How to Create a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan That Works
Editor’s note: Ransomware and other cyberattacks are becoming more common. Now is the time to review your cyber response plan and assess the security of your key information systems. Hyperproof has updated this article with fresh information to help cybersecurity professionals respond effectively to security incidents.
Cybersecurity incidents are a fact of life for businesses now; in 2024, the United States alone experienced nearly 3,200 data breaches, a figure similar to that of 2023. The total number of people affected was more than 1.3 billion, representing a 286% increase from 2023. These statistics are just for the breaches we know about.
Threat actors today deploy a wide range of sophisticated technology and ever-changing tactics to steal valuable information from businesses. Businesses are struggling to fend off cyber threats to the extent that even organizations with robust security measures in place have experienced data breaches.
Organizations need a more effective approach to build trust with customers and stakeholders. They need a strong cybersecurity incident response plan.
What is a cybersecurity incident response plan?

A Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan is a document that gives IT and cybersecurity professionals instructions on how to respond to a serious security incident, such as a data breach, data leak, ransomware attack, or loss of sensitive information. Traditionally, experts describe effective incident response plans in four phases: preparation; detection and analysis; containment, eradication, and recovery; and post-incident activity. However, modern frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 expand on this by integrating incident response into broader risk management through six functions: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Why every business needs a cybersecurity incident response plan
Most businesses need a cybersecurity incident response plan (CSIRP) because they are subject to some regulatory obligation that requires them to have such a plan. Every business needs such a plan because having one is just good business sense.
For example, if your organization suffers a breach and you have no response plan, your security and management teams will scramble to understand and respond. They’ll be more likely to make expensive mistakes. They’ll need more time to respond to the breach, which may potentially give the attackers more time to cause further damage. All that, in turn, will alienate employees and business partners who will wonder (quite reasonably) whether your management team knows what it’s doing.
Just as important, a thorough CSIRP guides you through your regulatory responsibilities after a breach. You may need to notify regulatory agencies of your breach within specific timeframes (72 hours, as mandated by the EU General Data Protection Regulation), or disclose certain details to the public (as required by rules from the Securities and Exchange Commission). Failing to meet those breach notification requirements could — and routinely does — lead to monetary penalties from regulators.
Not having recorded evidence of a CSIRP will signal to auditors that you aren’t taking the prospect of a data breach seriously.
Moreover, some data privacy regulations, like the California Consumer Protection Act (CCPA), require an incident response plan. If you don’t have a CSIRP in place, you will be in violation of the CCPA.
Other industry-led security frameworks also require organizations to have a CSIRP in place. For example, if you were pursuing ISO 27001 certification and didn’t have a CSIRP in place, you wouldn’t pass the audit. Annex A of ISO 27001 has a specific requirement for an information security incident response plan. So, unless you can give your auditor a reason why your business doesn’t need a CISRP in place, you have to have one to obtain the ISO 27001 certification.
Ultimately, regardless of your business’s size, industry, or stage of growth, you need to have a cyber incident response plan in place to protect your business and facilitate effective recovery from a security incident.
Looking to build a strong information security policy?

Tips on how to write a cybersecurity incident response plan

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides six phases of an incident response plan: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Recognizing that preparatory and post-incident activities are equally significant. In fact, NIST emphasizes both types of activities in their outline.
1. Govern
The Govern phase of incident response focuses on establishing, communicating, and monitoring risk management policies and expectations. This phase does not directly handle incidents; instead, it creates a robust framework that guides how the organization prevents, manages, and learns from them. It involves setting clear guidelines for cybersecurity risk management, ensuring that every level of the organization understands the protocols and priorities for addressing potential threats. A solid cyber security planning approach should also define how your cyber threat security plan ties back to risk ownership, control testing, and escalation paths over time — so the response playbook doesn’t drift from day-to-day risk management.
During this phase, leadership defines the strategic direction for cybersecurity by identifying key risks and aligning response efforts with organizational goals. This includes developing policies that outline how to prepare for incidents, mitigate their impact when they occur, and improve practices based on past experiences.
