Safeguarding Patient Data with HITRUST Compliance: A Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare Technology Companies

Healthcare organizations increasingly rely on technology to store, manage, and transmit sensitive patient information. As a result, safeguarding patient data against cyber threats and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is critical, and many companies are contractually obligated to protect this sensitive data. Among the myriad of compliance frameworks available, HITRUST is a framework developed in response to HIPAA for companies looking to demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding patient data. Let’s delve into the intricacies of HITRUST compliance, exploring its history, significance, assessment process, and benefits for healthcare IT professionals.
What is HITRUST?

HITRUST, an acronym for Health Information Trust Alliance, is a robust framework designed to address the unique security challenges faced by healthcare organizations. Developed in response to HIPAA, HITRUST was collaboratively developed by healthcare and information security professionals and offers a comprehensive approach to managing security risks and protecting sensitive data.
HITRUST offers the flexibility to customize and adjust controls to maintain system integrity and ensure consistency across applications. With a versatile framework designed for organizations of all sizes, systems, and regulatory needs, HITRUST certification enables organizations to assess their compliance status with a high degree of assurance. Moreover, it provides assessors with the tools and resources they need to measure how well an organization mitigates its risks.
A brief history of HITRUST
HITRUST originated in 2007 as a response to the increasing number of data breaches in the healthcare sector and their resulting legal cases under HIPAA. Its primary objective is to provide a standardized framework for managing information security risks and protecting sensitive health information. Over the years, HITRUST has evolved into a widely recognized compliance standard adopted by healthcare organizations of all sizes.
The Health Information Trust Alliance was established by a consortium of healthcare organizations, including providers, payers, technology vendors, and security experts. Recognizing the need for a unified approach to healthcare data security, these stakeholders collaborated to develop a comprehensive framework that addresses the industry’s unique challenges.
Why choose HITRUST?

Healthcare IT professionals opt for HITRUST compliance for several reasons:
Comprehensive security controls
HITRUST CSF provides security controls curated specifically for the healthcare industry, addressing common threats and vulnerabilities.
Data security
HITRUST’s comprehensive security controls help protect sensitive health information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse.
Alignment with regulatory requirements
HITRUST aligns with regulatory mandates such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), offering organizations a structured approach to compliance. It’s the only guaranteed way to achieve HIPAA compliance, which we will discuss below.
Enhanced trust and reputation
Achieving HITRUST certification demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding patient data and instilling trust among patients, partners, and stakeholders.
Competitive advantage
HITRUST certification can be a competitive differentiator, attracting patients and partners who prioritize data security and compliance.
What’s the difference between HITRUST and HIPAA?
When people start researching healthcare security frameworks, one of the first questions they ask is: “What is the difference between HIPAA and HITRUST?”
A better way to think about it is: What’s the best option for demonstrating HIPAA compliance for my organization? HIPAA is a U.S. law that defines privacy and security requirements for protected health information (PHI), while HITRUST is a certifiable framework you can use to prove you’re meeting those requirements in a structured, auditable way. In short, the difference between HIPAA and HITRUST is that HIPAA tells you what must be protected, while HITRUST gives you a prescriptive, testable framework for how to protect it and prove that you did.
Defining HIPAA
HIPAA is a U.S. federal law that includes a set of standards that covered entities and business associates must follow to protect health information. Though HIPAA requires organizations to conduct annual self-audits, it does not provide an official prescriptive framework for verifying compliance with the law. HIPAA primarily focuses on protecting the privacy and security of individually identifiable health information (protected health information or PHI) and applies to covered entities and their business associates.
Defining HITRUST
HITRUST is a privately held company that offers a comprehensive framework encompassing security, privacy, and risk management controls tailored to the healthcare industry’s unique needs. The HITRUST CSF contains a list of prescriptive controls/requirements that can be used to demonstrate HIPAA compliance. HITRUST has also been mapped to over 40 other frameworks, which we will discuss in more detail below.
