
The Ultimate Guide to
NIST Privacy Framework
What is the NIST Privacy Framework?
Created by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the Privacy Framework is a voluntary tool any organization can use to create or improve a privacy program. Effective privacy risk management can help you build trust in your products and services, communicate better about your privacy practices, and meet your compliance obligations.
By implementing the Privacy Framework, your organization will gain a better understanding of the privacy impacts individuals can experience as they interact with your products and services and how they pose risks to your organization. Using it will bring more rigor to your privacy program, help you secure resources for privacy enhancements, and communicate your privacy posture to stakeholders such as customers, employees, partners and board members.
The Privacy framework is flexible and outcome-driven. Because it helps organizations sharpen their focus on desired privacy outcomes and create granular action plans, implementing this framework will help your organization comply with various global data privacy laws (e.g.,GDPR, CCPA, LGPD) more easily and efficiently. Related: Guide to NIST 800-53
Who’s Using the NIST Privacy Framework?
Any organization that wants to use data to develop innovative products and services while minimizing adverse impacts to individuals can use the NIST Privacy Framework as a tool to help them create or improve a privacy program. The first edition of the Privacy Framework was released in January 2020. An International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP) and FairWarning report found that more than a quarter of survey respondents had adopted the NIST Privacy Framework less than a year after its release.
Business Benefits of Using the NIST Privacy Framework
Until now, many organizations have treated privacy as transactional. Organizations evaluate data privacy laws separately and initiate separate work streams to achieve compliance as laws get enacted.
Given that data privacy laws are evolving rapidly and businesses must navigate through a complex regulatory landscape, having a unified, enterprise-wide approach to managing privacy risks on a continuous basis has become critical. If you’re operating in multiple geographic locations, taking a transactional approach to privacy is not sustainable or cost effective. You’ll likely end up duplicating effort as different teams in different regions or business units work in silos.
The NIST Privacy Framework helps your organization answer the fundamental question: “How are we considering the impacts to individuals as we develop our systems, products, and organizations?” It can be the system your organization relies on to organize its thinking, to map out its compliance goals, and to strengthen stakeholder trust.
By adopting a framework, your organization will mature in your approach to managing privacy risks. Instead of taking a compliance-oriented approach, you’ll be turning privacy into a business capability – much the same way that security has become a business capability — and design a system that’s future-proof.
What Are the Key Components of the NIST Privacy Framework?
The Privacy Framework is structurally the same as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. It consists of three parts: Core, Profiles, and Implementation Tiers.
The Core
This is a set of privacy protection activities and outcomes that enable an organization to dialogue with stakeholders about managing privacy risk. The core is further divided into key Categories and Subcategories — which are distinct outcomes – for each Function.
Profiles
A profile represents an organization’s current privacy activities or desired outcomes. An organization can develop a Target Profile by selecting and prioritizing specific Functions, Categories, and Subcategories from the Core based on its priorities and risk appetite. Profiles can be used to conduct self-assessments and to communicate with an organization or between organizations about how privacy risks are being managed.
Implementation Tiers
These provide a point of reference for how an organization views privacy risks and whether it has sufficient processes and resources in place to manage privacy risk and achieve its Target Profile.
What’s In the Privacy Framework Core?
