Conducting a Risk Management Audit: Best Practices and Guidelines
Organizations are under relentless pressure to anticipate emerging threats, comply with complex regulations, and ensure operational resilience. This means conducting a comprehensive risk management audit is no longer a to-do list task, but a strategic imperative. A structured audit cadence is a best practice in risk management because it helps leaders spot gaps early and make decisions with evidence, not assumptions.
A well-executed audit offers far more than a snapshot of your organization’s risk posture. It provides actionable insights that align risk management with business objectives, fortify stakeholder confidence, and position you to seize opportunities in an unpredictable world.
However, a risk management audit isn’t just about finding flaws. It’s about providing clarity for better decision-making. For example, if an audit confirms strong controls, it reinforces confidence in existing strategies. If it uncovers gaps, it highlights opportunities to optimize resource allocation, strengthen compliance, and enhance resilience.
Beyond risk mitigation, audits can drive smarter business decisions by aligning risk insights with strategic planning. A company may use audit findings to improve cybersecurity resilience, refine supply chain strategies, or adjust its risk appetite to foster innovation. Whether the results show minor refinements or significant improvements, a well-executed audit turns risk management into a competitive advantage.
How do you execute a risk management audit that delivers actionable insights and strengthens your organization’s resilience? Let’s break it down into best practices and actionable guidelines tailored for your success.
Why a risk management audit matters
Before diving into the how, let’s consider the why: a risk management audit evaluates how well your organization identifies, assesses, and mitigates risks. Think of it as a health check for your risk strategy. It helps you pinpoint gaps, streamline processes, and reinforce your defenses — whether they involve cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, or operational vulnerabilities.
By auditing your risk management practices, you gain the power to anticipate challenges, improve decision-making, and show stakeholders that you’re proactive about safeguarding your organization. A robust audit ensures that risks are adequately identified, assessed, and mitigated to safeguard the organization’s assets and achieve its objectives. Plus, a robust audit aligns your risk strategy with your business goals, giving you peace of mind and the confidence to scale responsibly.
A risk management audit is only the first step to identify areas for improvement, but the real value comes from acting on those findings. An audit provides a roadmap, but without follow-through, risks remain unaddressed, and vulnerabilities persist. Organizations must prioritize remediation efforts, assign accountability, and integrate risk mitigation into their strategic planning to drive meaningful change.
Without a structured post-audit action plan, even well-documented risks can fall by the wayside due to competing priorities. To ensure progress, organizations should establish clear timelines, designate responsible teams, and track improvements over time. Embedding risk management into daily operations long-term ensures that audits lead to tangible improvements.
Importantly, the independence of the internal audit function makes it an ideal choice for conducting a risk management audit. Because the team operates with adequate autonomy from management, they are able to provide unbiased recommendations and findings. This impartiality is critical for ensuring the reliability and credibility of the final report, which ultimately strengthens trust among stakeholders and enhances the overall effectiveness of your risk strategy.
While internal audit independence is ideal, smaller organizations often have auditors reporting to senior management, which can limit objectivity. To maintain credibility, companies can establish cross-functional risk committees or have audit findings reviewed by the board. Even if full independence isn’t possible, safeguards like periodic external reviews or benchmarking against industry standards help ensure audits remain unbiased.
The level of audit team autonomy can vary based on organizational structure. In some cases, internal auditors may face pressure from management, which can impact audit objectivity. This is why external audits, conducted by third-party professionals with no direct ties to the organization, are often considered more impartial. However, even internal audits can maintain credibility by implementing safeguards such as direct board reporting, external validation, or adherence to established auditing frameworks like ISO 31000 or COSO ERM.
Now let’s look at the steps to completing a successful risk management audit.
Step 1: Prepare for the audit
Preparation sets the tone for your entire audit. Clarity here ensures the final audit’s findings align with your priorities.
