How to Assess Your Cloud Security Posture
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) gives organizations a clear view of how their cloud resources are configured, whether they meet compliance standards, and where threats could arise. By spotting misconfigurations, unpatched software, and weak access controls early, companies can prevent unauthorized access and data loss. This helps protect sensitive assets and maintain customer trust.

A solid cloud security posture serves as a first line of defense in today’s cloud-centric environment. Regular assessments create a baseline, track security health, and inform where defenses need strengthening. Integrating shift-left practices embeds security into development pipelines, catching vulnerabilities before production. Pairing static configuration reviews with continuous runtime monitoring adds visibility into active threats, allowing teams to prioritize remediation efficiently. Together, these measures form a resilient cybersecurity strategy that adapts to changing risks.
The key components of cloud security posture
Identity management
Data protection
Network security
Compliance elements
Compliance shapes an organization’s cloud security posture by imposing legal, regulatory, and industry standards that dictate how data must be protected, encrypted, and accessed. They force organizations to continuously assess configurations, use automated scans for gaps, and document controls. This in turn builds customer trust and reduces the risk of penalties. Meeting the requirements for frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS necessitates regular internal or third-party audits that demonstrate adherence and identify areas for improvement.
How do cloud provider and customer responsibilities affect cloud security posture assessment?
The shared-responsibility model splits security duties. Providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers secure everything they run on top of it. Assessments must focus on customer-controlled elements, like identity management, encryption, and application flaws, while verifying the provider’s baseline protections through their certifications.
Providers manage physical hosts, hypervisors, and core services, delivering tools and compliance reports that establish a secure foundation. Customers must continuously audit access controls, patch operating systems, and verify that their configurations meet regulatory standards. Effective posture evaluation requires clear delineation of responsibilities, ongoing collaboration, and transparent communication to maintain a strong security stance in the cloud.
Establishing your assessment framework
How can you use the CIS Benchmarks as a universal security language across cloud platforms?
The CIS Benchmarks act as a universal security language, providing a single set of concrete controls, like encryption, access policies, and logging. These can be mapped to AWS, Azure, and GCP configurations. Organizations adopt the relevant benchmark for each service, use automated scanners to compare actual settings against the standard, and remediate gaps, ensuring consistent security posture across all clouds. Because the benchmarks are vendor-agnostic yet detailed, they simplify communication with auditors and partners, align with many regulations, and receive regular updates to stay current with threats. By treating the benchmark as a baseline, organizations can prioritize fixes, maintain compliance, and avoid misconfigurations in multi-cloud environments.
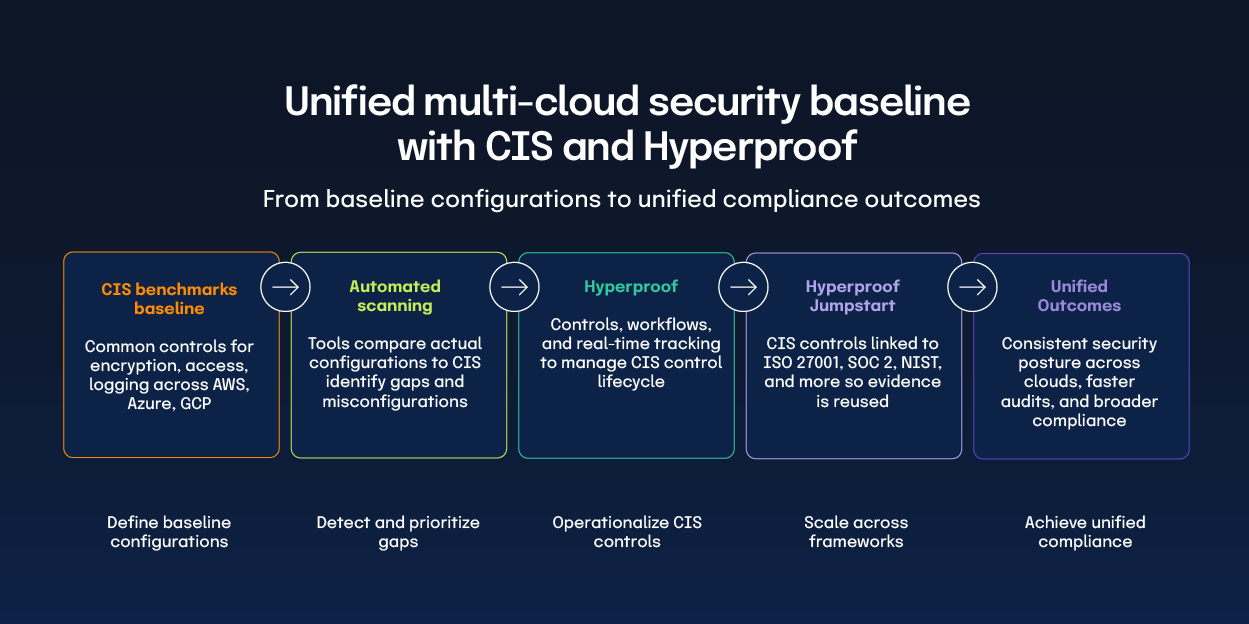
The CIS Benchmarks serve as the foundation that defines exactly what secure settings should look like across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Once those baseline controls are in place, Hyperproof can turn that foundation into a living program that keeps the controls aligned with broader compliance goals.