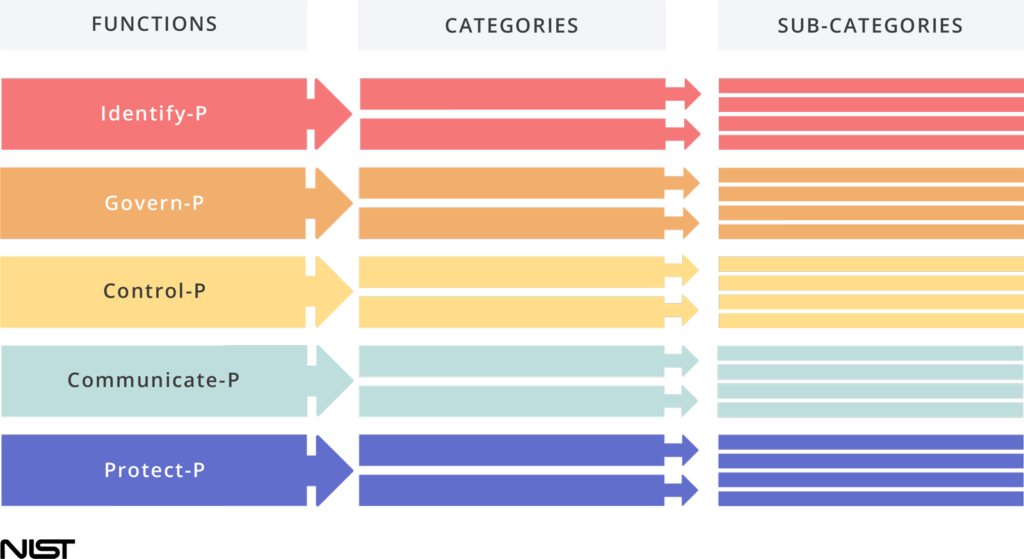
The Core elements work together.
The Core has five high level Functions, which organize foundational privacy activities at their highest level.
Categories are subdivisions of a Function organized into Groups of privacy outcomes closely tied to programmatic needs and particular activities.
Sub-categories further divide a Category into specific outcomes of technical and/or management activities. They provide a list of results that support the achievement of Outcomes in each category.
The five functions can be used to manage privacy risks arising from data processing. They are:
These activities give an organization a solid foundation for identifying and managing privacy risks. They include activities such as understanding what data they’re processing and mapping out data flow through systems throughout the full data lifecycle – from collection to disposal. They include conducting privacy risk assessments to assess how data processing activities could create problems for individuals (e.g., embarrassment, discrimination, or economic loss).
These activities include determining which privacy values your organization is focused on, knowing your privacy-related legal obligations and helping your workforce know their roles and responsibilities so they can effectively manage privacy risks in the design and deployment of your products and services.
These activities include thinking through your data processing practices and how the design of your products and services can introduce or mitigate your privacy risks and impact your ability to fulfill legal obligations.The Control Function also includes technical measures to disassociate data from individuals and devices.
These activities are concerned with crafting policies for communicating internally and externally about your data processing activities. It also includes actions around making your privacy practices clear and transparent to customers.
These are security measures designed to protect data, such as using security software, encrypting sensitive data, conducting regular backups of data, and more.
The NIST Privacy Framework also includes express references within the framework to the data processing ecosystem within which an organization operates. For instance, GDPR includes distinction between a data controller and data processor. The Privacy Framework allows for that distinction.
Additional resource: Critical Data Security Controls Every Organization Needs
What Are the Best Practices for NIST SP 800-53 Compliance?
To work your way towards full compliance, you’ll need to understand and work through some key steps:
Start by locating and securing all your sensitive data and then classifying it based on your business policy. You want to conclude this phase of discovery with knowledge of your sensitive data, the vulnerabilities within your system, and potential threats in your environment.
Here you want to establish an understanding of who can access what data. The critical action step is identifying all user, group, folder, and file permissions within your system.
Managing access starts with creating rules to govern who can access what information. These rules must be well known and strictly enforced. Action steps for improved access control involve inactivating stale user accounts, proactively managing user and group memberships, and working from a “least privilege” model, which involves giving users the least amount of access they need to do their job.
Start by keeping records of how users access systems and data files. Use these records to create a baseline of regular activity to help identify anomalies such as weird access locations, rapid access upgrades, and sudden mass movements of data. Be sure to install a set of controls designed to monitor and detect insider threats, malware, and misconfigurations. Any vulnerabilities, anomalies, or attempted breaches should be discovered and remediated as quickly as possible.
It’s important to educate your employees on what they need to do (and what to avoid) to keep networks and company data secure. Management should provide employees with tactical knowledge on how to deal with the cyberthreats organizations are most likely to face, such as email scams, malware, insecure passwords, unsafe internet browsing habits, removable media, etc.