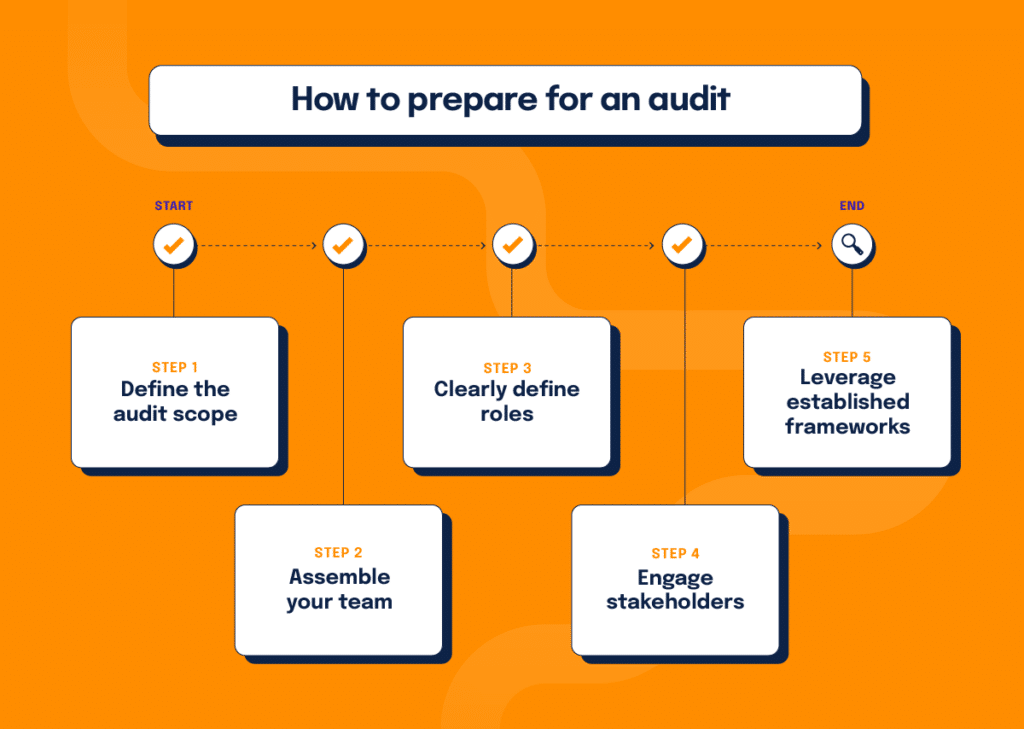
1. Define the audit’s scope and objectives
A successful risk audit begins with clear boundaries and objectives. Are you evaluating enterprise-wide risk or focusing on specific areas such as cybersecurity, compliance, or operational risk? Defining the scope ensures your audit aligns with strategic priorities and delivers actionable results. Use an audit risk assessment checklist to confirm scope, key risks, control owners, evidence sources, and timelines before fieldwork begins. This early alignment is the backbone of the audit risk assessment process, because it prevents scope creep and clarifies what “good evidence” looks like before fieldwork begins.
2. Form the audit team:
Include members from risk management, compliance, and internal control departments who possess expertise in organizational operations and relevant regulations.
3. Clearly define roles
Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member to ensure accountability, meaningful collaboration, and effective communication.
4. Engage the right stakeholders
Collaboration is critical. A multidisciplinary team, including representatives from IT, compliance, finance, legal, and operations, brings diverse perspectives that enrich the audit process. Their collective expertise ensures a thorough evaluation.
5. Leverage established frameworks
Aligning your audit with established frameworks enhances its credibility and rigor. Standards such as ISO 31000:2018, IAA Standard 2120, and other compliance frameworks provide proven methodologies for assessing and managing risk.
2. Review the current risk management framework
In a formal risk management audit, the audit team should review the current risk management framework by evaluating its alignment with established standards such as ISO 31000 and 27005. In other words, you’re auditing risk management process maturity: governance, decision rights, and whether risk practices actually connect to strategy and operations. The audit team should also ensure that there are adequate procedures for decision-making related to strategy, tactics, operations, and compliance. The governance structure should support effective risk management by providing direct responsibility for risk management, coordination and oversight of the risk management framework, and independent assurance through internal and external audits.
Key considerations
Governance structure: Evaluate the roles and responsibilities of the board, risk committees, and management in overseeing risk management activities.
Risk management culture: Consider the organization’s risk culture and maturity. Determine if there is a risk-focused culture that supports the implementation of the risk management framework.
Integration with strategic objectives: Assess how well the risk management framework is integrated with the organization’s strategic and business objectives. Ensure that risk management is aligned with the organization’s mission and goals.
Documentation and communication: Evaluate the documentation of the organization’s implementation of the risk management framework and its communication across the organization. Ensure that policies, procedures, and risk management practices are well-documented and accessible to relevant parties.
Step 3: Assess risk identification processes
Risk identification is a fundamental component of effective risk management and a critical step in ensuring risks are managed systematically and comprehensively. The audit should evaluate whether your organization has a structured, iterative process to identify risks across all relevant areas, including strategic, operational, financial, compliance, and external environments.
Key considerations
Centralized risk register: Examine the organization’s inventory of identified risks to ensure it is comprehensive and up-to-date. Verify that all potential risk scenarios are considered and documented.
Evaluate risk categorization: Check if risks are appropriately categorized based on their nature, source, and potential impact. This helps in understanding the scope and scale of risks faced by the organization.
