Guide
From Audit to ComOps: How to Transform Your Compliance Operations

Introduction
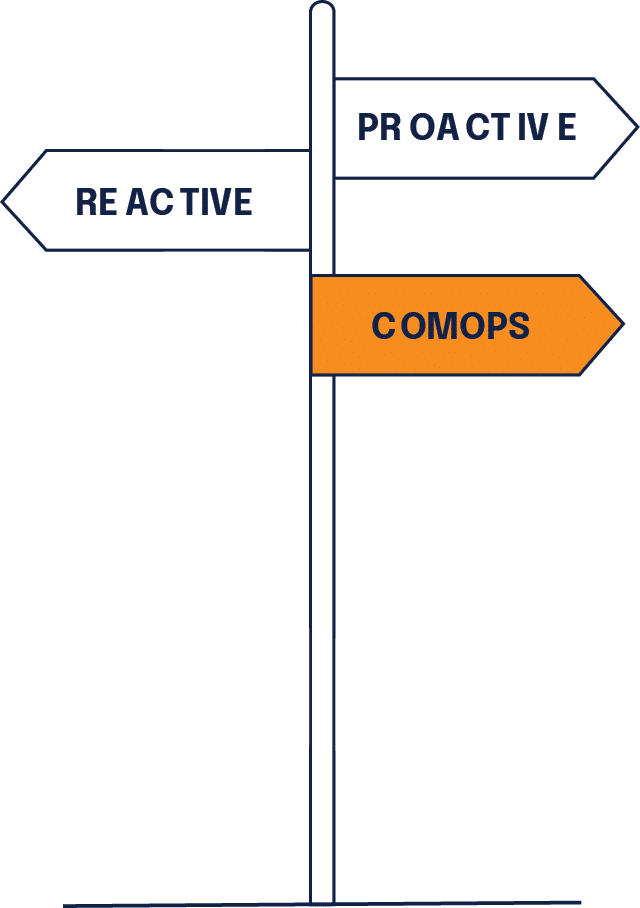
Organizations today face a seemingly impossible choice: maintain operational efficiency or pass audits successfully. The shift from reactive audit preparation to proactive compliance operations, however, represents one of the most transformative changes possible in governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) programs. Rather than accepting this false dichotomy, implementing continuous compliance operations offers a third path forward.
Beyond the traditional cycle of audit preparation panic followed by post-audit relief lies something more sustainable. This transformation represents a future where compliance activities flow seamlessly into daily operations, creating value rather than consuming it.
Recognizing the audit-first trap
The reactive compliance cycle
Predictable patterns emerge when organizations fall into audit-first thinking. Resource allocation follows these patterns, and so does stress distribution throughout the compliance calendar.
The patterns typically begin months before scheduled audits. Teams receive requests for evidence that should have been continuously collected. What follows reveals fundamental weaknesses in organizational compliance architecture, a scramble that could have been avoided.
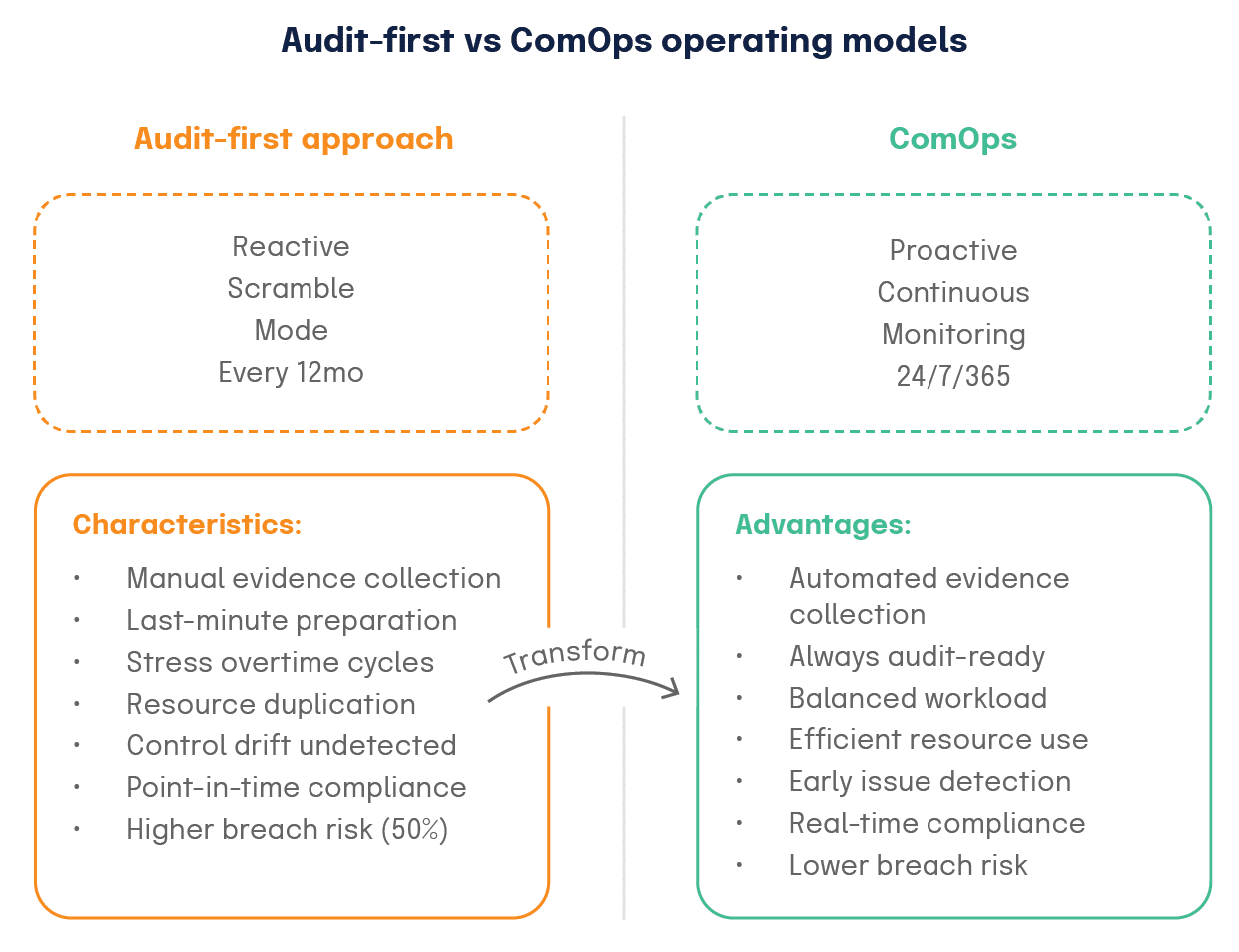
Common symptoms of reactive compliance
Perhaps most tellingly, organizations search desperately for proof that controls operated effectively during periods when no one was monitoring performance. This reactive approach creates what we might call “compliance debt.” Similar to technical debt in software development, it compounds over time and requires increasingly significant resources to resolve.
The mental toll on compliance teams operating in this cycle can’t be understated. Periods of intense preparation followed by relative inactivity create unsustainable work environments. Burnout and staff turnover often result, and when experienced team members leave, institutional knowledge about compliance procedures and evidence locations walks out the door with them.
Hidden costs beyond the obvious
Consultant fees and staff overtime during audit preparation represent only the visible costs of audit-first operations. Far more significant are the hidden financial implications that extend well beyond these obvious expenses.
|
Cost category |
Description |
Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Control drift |
Controls may drift from the intended operational state without detection |
Actual compliance violations remain undiscovered until the next review cycle |
|
Business opportunities |
Inability to quickly demonstrate compliance posture |
Lost competitive advantages, slower sales cycles, and complicated due diligence |
|
Resource inefficiencies |
Teams repeatedly collect the same evidence for different audits |
Redundant work across different compliance initiatives |
Most significant of all: opportunity costs accumulate as experienced professionals spend months on reactive preparation rather than strategic program advancement.