NIST SP 800-53 recommends organizations deploy security assessment tools to gauge their real-time security posture. These software tools, created by security experts, measure the effectiveness of all organizational security measures and suggest system improvements based on empirical evidence.
But once your team has installed the appropriate controls and implemented NIST SP 800-53 security and privacy controls, you’ll need to make sure that your controls are implemented correctly and produce the desired outcome for meeting your organization’s security requirements.
NIST Special Publication 800-53A establishes standard assessment procedures to assess security controls’ effectiveness in information systems, specifically those controls listed in NIST SP 800-53. These recommended assessment procedures provide a starting point for developing more specific procedures and can be supplemented by your organization if it’s deemed necessary according to your risk assessment. Keep in mind that your organization may create additional assessment procedures for those security controls not contained in NIST Special Publication 800-53.
Use Cases For the NIST Privacy Framework
Key Considerations for Implementing the Privacy Framework
Getting buy-in from internal stakeholders is one of the biggest considerations for success, given that privacy will likely touch every aspect of your business. Because virtually all business functions from Engineering to Sales to HR are involved in data processing of one type or another, it’s important to involve leaders from all business groups in privacy initiatives. The tone comes from the top. If your organization is going to instill a culture where privacy is a priority, everyone needs to know their leaders take the topic seriously.
Once you start to understand your current privacy posture and where you’d like to be, it’s time to prioritize your target outcomes and create an action plan. You’ll also want to discuss your plan as an organization and use it to work towards acquiring the resources and people needed to meet your goals.
How Does the NIST Privacy Framework Relate to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
Privacy and security are tightly linked. Cybersecurity risks are associated with cybersecurity incidents arising from the loss of confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
Privacy goes beyond cybersecurity. It’s focused on data processing — the full information lifecycle of data from collection to disposal — arising from organizations’ need to use data for business purposes. Individuals can experience problems from data processing.
Where privacy overlaps with security is when the loss of personal information occurs. The loss of personal information can cause an individual to suffer embarrassment, discrimination, and economic loss.
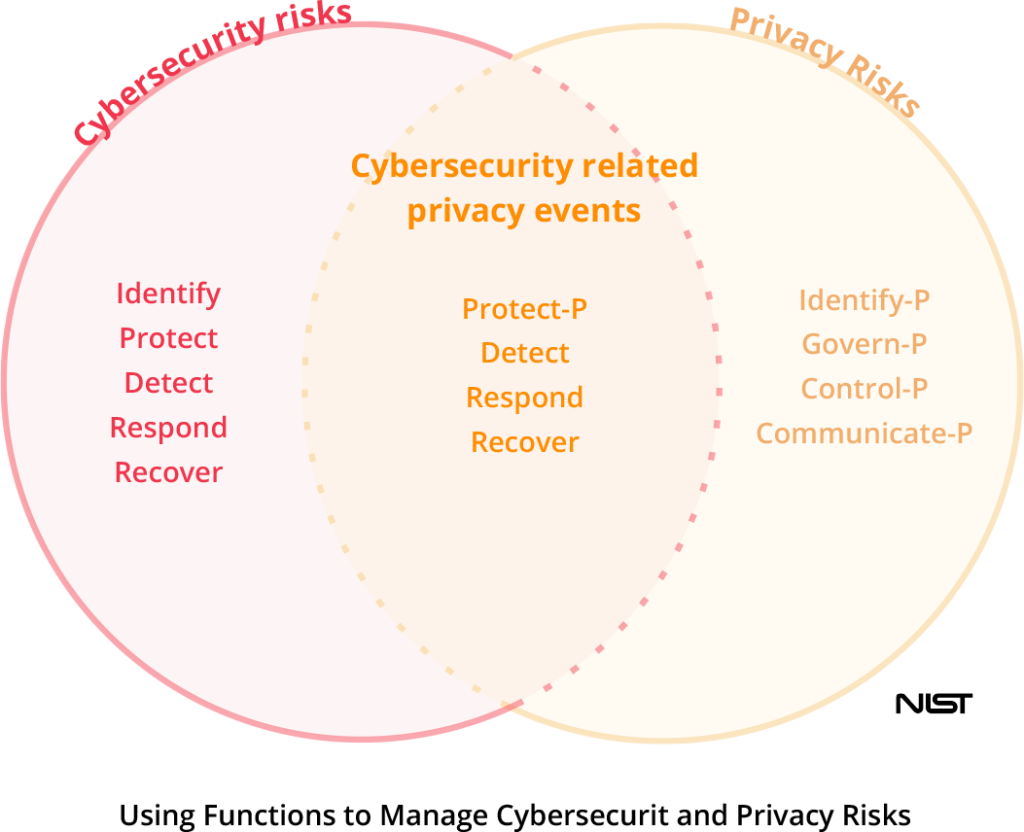
Organizations can have follow-on impacts from privacy incidents that can manifest as customer abandonment, noncompliance costs, and harm to their reputation or internal culture.