Analyze risk identification methods: Assess the methods and tools used for risk identification, such as workshops, interviews, and data analysis. Ensure that these methods are systematic and involve relevant stakeholders.
Stakeholder engagement: Ensure that the risk identification process involves input from various stakeholders, including management, employees, and external partners, to capture a wide range of perspectives.
Organizations aiming for best practices in risk identification should ensure their methods are tailored to their objectives, context, and the dynamic nature of risks. Leveraging tools like predictive analytics, scenario analysis, and threat intelligence aligns with ISO 31000’s emphasis on continuous improvement and informed decision-making, enabling the organization to remain proactive and resilient in the face of emerging challenges.
Step 4: Evaluate risk assessment processes
Once risks are identified, how do you prioritize them? Your audit should evaluate whether risk assessments are systematic, data-driven, and aligned with business priorities and the organization’s risk appetite. Interestingly, priorities and risk appetite don’t always align, so it’s essential to assess whether your prioritization approach accounts for these potential discrepancies.
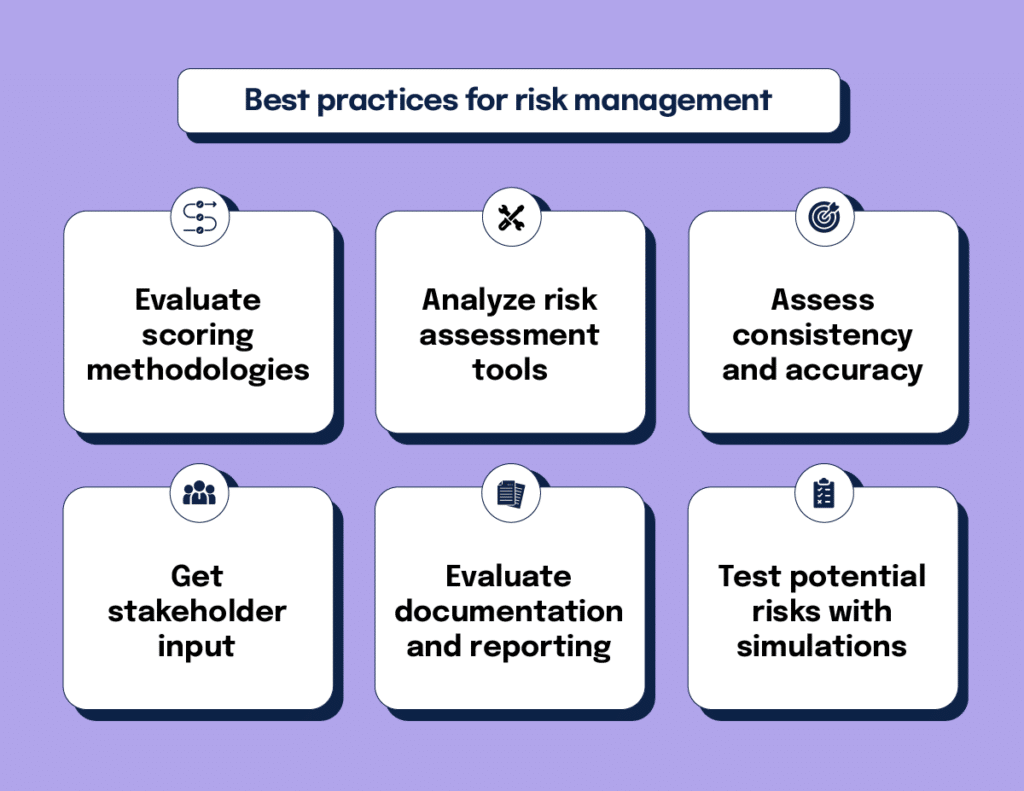
Best practices for risk assessment and management
Assess scoring models
Examine the criteria and methodologies used to assess risks, including impact and likelihood measures. Use quantitative or qualitative models to assess likelihood and impact, integrating financial, reputational, and operational dimensions. Ensure risk scoring methodologies are uniform across departments to enable apples-to-apples comparisons.
Analyze risk assessment tools
Evaluate the tools and techniques used for risk assessment, such as risk matrices or heat maps. Confirm that these tools effectively support the analysis and prioritization of risks.
Assess consistency and accuracy
Check for consistency and accuracy in the risk assessment process. Ensure that risk assessments are conducted regularly and that the results are reliable and valid.
Get stakeholder input
Engage cross-functional teams for diverse perspectives on risk prioritization.
Evaluate documentation and reporting
Review the documentation of risk assessments to ensure they are well-documented and communicated to appropriate parties. Confirm that the results are used to inform decision-making and strategic planning.