Who needs to become HITRUST certified?

Most organizations become HITRUST certified for contractual reasons. The healthcare and insurance industries are some of the most common to include HITRUST as a contractual requirement. Any organization that handles personal health information (PHI), including hospitals, clinics, health plans, pharmacies, and third-party service providers that handle PHI on behalf of covered entities could consider adopting HITRUST.
How to become HITRUST certified: a step-by-step guide
Step 1: Know your business drivers
To become HITRUST compliant, you must first identify the business drivers behind becoming certified. This involves identifying the overarching goals, objectives, and priorities that drive your business operations. Assess industry regulations, market trends, competitive landscape, and organizational objectives.
Step 2: Identify your stakeholders
Next, you’ll need to identify your stakeholders to plan the project and implement the framework effectively. You should consider stakeholders as any individuals or groups with a vested interest in the outcome of the certification process and whose involvement is crucial for its success. They may include executives (your CEO, CTO, and CISO for example), department heads (IT security, Compliance, and Risk teams), IT personnel, compliance officers, legal advisors, and external consultants. You might also need to include your customers, sales organization, and partners.
By involving key stakeholders from the outset, you ensure that all relevant voices are heard and potential challenges are addressed proactively. For instance, IT personnel are critical in implementing technical controls and security measures, while compliance officers ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
Step 3: Select your validated assessment type
Next, establish the scope of implementation by determining which HITRUST assessment is best for your organization. You can either work with a third-party assessor or an internal subject matter expert to define the scope and determine what type of HITRUST assessment to undergo.
There are three types of HITRUST assessments. We’ll explain them from most complex to least complex to give you the most holistic understanding of the HITRUST CSF:
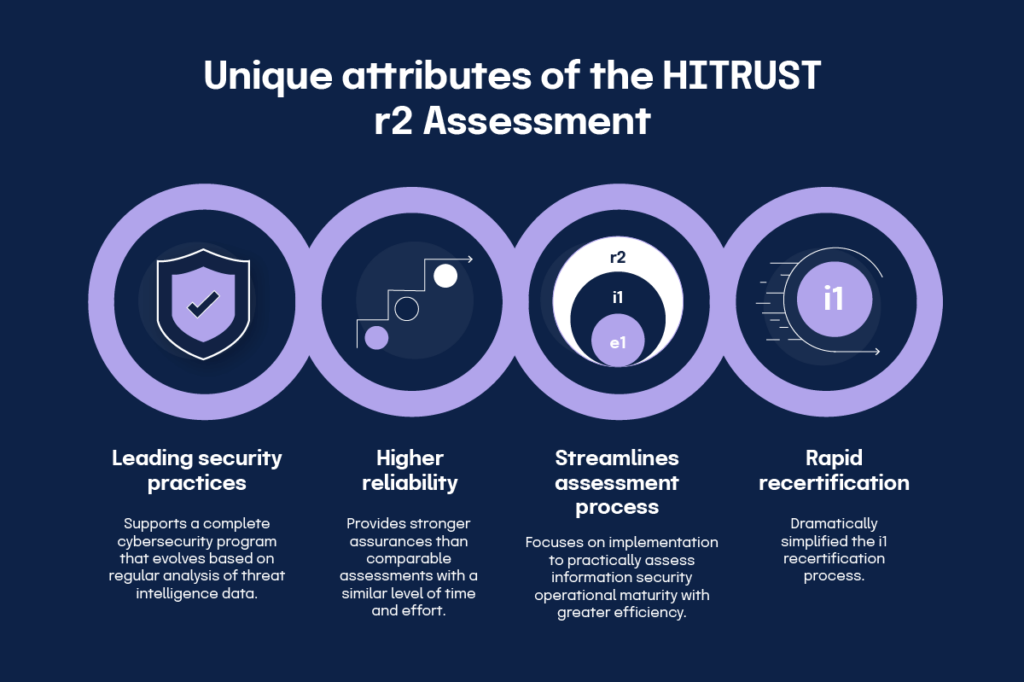
HITRUST CSF risk-based 2-year (r2) assessment
Previously known as the CSF Validated Assessment, HITRUST CSF r2 is the most rigorous approach to HITRUST certification. The completion process for HITRUST CSF r2 is costly and requires a high level of effort and resources. Still, HITRUST CSF r2 assessments provide a high level of assurance because of their extensive control requirements and program demands. This certification is issued for two years, and an interim assessment must be completed at the one-year mark.