For organizations familiar with the NIST CSF, they can use Functions from both the Cybersecurity Framework and the Privacy Framework in varying combinations to manage different aspects of privacy and cybersecurity risks.
How Does the NIST Privacy Framework Map to Data Privacy Laws, Standards, and Frameworks?
While the NIST Privacy Framework is intentionally regulations-agnostic, the privacy community has created crosswalks to help organizations understand which Privacy Framework Functions, Categories, and Sub-categories may be most relevant to addressing the provisions of several data privacy regulations, standards, and frameworks.
On the NIST website, you can find crosswalks to the following laws, regulations, standards and frameworks:
Hyperproof has also created crosswalks to multiple standards and frameworks (these are automatically available to all Hyperproof users):
- GDPR
- CMMC
- NIST Special Publication 800-53
NIST Privacy Framework: Frequently Asked Questions
Hyperproof for NIST Privacy Compliance
Hyperproof can support the five high-level Functions outlined in the NIST Privacy Framework Core. We can help you build and maintain an enterprise-wide data privacy program and efficiently comply with a growing set of data privacy and cybersecurity laws and frameworks.

In Hyperproof’s compliance operations platform, you can conduct privacy risk assessments (internally and with vendors) and track all risks in a central Risk Register. Controls can be tied to risks so you can get an accurate understanding of residual risk.
With Hyperproof, you can easily assign privacy-related responsibilities and tasks to your workforce and ensure everyone understands the part they need to play. Privacy and security controls can be documented centrally in Hyperproof so that they can be implemented once and then easily mapped to multiple data privacy laws, regulations, standards and frameworks, allowing organizations to scale up their compliance efforts efficiently.
In Hyperproof, privacy professionals can document privacy controls and technical measures around dissociating data from users and devices — and gather evidence that those measures are happening as intended. Compliance and privacy professionals can see whether internal stakeholders are doing their part and follow-up with teams or individuals when certain privacy duties aren’t being performed on time.
In Hyperproof, privacy professionals can document privacy controls and technical measures around dissociating data from users and devices — and gather evidence that those measures are happening as intended. Compliance and privacy professionals can see whether internal stakeholders are doing their part and follow-up with teams or individuals when certain privacy duties aren’t being performed on time.
With Hyperproof dashboards and reports, gauging progress within your privacy program is straightforward. Business leaders can see how well privacy risks have been mitigated and understand risk trends. Compliance and privacy professionals can see how their organization is doing in specific privacy functions and sub-categories and prioritize their controls evaluation and risk mitigation activities. When Hyperproof serves as the single source of truth for all privacy risk management activities organization-wide, it’s simple to produce proof to show customers, regulators, and other stakeholders that privacy is a priority for your organization.
Hyperproof partners with professional service firms with proven track records and deep expertise in helping organizations get NIST SP Privacy ready. Our partners help customers design their compliance programs, build them out, and conduct readiness assessments to ensure there are no surprises when the audit occurs. If you need a referral, we’d love to talk.
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?