Scenario planning
Test potential risks using “what if” scenarios to gauge preparedness. Simulations help you understand potential downstream impacts of critical risks.
Your audit should highlight whether these processes are consistent, transparent, and adaptable to new challenges. A high-quality assessment process moves beyond intuition and qualitative judgments, empowering your organization to make evidence-based decisions.
Step 5: Audit risk mitigation strategies
Even the best risk assessment falls flat without effective mitigation strategies. This step of the audit examines the controls, policies, and technologies you’ve implemented to address risks. Accountability is another crucial aspect, ensuring that risk owners are held responsible for lapses while also confirming that the board and senior management are providing adequate resources to support those risk mitigations.
Key considerations
Review mitigation plans: Examine the risk mitigation plans to ensure they are comprehensive and aligned with the identified risks. Verify that each plan includes specific actions, timelines, and responsible parties for mitigating risks.
Assess the effectiveness of mitigation actions: Evaluate the effectiveness of implemented mitigation actions in reducing risk levels. Consider whether the actions have successfully addressed the root causes of risks and if they are achieving the desired outcomes.
Analyze resource allocation: Check if resources for risk mitigation are allocated strategically based on risk priorities and impacts. Ensure that there is adequate support for implementing mitigation strategies.
Evaluate continuous improvement: Assess whether there is a process for regularly reviewing and improving risk mitigation strategies. Ensure that lessons learned from past mitigation efforts are used to enhance future strategies.
Don’t just look at what’s documented — validate strategies through interviews, process walkthroughs, and live testing. For instance, if you have a cybersecurity policy, test how employees respond to simulated phishing attempts.
Step 6: Examine monitoring and reporting mechanisms
Risk management is a dynamic process, not a one-time task. Continuous monitoring and transparent reporting are hallmarks of mature risk management programs. An audit should examine how effectively your organization tracks and communicates risk data.
Consider a financial services firm that conducted a risk management audit, identified cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and implemented new controls — but they didn’t assess risks over time. Imagine a year later, a phishing attack exploited a weakness in their outdated authentication process, leading to a data breach and regulatory fines. Since the company treated risk management as a one-time event, it missed evolving threats that could have been mitigated through continuous monitoring and regular risk assessments.
Risk audits must be an ongoing process. Threat landscapes, regulations, and business environments change. A defined audit monitoring process helps teams validate control effectiveness over time, spot drift early, and reduce repeat findings. Without frequent reassessment, organizations can be blindsided by risks they once thought were under control.
Key considerations
Your audit should ensure that monitoring tools are not only in place but are also delivering value. Leading organizations embrace advanced analytics and AI-driven insights to enhance monitoring, enabling faster, more informed responses to evolving risks.
To measure the value of monitoring tools, organizations should track key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) that reflect both risk reduction and operational efficiency. Useful KPIs include incident response time, mean time to detect (MTTD), and mean time to respond (MTTR), which indicate how quickly threats are identified and mitigated. KRIs, such as the number of high-risk vulnerabilities detected, the percentage of compliance violations identified, and risk exposure trends over time, help assess whether the organization is effectively reducing its overall risk posture. Additionally, false positive rates and automation success rates can highlight whether monitoring tools are delivering actionable insights or overwhelming teams with noise.
While AI-driven analytics and automation enhance risk detection and response, they have limitations. For example, an AI-powered fraud detection system might flag anomalies faster than manual reviews, preventing financial losses. However, if the system isn’t fine-tuned, it may generate excessive false positives, leading to wasted resources and alert fatigue. This underscores the need for a balanced approach, combining technology with human oversight to ensure that monitoring remains accurate, adaptive, and truly valuable to risk management efforts.
Step 7: Test regulatory compliance
Failing to comply with regulations can lead to significant fines, reputational damage, and even operational shutdowns. Your audit should include a thorough compliance check, focusing on industry-specific standards and frameworks.

Steps for compliance validation
1. Review compliance requirements
Map your controls to specific regulatory frameworks, such as NIS2, DORA, or PCI DSS.
2. Assess compliance monitoring
Review audit trails and evidence to ensure they withstand scrutiny from regulators or auditors.
3. Verify documentation and record-keeping
Ensure that compliance-related documentation is thorough and up-to-date. This includes records of compliance assessments, corrective actions, and communication with regulatory bodies.
4. Horizon scanning
Monitor emerging regulations to stay ahead of potential compliance risks.
A strong compliance program not only protects you legally but also fosters trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
Step 8: Identify gaps and build an action plan
No audit is complete without actionable recommendations. After analyzing findings, focus on identifying gaps in your risk management practices.