Hyperproof supports the CIS Critical Security Controls® by offering an out-of-the-box framework template, automated workflows, and real-time tracking. This enables organizations to quickly adopt the controls, assess compliance, and remediate gaps in access management and data protection. Through jumpstarts, Hyperproof also maps each CIS control to the equivalent requirements in ISO 27001, SOC 2®, and NIST frameworks. Evidence and assessments collected for CIS can be reused to satisfy those standards. This accelerates broader compliance initiatives, reducing manual effort and errors. By linking CIS to multiple regulations, organizations can build a unified security posture and move efficiently to comprehensive compliance.
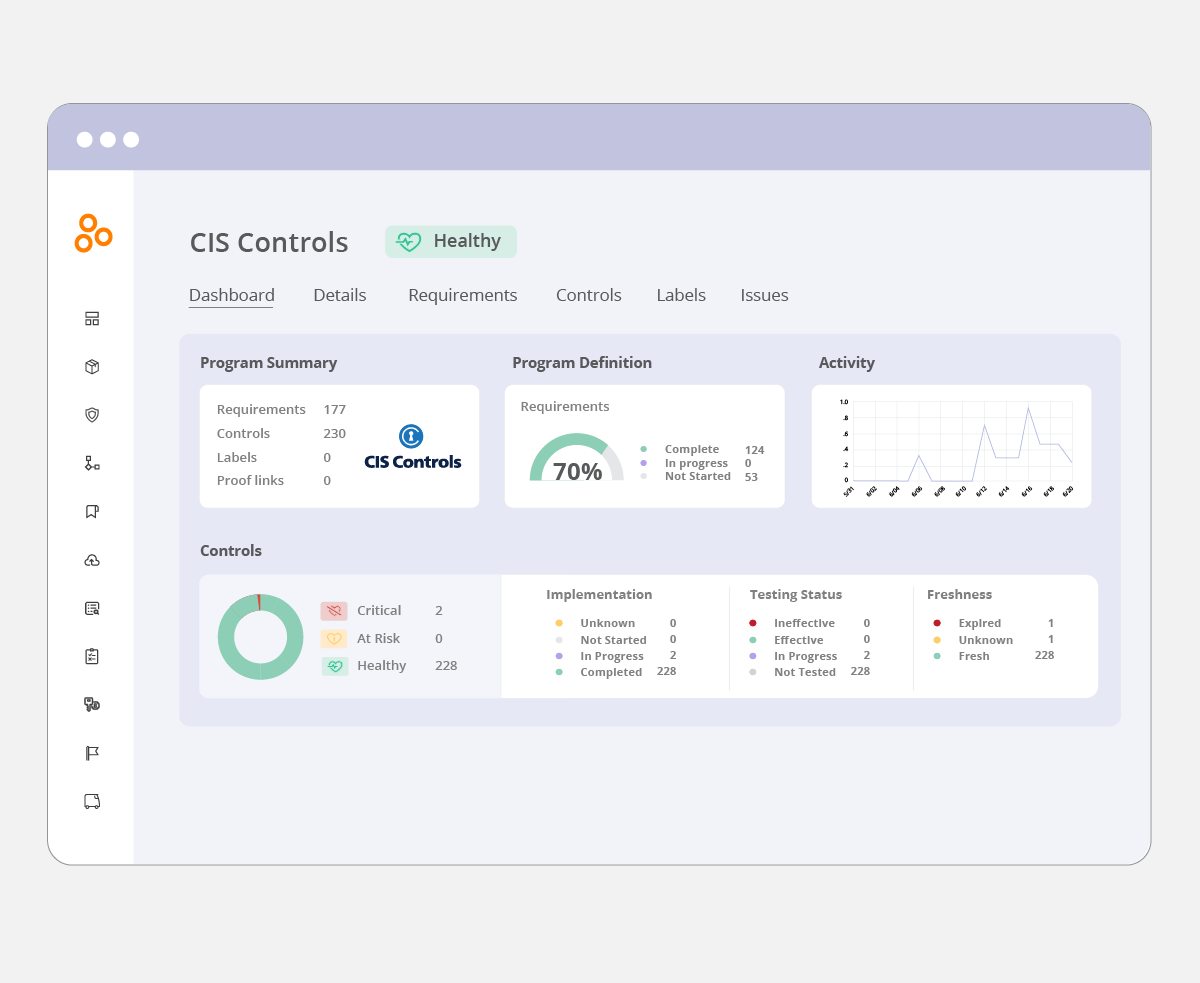
Assessment tools and implementation strategy
What strategies ensure consistent security assessment across AWS, Azure, and GCP environments?