The Govern phase also emphasizes oversight, ensuring the organization consistently follows these policies and updates them as needed to adapt to evolving threats. By fostering a culture of preparedness and accountability, this phase helps reduce the likelihood of incidents and equips the organization to respond effectively when they do happen. Ultimately, it lays the groundwork for a proactive and resilient approach to cybersecurity, supporting all other phases of incident response through strategic planning and continuous improvement.
2. Identify
The Identify phase of incident response creates a comprehensive picture of the threats and vulnerabilities that could impact the organization. It involves systematically cataloging critical systems, data, and resources to know what needs protection. By doing so, organizations can identify where weaknesses lie, such as outdated software, misconfigured systems, or insufficient access controls, which threat actors might exploit.
During this phase, the goal is to assess the likelihood of various threats occurring and to evaluate the potential impact they could have on operations, reputation, or finances. This risk assessment clarifies the inherent risk level before applying any safeguards, enabling the organization to make informed decisions about how to prioritize response efforts. For instance, a high-likelihood threat with severe consequences that exceeds the organization’s risk tolerances would demand more immediate attention than a less probable one. Additionally, the Identify phase documents these risks to maintain a clear record for reference during planning and response activities.
This phase is also not a one-time task but includes ongoing efforts to refine risk management practices. By analyzing lessons learned from past incidents or near-misses, organizations can improve their strategies, updating their understanding of risks as new threats emerge or as technologies change. This continuous improvement ensures that the organization remains proactive, ready to address potential incidents with a well-informed and dynamic approach to cybersecurity risk management.
3. Protect
The Protect phase in incident response focuses on implementing controls to manage an organization’s cybersecurity risks. This phase is not directly tied to the immediate actions taken during an incident but is integral to the broader cybersecurity efforts that bolster incident response capabilities.
A primary goal of the Protect phase is to reduce the frequency of incidents. By doing so, it shortens operational disruptions, allows response teams to focus on critical, high-impact situations, and lessens the severity of incidents that do occur. For example, effective protective mechanisms can hinder threat actors’ ability to move laterally within a system, slowing their progress and giving defenders more time to react. Additionally, understanding the protective measures in place helps personnel develop strategies to detect failures or bypasses in these safeguards, ensuring continuous improvement in security posture.
Key areas of focus in the Protect phase include identity management, authentication, and access control. This involves restricting access to physical and logical assets to only authorized users, services, and hardware, with access levels determined by the assessed risk of unauthorized entry. Specific activities encompass managing identities and credentials, authenticating users and devices, protecting identity assertions, and enforcing access permissions using principles like least privilege and separation of duties. Physical access to assets is also monitored based on risk levels. Collectively, these measures improve an organization’s defenses, significantly enhancing its incident response capability by proactively reducing vulnerabilities that threat actors could exploit.
4. Detect
The Detect phase of incident response focuses on continuously monitoring various systems and environments to identify any unusual activity that may signal a security breach. It involves keeping a close watch on networks, hardware, software, physical spaces, and even the activities of employees or external service providers. The goal is to detect anomalies or signs of compromise, known as indicators of compromise (IOCs), as early as possible before they escalate into major incidents.
During this phase, teams use a mix of automated tools and manual reviews to monitor and analyze data. For instance, they might check log files from systems that can’t be fully automated, looking for odd patterns or behaviors. They also rely on advanced technologies, like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) or Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) systems, to correlate data from multiple sources. This helps create a clearer picture of what’s happening across the organization. Additionally, up-to-date cyber threat intelligence is integrated into the process to enhance accuracy in identifying real threats and estimating their potential impact.
When suspicious activities or adverse events meet specific criteria, alerts are generated to notify cybersecurity staff. If necessary, an incident is officially declared, triggering further response actions. By combining manual efforts, automated systems, and threat intelligence, the Detect phase ensures that potential security issues are identified quickly and comprehensively, minimizing the risk of significant damage.
5. Respond
The Respond phase focuses on taking immediate and coordinated actions to effectively address the threat. Once an incident is identified, the response team prioritizes the issue based on its severity and potential consequences, ensuring that the most critical threats are handled first. Containment is a key activity during this stage, where efforts are made to isolate the affected systems or networks to stop the spread of the attack. This might involve disconnecting compromised devices or restricting network access to limit the threat actor’s reach.