Building a strategic action plan
Action plans are where your audit findings turn into tangible improvements. A detailed, prioritized approach ensures buy-in from leadership and accountability across teams.
Step 9: Communicate findings effectively
A risk management audit isn’t just about what you uncover — it’s about how you communicate your findings. Your audit report should be clear, concise, actionable, and tailored to your audience. It should not only highlight findings but also articulate their implications and recommended next steps.
Essential elements of a high-impact audit report
When presenting your findings, focus on how recommendations will enhance resilience, efficiency, and long-term growth. A well-delivered report builds trust and encourages action.
Leveraging technology to enhance audit effectiveness
Many teams evaluate audit and risk management solutions here because the right platform reduces evidence chaos, improves consistency, and shortens audit cycles. Modern risk management audits are incomplete without the strategic use of technology. An advanced governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) platform enables you to automate workflows, centralize data, and enhance collaboration—capabilities many teams look for when evaluating audit risk management solutions.
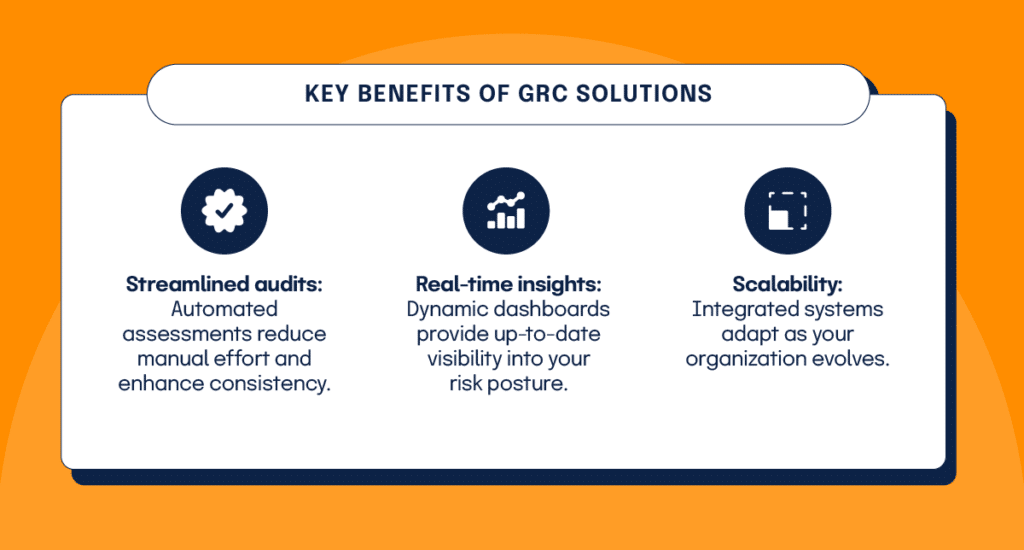
Key benefits of GRC solutions
Technology not only improves audit efficiency but also positions you to respond more effectively to the dynamic risk landscape.
Building a resilient risk culture
An audit is never an end-game exercise — it’s an opportunity to strengthen your organization’s risk culture for the long haul. Embedding risk management into daily operations fosters a proactive mindset that transcends silos and enables agility.
How to cultivate risk awareness
A resilient risk culture empowers your organization to navigate uncertainty with confidence, ensuring long-term success.
How modern platforms simplify risk management audits
Conducting a risk management audit is a complex, multifaceted process, but leveraging the right technology can transform it into a streamlined and effective exercise. Hyperproof is an audit and risk management software platform that helps organizations manage audits with precision, efficiency, and confidence. By centralizing data, automating workflows, and enhancing collaboration, we simplify even the most challenging aspects of risk management.
Here’s how Hyperproof can transform your audit process:
Centralized data management
A common challenge in risk management audits is the fragmentation of data across departments, systems, and stakeholders. Hyperproof provides a centralized repository where all documentation, risk assessments, control evidence, and compliance records are stored securely and are easily accessible.
Benefits:
Automated risk assessments
Manual risk assessments are prone to inconsistencies and inefficiencies. Hyperproof eliminates these challenges by automating key aspects of the risk assessment process, ensuring your methodology is consistent, scalable, and precise.