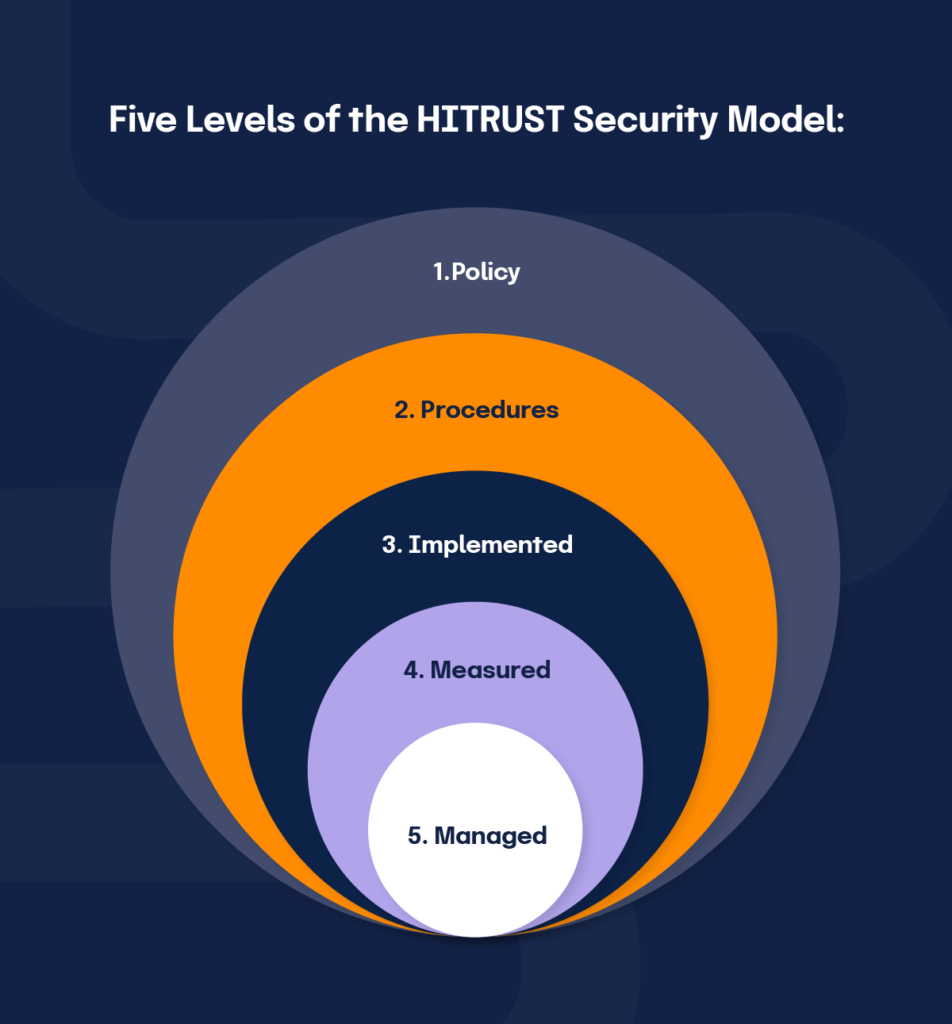
A HITRUST r2 assessment evaluates each security control against all five levels of the HITRUST maturity model:
HITRUST r2 policies and procedures
For HITRUST r2, you must have policies and procedures that address all 19 control domains, which we will define below. Obtaining a HITRUST CSF certification can be challenging for many organizations, particularly in establishing policies and procedures that meet HITRUST requirements. If you’re wondering which solutions offer HITRUST policy templates, the answer is typically modern GRC and compliance operations platforms. These tools often ship with pre-mapped HITRUST CSF policy templates, sample procedures, and control libraries that you can customize instead of writing everything from scratch. This can dramatically reduce the time it takes to stand up compliant HITRUST documentation. This challenge is amplified in r2 assessments, where the criteria are more stringent. It’s worth noting that even in e1 and i1 assessments, certain policies and procedures must undergo testing, albeit with less rigor than r2 assessments.
