level ‘substantial’ correspond to certificates that cover AVA_VAN Common Criteria level 1 or 2.
High
EUCC certificates at assurance level ‘high’ correspond to certificates that cover AVA_VAN Common Criteria level 3, 4 or 5.
The AVA_VAN (Vulnerability Analysis) component of the Common Criteria framework specifies different levels of vulnerability assessment. These levels indicate the depth and rigor of the analysis conducted to identify and assess vulnerabilities in an IT product or system. Each level builds on the previous one, increasing the comprehensiveness and sophistication of the vulnerability assessment.
The AVA_VAN levels are designed to complement the Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs) by providing a detailed analysis of the product’s vulnerabilities. While EALs focus on the overall assurance and rigor of the evaluation process, AVA_VAN levels address the identification and mitigation of specific vulnerabilities.
Transparency through reporting requirements
If a EUCC certificate holder discovers a product vulnerability that might affect its certification status, they must provide a vulnerability impact analysis report. These reports ensure transparency and accountability in managing cybersecurity risks. This approach aligns with broader regulatory frameworks such as the EU Cybersecurity Act and NIS2.
Subsequently, certificate holders must present appropriate remedial actions to the certification body. Certification status is then reviewed based on the proposed vulnerability remedies. The goal is to make sure vulnerabilities are identified, reported, and remediated to maintain the integrity and security of certified products.
Manufacturers are also expected to commit to continuous product improvement to remain in compliance with EUCC standards. This ensures their products maintain high levels of cybersecurity throughout their lifecycle. This commitment enhances the resilience of Europe’s digital infrastructure, contributing to a competitive and secure digital market.
Critical needs answered by the EUCC
It’s no secret that the EU cyber landscape is under attack, just like the rest of the world. The hope is that rigorous and uniform certification will help reduce the impact of cyber breaches and hacks. Some key EUCC actions to address this critical need include:
Establishes a common standard for product security
By setting a common standard for cybersecurity certification, the EUCC ensures that all ICT products and services across EU member states adhere to a consistent level of security. Standardization is imperative for safeguarding critical infrastructures and sensitive data against evolving cyber threats to foster a secure digital environment.
Streamlines market entry
The EUCC streamlines market access for ICT vendors by providing a single certification recognized across the EU. This eliminates the arduous process of obtaining multiple certifications for different markets, expediting the introduction of innovative security technologies to the market.
Boosts consumer and business confidence
Certification under the EUCC enhances confidence in ICT products for businesses and consumers alike. A recognized and rigorous certification scheme assures users that certified products have undergone comprehensive evaluation and are deemed secure for their intended use.
Encourages global collaboration
Alignment with global cybersecurity standards ensures that European ICT products remain competitive and trusted internationally. This alignment is pivotal for fostering international collaborations and ensuring that European businesses can effectively operate in the global marketplace with trusted and compliant products.
Future directions for EU Cybersecurity Certification
As the EU Cybersecurity Certification Scheme evolves, ENISA and stakeholders will continue to address emerging cybersecurity challenges and develop new certification schemes for evolving technologies.
Future initiatives focusing on cloud services, 5G networks, and artificial intelligence (AI) underscore a commitment to innovation and resilience in combating dynamic cyber threats. These ongoing efforts ensure that Europe remains at the forefront of cybersecurity innovation, capable of addressing evolving challenges in the digital age.
Is EUCC certification worth it?
It’s no secret that meeting ICT certification standards can be tedious. The amount of information that you need to compile, process, and get approved can seem daunting. And some companies might even decide it’s not worth the investment.
However, keep in mind that EUCC certification may be a requirement for some vendor contracts. Many Fortune 500 companies, national and local governments, healthcare organizations, and other organizations that handle sensitive information often require their vendors and partners to be compliant with certain frameworks. Depending on your industry, you might need to be HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO 27001, or FedRAMP compliant. Now EUCC is being added to the list.
The push to unite ICT compliance under one umbrella is commendable. The reality is that many disparate compliance frameworks still exist. A single global international standard is a long way off, and there’s a good chance it will never come to fruition. Still, efforts such as the EUCC should be supported to help simplify compliance issues.
If you’re thinking about implementing EUCC, an automated SaaS platform can help jumpstart the process. Hyperproof optimizes your compliance work by mapping common controls across frameworks, automating evidence collection, and streamlining your risk and compliance workflows.
Looking beyond Europe
EUCC represents a paradigm shift towards a unified, secure, and resilient digital landscape in Europe. By establishing common standards, streamlining market access, and enhancing consumer and business confidence, the EUCC lays a strong foundation for a competitive and secure digital ecosystem. Continued collaboration among stakeholders is crucial to realizing the EUCC’s potential in creating a trusted and resilient digital environment for everyone.
As a response to growing cyber threats, the pivot towards cybersecurity standardization, like the EUCC, is being seen across in the U.S. and across the globe. This includes government mandated regulations, especially for critical infrastructure. Organizations that place themselves ahead of the curve will benefit as they navigate these frameworks with more agility and effectiveness. Not only will they reap the rewards of compliance, but they will also benefit from improved cyber resilience.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?