Deploy a centralized security platform that ingests configuration data from all three clouds and maps it to common frameworks like CIS, NIST, or ISO 27001. This provides a single view, simplifies reporting, and instantly highlights deviations. Schedule regular audits paired with real-time scans to catch misconfigurations before they become risks. By aligning on universal controls, leveraging cross-cloud tooling, and maintaining ongoing oversight, organizations can achieve a consistent security posture across diverse cloud environments.
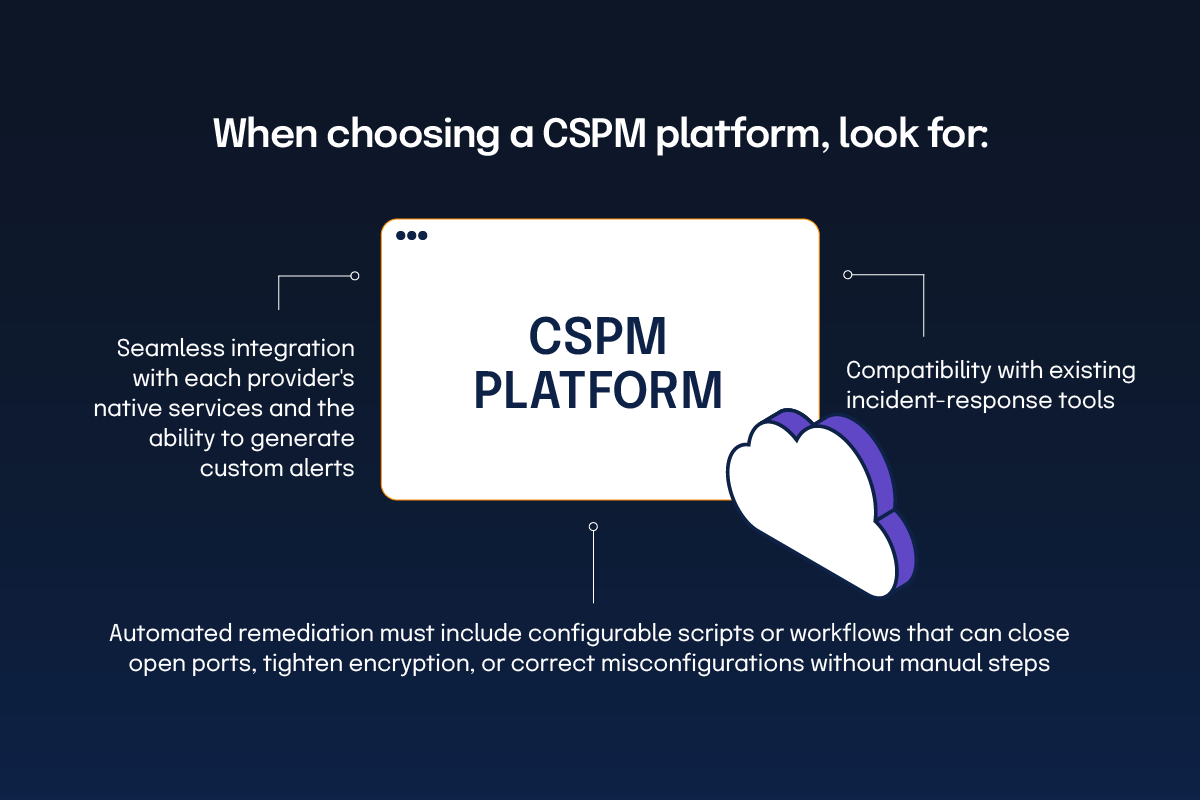
What evaluation criteria should be used for continuous cross-cloud governance and automated remediation capabilities?