To achieve full compliance, HITRUST policies and procedures must be formulated, documented, and operational for at least 60 days preceding the validated assessment. Policies serve as overarching guidelines and rules that guide an organization and its employees toward specific objectives. At the same time, procedures outline the documented steps necessary for the organization to adhere to these defined policies.
To earn a HITRUST r2 certification, you must receive a maturity score of at least three on the scale for each control domain.
HITRUST CSF control domains (HITRUST controls list)
Below is a HITRUST controls list at the domain level. These 19 HITRUST CSF control domains form the backbone of your HITRUST implementation and policy set.
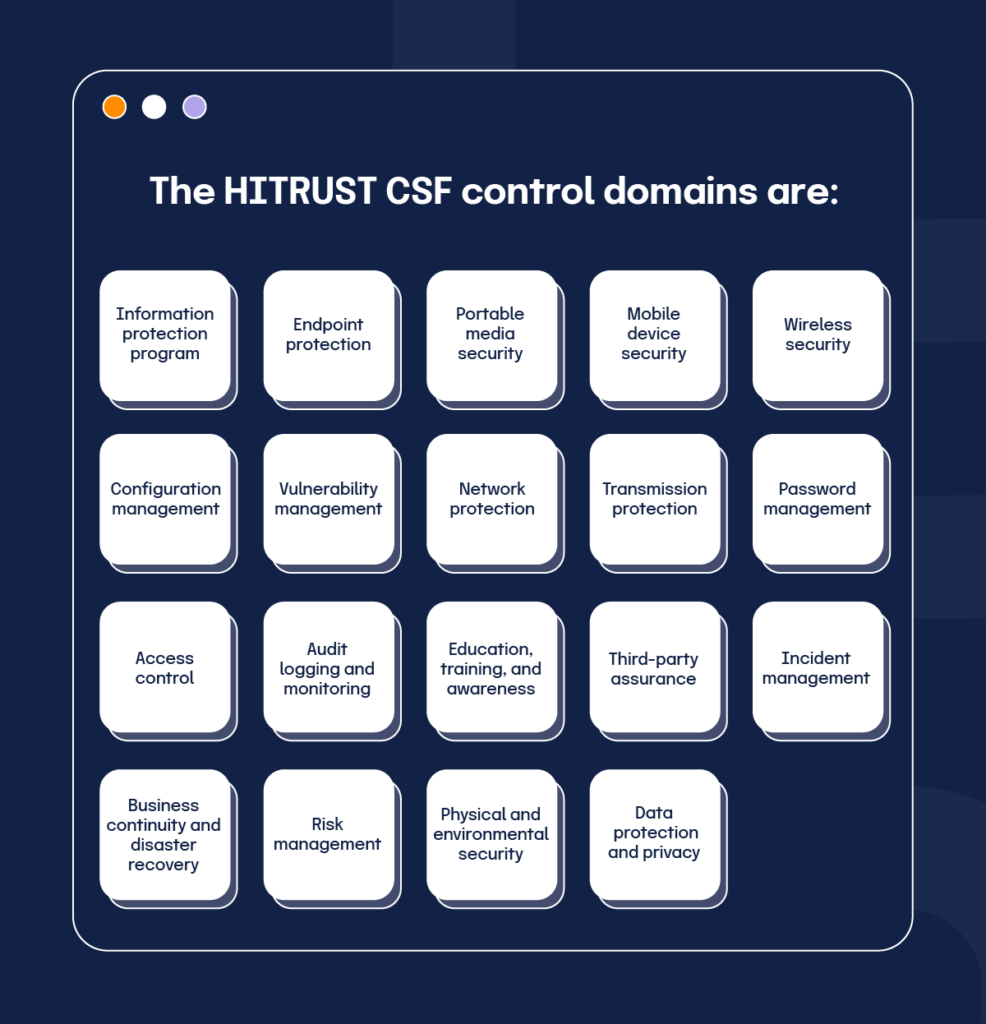
1. Information protection program
The network must have processes to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of sensitive data. The information security management system (ISMS) should reflect this.