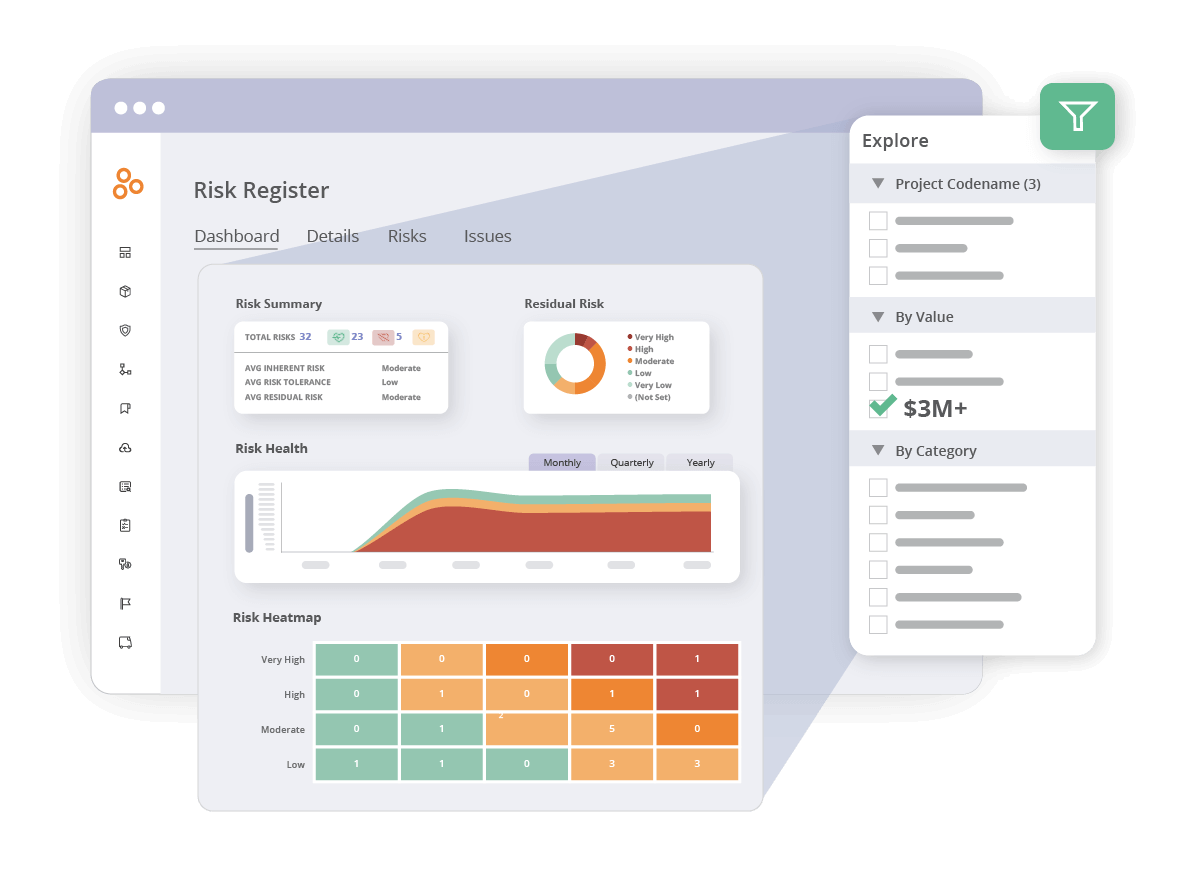
Features:
Real-time monitoring and dashboards
Hyperproof enables continuous monitoring and reporting of your risk posture through intuitive dashboards and real-time analytics. This functionality is crucial for organizations aiming to maintain a proactive approach to risk management.