When choosing a CSPM platform for continuous cross-cloud governance and automated remediation, prioritize unified visibility, real-time configuration scanning, policy enforcement, and built-in remediation across AWS, Azure, and GCP. The solution should map findings to NIST and CIS benchmarks, support multiple compliance frameworks, and provide actionable recommendations.
Look for:
Risk scoring and prioritization methodologies
How can consistent risk scoring be created across different platforms and service architectures?
Consistent risk scoring across cloud platforms starts with mapping each provider’s native severity levels to a common framework such as CVSS. Understand AWS Security Hub, Azure Security Center, and GCP Security Command Center scales, then translate them into CVSS base scores. This creates a shared language for risk. Next, tailor the model to service architectures — containers, serverless functions, or VMs — by applying custom CSPM policies that weight findings according to data sensitivity and exposure. Feed normalized scores into a central SIEM to maintain a unified view and prioritize remediation uniformly across all environments. Regularly review mappings as providers update their scoring to keep the unified model accurate.
How are data sensitivity, regulatory requirements, and system criticality incorporated into risk calculations?
Risk calculations weight each asset by its data sensitivity, regulatory obligations, and system criticality. Higher scores are assigned to highly confidential data, strict compliance regimes, and mission-critical services.
By integrating these three dimensions into CSPM or security platform scoring models, organizations prioritize protections where business impact, legal exposure, and operational continuity intersect.
How can scores be adjusted based on threat landscapes, compensating controls, and defense-in-depth strategies?
Dynamic risk assessment is a forward-thinking approach that adapts by adjusting risk scores in response to real-time factors. Scores rise when the threat landscape intensifies, fall when compensating controls or defense-in-depth layers mitigate exposure, and are continuously recalibrated to reflect current conditions. Real-time threat intel — like new vulnerabilities, active exploits, or heightened attacker activity — triggers score increases for impacted assets. While existing safeguards like firewalls, encryption, access restrictions, or temporary workarounds lower the calculated risk, recognizing their protective effect. By embedding threat feeds into cloud security posture tools and configuring assessments to consider layered defenses, scores become a nuanced, context-aware reflection of an organization’s security posture across multi-cloud environments.
Conducting comprehensive security assessments
How can you identify and catalog all cloud resources across multiple environments and accounts?
Use automated discovery tools that call each cloud provider’s API, collect inventory data, and store it in a central repository. Schedule regular scans of AWS, Azure, and GCP accounts, recording resource type, region, owner, and sensitivity tags. Apply consistent tagging so you can filter items such as storage buckets containing personal data. A centralized dashboard gives continuous visibility, supports compliance reporting, and feeds policy engines that enforce security rules.
How can automated scanning schedules and alert mechanisms be implemented for ongoing security posture management?
Deploy a CSPM solution and set scan intervals based on asset criticality, like daily for high-risk services, and weekly for lower-risk workloads. Each scan compares configurations to benchmarks like CIS, NIST, GDPR, or PCI-DSS, and links findings to the latest CVE database for risk ranking. Connect scan results to a SIEM platform and create alert rules that trigger notifications via email, SMS, or incident-response hooks when critical issues or unauthorized changes occur. Context-rich alerts include the affected resource, severity, and recommended remediation, enabling rapid response and demonstrating a proactive posture to stakeholders.
How is continuous monitoring implemented for security vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors?
Continuous monitoring relies on automated scanners that constantly probe workloads, containers, and endpoints for known flaws and misconfigurations. The tools ingest CVE feeds, compare assets against policy baselines, and watch for anomalous logins or configuration drift. Threat-intelligence feeds enrich detections with the latest attacker techniques, while log aggregation correlates events across servers, networks, and devices to reveal multi-stage attacks. Integration with native services in AWS, Azure, and GCP ensures the solution scales with resource changes and stays synchronized with the inventory. Embedding these processes in a security operations center reduces exposure windows, meets regulatory requirements, and maintains confidence in the organization’s security posture.
Next steps to evaluate your cloud security posture
First, map each control to the CIS Benchmark or your chosen framework and run an automated scan. Record any misconfigurations, missing MFA, weak encryption, or unexpected open ports in a central inventory. Then assign risk scores based on data sensitivity, regulatory impact, and system criticality. Last, prioritize remediation for the highest-scoring findings and schedule repeat scans to track improvements. Follow these steps to conduct a practical assessment that highlights your cloud environment’s strengths and areas that require improvement.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?