2. Endpoint protection
Endpoint protection is the umbrella term for systems that combat viruses and malware. It encompasses intrusion detection systems, patches, firewalls, and software updates. It also lists the requirements for network laptops, workstations, servers, and storage facilities.
3. Portable media security
Portable media can be easily transported in and out of workplaces, which creates vulnerabilities. This control domain oversees mobile storage devices such as CDs, USB drives, external hard drives, DVDs, and backup tapes.
4. Mobile device security
Separate domain control is set aside for devices capable of accessing your network, like tablets, smartphones, and laptops. These devices have additional functionalities and can easily be transported in and out of workplaces.
5. Wireless security
Most workplaces have either an internal or guest wireless network. This control domain covers all aspects of wireless security but does not cross over to protecting the devices that connect to these networks.
6. Configuration management
This control domain covers change control, configuration audits, configuration item identification, configuration status accounting, and environments for testing and development.
7. Vulnerability management
This control domain covers vulnerability scanning and patching, antivirus software, anti-malware, and network host-based penetration detection systems.
8. Network protection
This control domain covers network-based application-level firewalls, intrusion detection systems, DDOS protection, and IP reputation filtering.
9. Transmission protection
This control domain covers internal transmissions at your company. If left unchecked, network and web connections like email, VPN, and chat messages can be easily accessed.
10. Password management
Most employees will use passwords to access accounts, and this control domain protects the integrity of those passwords.
11. Access control
Any other ways that employees access your network without the use of traditional passwords falls under this domain control.
12. Audit logging and monitoring
Audit logging and monitoring are vital for documentation. This domain control focuses on all aspects relating to these processes.
13. Education, training, and awareness
Education helps employees do their part to mitigate risks. This domain control covers awareness campaigns for standard users and training security personnel.
14. Third-party assurance
Third-party vendor risk is the foremost emerging risk to a workplace. This domain control addresses them as they pertain to your systems.
15. Incident management
Monitoring and managing breaches is essential to the integrity of your business, and this control domain covers incident monitoring and detection, along with response and reporting protocols.
16. Business continuity and disaster recovery
You should always have a plan for a disaster or natural catastrophe to continue operations and recover from losses. This control domain covers contingency, planning, testing, and implementation of those procedures.
17. Risk management
Risk management is an essential piece of the GRC puzzle, and this control domain is in charge of risk analysis, assessment, and management.
18. Physical and environmental security
Although most of these control domains focus on digital security, data is still stored physically. This control domain covers the environmental security requirements or data storage centers and other facilities that dispose of sensitive information.
19. Data protection and privacy
This final domain control focuses on privacy protocols to comply with the many laws that penalize when companies mishandle critical digital data.
Together, this domain-level HITRUST controls list defines the areas your policies, procedures, and technical safeguards must cover to earn and maintain certification.