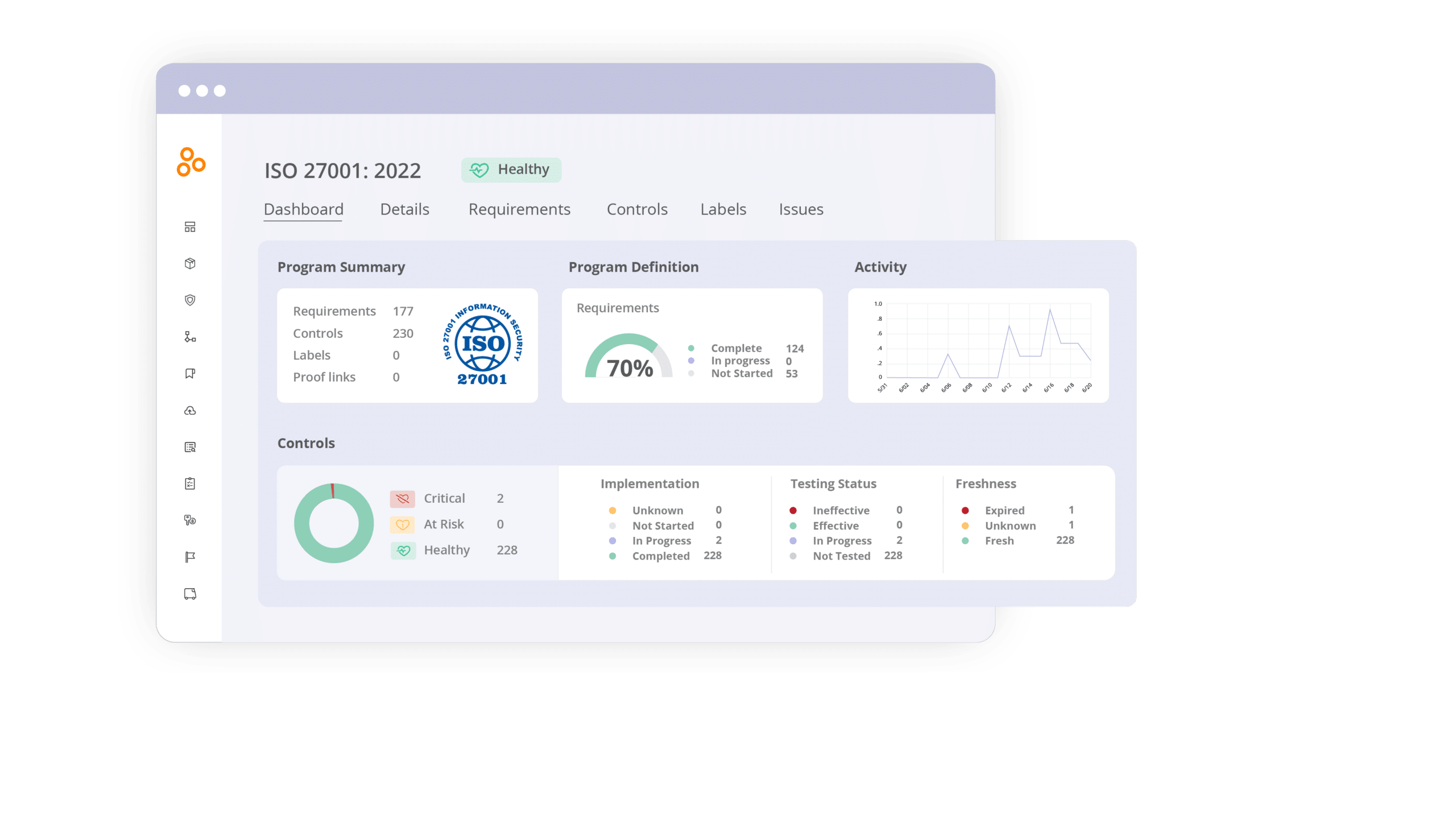
Key advantages:
Streamlined audit processes
Traditional audits often involve cumbersome back-and-forth communication, redundant processes, and disjointed tools. Hyperproof transforms this experience by providing a unified platform that facilitates every stage of the audit lifecycle.
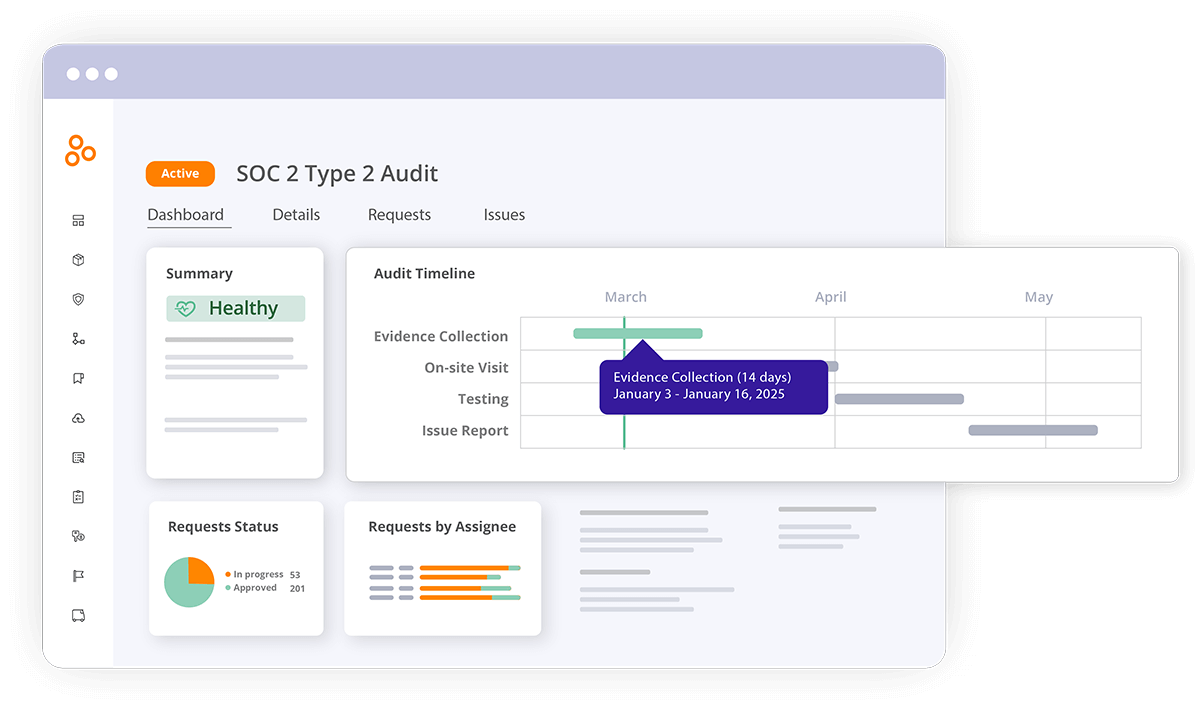
Capabilities:
Enhanced compliance management
Compliance is an integral part of risk management audits, and keeping up with evolving regulations can be daunting. Hyperproof simplifies compliance by mapping controls to multiple frameworks, automating evidence collection, and providing updates on regulatory changes.