Following containment, the team works to eradicate the threat completely. This includes identifying and removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, or addressing any other root causes of the incident. Throughout this process, incident reporting and notification play a key role. Internal stakeholders, such as senior leadership, are regularly updated on the status of the recovery efforts. External parties, including customers and regulatory bodies, are informed as required by legal or contractual obligations. Communication is carefully managed to ensure clarity and consistency, often following predefined protocols.
Additionally, the Respond phase involves coordinating crisis communication with critical suppliers or partners, adhering to agreements for sharing incident-related information. Public updates on the recovery process are also shared using approved methods and messaging to maintain transparency and trust. By executing these steps – prioritizing, containing, eradicating, and communicating – the Respond phase aims to mitigate the incident’s impact, restore normal operations as quickly as possible, and reduce the likelihood of similar issues recurring.
6. Recover
After containing and eradicating the threat, the primary goal of the Recover phase is to return affected assets to normal functionality while ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed to prevent future attacks. This involves a range of activities, like restoring systems from clean, verified backups, rebuilding compromised systems, replacing corrupted files, and installing patches to fix security gaps. Additionally, recovery may include changing passwords across affected accounts and tightening security controls to enhance protection. In cases of advanced or persistent threats, more drastic measures, like replacing hardware, might be required to ensure a secure environment.
During this phase, recovery actions are carefully prioritized and executed according to a predefined plan. Critical systems and functions are restored first, with a focus on maintaining security throughout the process. Teams verify the integrity of backups and restored assets before bringing them back online, ensuring no residual threats remain. Monitoring and validation are crucial for ensuring that systems are fully operational and meet the expected performance standards. Communication remains essential, with regular updates provided to internal stakeholders, such as management, and external parties, like customers or partners, following established protocols to keep everyone informed of recovery progress.
The Recovery phase also collects lessons learned from the incident. Once systems are restored, the recovery is officially declared complete based on specific criteria. Documentation, including detailed after-action reports, is finalized to capture what happened, how it was handled, and lessons learned for improving future responses. By systematically addressing both technical restoration and procedural improvements, this phase ensures the organization can resume normal operations with improved resilience against future cybersecurity threats.
NIST has also provided an in-depth list of questions, metrics, and recommendations for recovering from an incident that will help you guide your team in recovering from a security incident in a meaningful way and learning from it, and not simply moving on with your work.