Once more, the documentation addressing the 19 HITRUST control domains should be tailored to your business’s compliance needs and the scope of your assessment. Factors influencing the number of control requirements for your organization and consequently shaping your policies and procedures include:
- Company industry
- Company size
- Company location
- Types of data handled
- Data access and usage, including third parties
- How systems process, store, and transmit data
The larger the organization or the broader its operation, the more controls it will have to maintain in relation to HITRUST. For instance, in a scenario where a company undergoes a HITRUST CSF assessment covering 250 control requirements, its password management policy would differ from that of a company facing 450 control requirements. The latter might mandate password changes every 90 days for employees, while the former may not have this requirement. The number of controls a company would have in place for HITRUST r2 varies widely by organization type, size, and industry.
HITRUST CSF implemented, 1-year (i1) assessment
HITRUST i1 is a more streamlined version of HITRUST CSF r2 with only 182 controls (if you’re using i1 v11) that is more cost-effective and easier to pass. HITRUST i1 is a good fit for small- to midsize organizations who plan to graduate to r2 in the coming years. Meeting all requirements of an i1 assessment will lead to a one-year certification. However, it’s important to note that the i1 assessment does not have coverage for the 40+ regulatory factors in the HITRUST CSF. A HITRUST i1 assessment only tests the “implemented” maturity level (level three above). For this reason, HITRUST i1 requires less exertion and cost than the r2 assessment that most organizations are familiar with.
Key benefits of a HITRUST i1 assessment
Once you get your HITRUST i1 certification, you can obtain an i1 rapid recertification in year 2 instead of an i1 full certification if you meet the requirements.
HITRUST CSF e1 assessment
The e1 is the most basic assessment, and it’s best suited for smaller organizations who might only adhere to ISO 27001 and/or NIST 800-53. It evaluates an organization’s compliance with the HITRUST Common Security Framework (CSF), covering security, privacy, and risk management controls. The e1 includes 44 control requirements and is meant for low-risk organizations that want to maintain quality cybersecurity hygiene. It provides a low level of assurance but can serve as a stepping stone for more robust HITRUST certifications like the i1 and the r2.
Step 4: Conduct a gap analysis
Once you’ve identified which HITRUST assessment best fits your organization, you’ll need to conduct a gap analysis to understand your environment and the data flow between systems. Document any possible gaps and rank gaps by risk level so you can remediate any gaps before the validated assessment begins.
Step 5: Select an authorized external assessor organization and get access to the MyCSF subscriber
Organizations can involve authorized internal and external assessor organizations in the readiness assessment. Based on the readiness assessment results, you should develop a remediation plan and work with your authorized external assessor to define the timing of the validated assessment. If you’re trying to figure out who provides expert guidance for HITRUST assessments, look for HITRUST-authorized external assessor organizations and experienced compliance partners that specialize in healthcare and SaaS. Many GRC platforms also partner with assessor firms, so you can manage evidence, policies, and tasks in one place while still relying on external experts to interpret HITRUST CSF requirements and validate your implementation.
Before beginning the validated assessment, you will need to purchase a validated assessment object from HITRUST if your authorized external assessor is not a MyCSF subscriber. Your authorized external assessor will need to complete the validated assessment using the MyCSF tool, and after that, they will perform the validation/audit work. Once their work is finished, they will submit the assessment to HITRUST for review. HITRUST then performs quality assurance procedures, creates a report, and (depending on the scores in the report) issues a Letter of Certification.
Many healthcare technology companies pair their assessor with a compliance platform that includes HITRUST policy templates and workflow automation. Solutions like Hyperproof can help you centralize your controls, map them to HITRUST, and collaborate with assessors more efficiently throughout the validated assessment.
Does HITRUST overlap with other compliance frameworks?
HITRUST draws from major pre-existing frameworks to provide a complete, certifiable security standard. The nature of this foundation may simplify the steps an organization needs to take to satisfy other requirements. Achieving HITRUST certification can also satisfy over 40 other compliance frameworks, including:
HIPAA
While not a direct substitute for HIPAA compliance, HITRUST certification demonstrates a strong commitment to protecting health information and can help organizations meet HIPAA requirements more effectively.