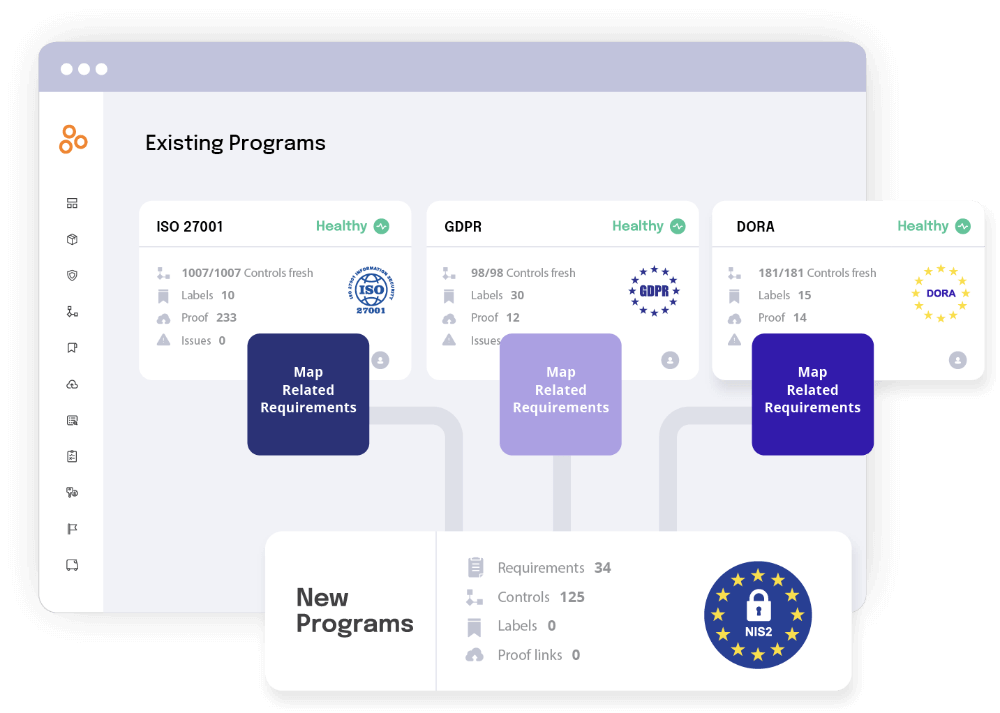
Features for compliance:
Encouraging a risk-aware culture
Beyond tools and features, Hyperproof fosters a culture of accountability and transparency by making risk management accessible and actionable for all stakeholders. Whether it’s through intuitive interfaces or easy-to-understand reporting, continuous compliance ensures that everyone in your organization can contribute to and benefit from a strong risk posture.
With Hyperproof, you move from reactive to proactive risk management, ensuring that your audits not only identify gaps but also deliver actionable, strategic improvements.
Make your risk management audit an advantage
A risk management audit is your organization’s opportunity to turn uncertainty into opportunity. By following best practices — preparing thoroughly, evaluating each stage of risk management, and closing gaps with actionable plans — you ensure that your organization isn’t just surviving but thriving in an unpredictable world.
Take charge of your risk strategy today. With the right approach, tools, and mindset, you can safeguard your organization against threats and create a foundation for sustainable success.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