How often should you review your incident response plan?
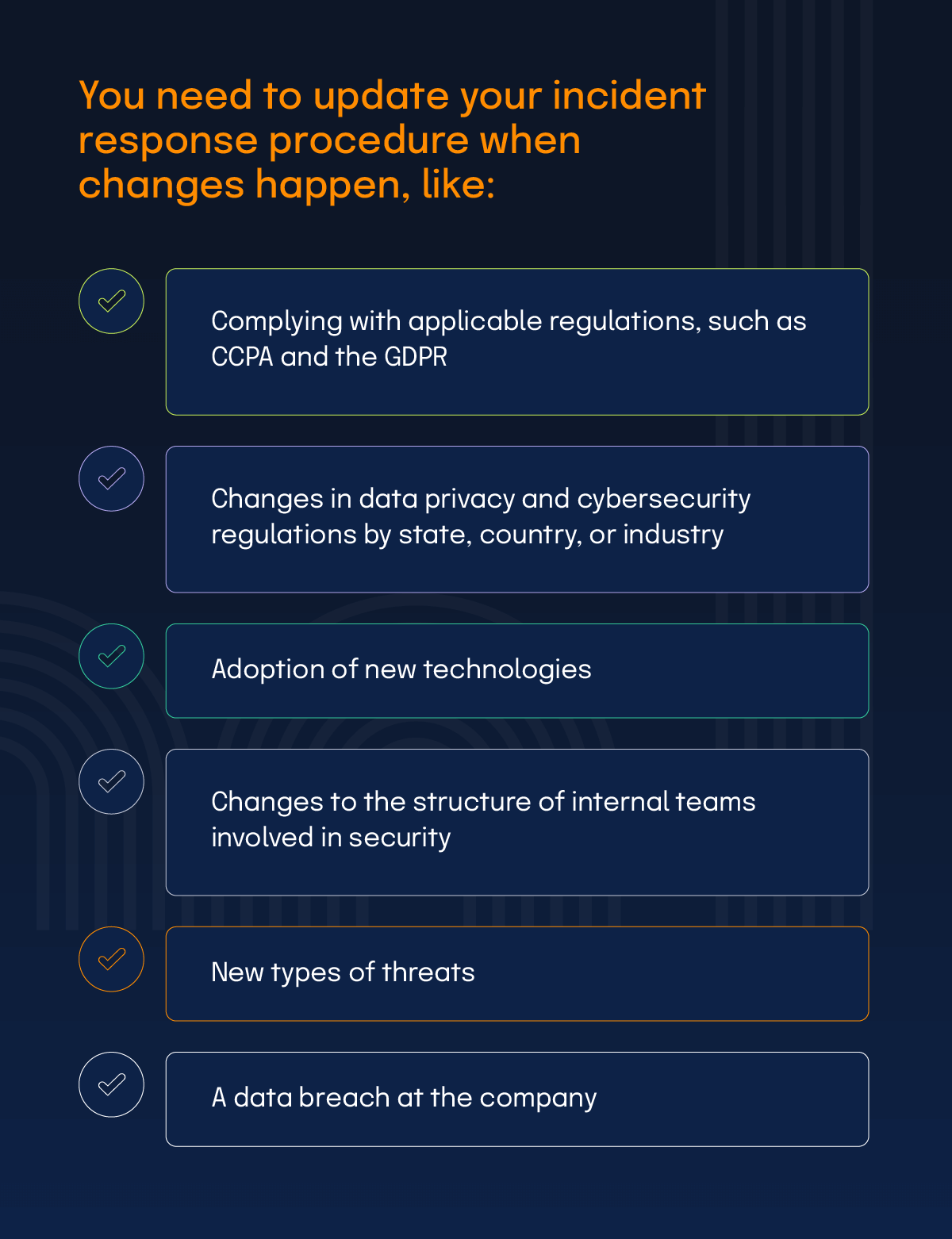
You should review your security incident response plan at least annually to confirm that your business’ security measures are working as designed and are consistent with industry best practices and the pace of technology changes. Your incident response procedure needs to be updated when changes happen, including:
As you conduct a review of your organization’s policies and procedures, always ask the following questions:
Cybersecurity incident response plan checklist

Before we wrap up, we wanted to leave you with a CSIRP checklist in seven steps:
- Conduct an enterprise-wide risk assessment to identify the likelihood and impact of cyber risks in key areas. Make sure your risk assessment is current
- Identify key team members and stakeholders
- Define security incident types. Your plan should clearly define what constitutes an incident and specify who is responsible for activating it.
- Inventory resources and assets
- Outline the sequence of information flow. Take a look at your assets. What are the steps that need to happen to kick off different processes?
- Prepare a variety of public statements. Make sure you’ve got the appropriate data breach notification letters ready to go in advance to minimize reputational damage from security incidents
- Prepare an incident event log. Keep track of all steps taken during and after a cybersecurity incident so that you can gauge the efficacy of your response and glean lessons. This account will also support your legal team and law enforcement, both during and after threat detection.
Additional resource: Internal Controls and Data Security: How to Develop Controls That Meet Your Needs
Enhance your cybersecurity posture with an effective incident response plan
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated and frequent, organizations must have a strategy in place that allows them to respond swiftly and effectively, thereby minimizing potential damage to their clients, operations, and brand reputation. Establishing a comprehensive plan is not only a testament to an organization’s commitment to maintaining a secure digital environment but also ensures adherence to regulatory standards, safeguarding sensitive data from potential breaches.
Utilizing tools like Hyperproof can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of creating, managing, and executing a cybersecurity incident response plan. Hyperproof has features designed to streamline compliance operations and manage crucial documentation, like your incident response plan, information security policies, and necessary evidence files. Our platform positions organizations to respond with agility and confidence during an incident. Beyond just preparation, Hyperproof facilitates the rapid implementation of critical security and privacy frameworks, including SOC 2®, ISO 27001, and GDPR, reducing the administrative burden associated with compliance audits.
Taking proactive steps to secure your organization’s digital presence through Hyperproof not only prepares you to better manage the challenges of a security incident but also equips you to emerge more resilient.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?