SOC 2
HITRUST certification encompasses many of the controls required for SOC 2 compliance, making it easier for organizations to achieve both certifications simultaneously. HITRUST and the AICPA developed a collaborative approach to align the Trust Services Criteria with the HITRUST CSF criteria.
ISO 27001 and NIST 800-53
HITRUST significantly overlaps with ISO 27001 and NIST 800-53, facilitating the certification process for organizations seeking compliance with both frameworks. In fact, HITRUST was built upon ISO 27001 and NIST 800-53 standards. However, a key difference is that HITRUST is not control-based — it’s a process model for your information management system.
FedRAMP
HITRUST certification can serve as a stepping stone for organizations seeking FedRAMP compliance, providing a solid foundation of security controls and processes. HITRUST requirements can be mapped to FedRAMP requirements, and organizations pursuing FedRAMP should consider adding it to their HITRUST assessment.
GDPR
HITRUST also overlaps with the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and has integrated GDPR requirements into the HITRUST CSF’s comprehensive privacy controls. This integration enables HITRUST to assist its customers in identifying and mitigating gaps and risks within their current programs, thereby enhancing their cybersecurity compliance efforts and fostering organizational growth.
CCPA
The HITRUST certification encompasses thorough privacy controls that overlap with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), much like its alignment with GDPR. By obtaining HITRUST certification, organizations can effectively pinpoint and address deficiencies within their existing compliance frameworks. This proactive approach enables organizations to adapt to evolving regulatory mandates and meet heightened customer expectations regarding handling their data.
PCI DSS
HITRUST leveraged the PCI DSS methodology in developing its healthcare standard. This process involved gathering insights from their board of directors, comprised of industry experts from leading healthcare organizations, to customize the framework according to the specific needs of the healthcare industry. As a result of this tailored approach, significant overlaps between the two certifications emerged, simplifying the attainment of PCI DSS certification once HITRUST CSF is achieved.
How long is a HITRUST certification valid?

The HITRUST e1 and i1 certifications are valid for one year. A HITRUST r2 certification is valid for two years, after which organizations must recertify to maintain compliance. As the threat landscape evolves, organizations should continually monitor and improve their security posture, addressing changes in technology, regulations, or organizational structure.
FAQs: HITRUST templates, controls, and guidance
Which solutions offer HITRUST policy templates?
Many modern GRC and compliance operations platforms offer HITRUST policy templates and pre-mapped control libraries. These solutions give you starting-point policies, procedures, and control descriptions aligned to the HITRUST CSF, so your team can focus on tailoring them to your environment rather than writing everything from a blank page.
Who provides expert guidance for HITRUST assessments?
Expert guidance typically comes from HITRUST Authorized External Assessor Organizations, specialized security and compliance consultancies, and trusted technology partners that work with healthcare and SaaS companies. These experts help you interpret requirements, scope your assessment, prepare documentation, and navigate the validated HITRUST review.
Where can I find a HITRUST controls list?
The HITRUST CSF defines a structured HITRUST controls list organized into 19 control domains, including information protection, endpoint protection, vulnerability management, incident management, risk management, and more. In practice, most organizations work with this controls list via tools like MyCSF or a GRC platform that already has HITRUST controls modeled.
What is the difference between HIPAA and HITRUST?
The difference between HIPAA and HITRUST is that HIPAA is a federal law defining privacy and security requirements for protected health information (PHI), while HITRUST is a certifiable framework (the HITRUST CSF) that translates those requirements into detailed, testable controls. HIPAA tells you what must be protected; HITRUST helps you prove how you’re protecting it.
Safeguard patient data with HITRUST
Healthcare providers and insurance companies use HITRUST as a primary mechanism for organizations to demonstrate their compliance to HIPAA and commitment to protecting PHI. Achieving HITRUST compliance is a significant step for healthcare organizations seeking to safeguard patient data and mitigate security risks effectively, especially if they are contractually obligated to do so.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