Transformation readiness indicators
Several organizational signals indicate readiness for transitioning from audit-first to continuous compliance operations.
- Collecting identical evidence across different audit cycles signals inefficient management
- Multiple frameworks create scaling problems with traditional approaches
- Staff report stress during audit periods, followed by underemployment
- Business leaders cannot obtain the current compliance status between formal audit cycles
When these symptoms appear, transformation becomes not just beneficial but necessary for sustainable operations.
The ComOps advantage
ComOps delivers measurable advantages across multiple business dimensions. These benefits extend far beyond simple efficiency improvements and compound over time, creating sustainable competitive advantages.
Legal and regulatory advantages
Early detection becomes possible when continuous monitoring allows organizations to identify non-compliance issues before they escalate into legal violations. This minimizes costly lawsuits and regulatory penalties by creating windows when corrective action remains possible, rather than discovering issues when penalties have already been triggered.
Detailed compliance records emerge from ongoing oversight. These serve as evidence of due diligence in legal proceedings or audits, demonstrating organizational commitment to compliance and providing stronger positions when regulatory questions arise.
Real-time compliance tracking ensures organizations remain aligned with changing regulations. This capability proves particularly valuable as regulatory environments become more dynamic and enforcement grows more aggressive, keeping companies audit-ready at all times.
Cybersecurity advantages
Control weaknesses are identified before they can cause significant damage when continuous monitoring operates effectively. Rather than discovering breaches through external notification or periodic assessments, organizations can detect and respond to control failures when mitigation remains most effective.
Consistent adherence to security controls reduces data breach risks and maintains compliance with data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA. This ongoing oversight confirms security controls are followed systematically rather than sporadically.
Operational efficiency advantages
Better resource allocation results from automated evidence collection and risk alerting. Organizations can redirect staff time from repetitive manual tasks toward strategic improvement activities that add greater value to the business.
The elimination of last-minute scrambles transforms the audit experience entirely. Teams collect evidence continuously rather than frantically before audits, which eliminates repeated requests for identical documentation. No longer do employees face repeated demands for the same evidence during different audits.
Rapid adaptation to new threats and regulatory changes becomes possible, maintaining organizational agility in dynamic environments. This adaptability grows increasingly valuable as regulatory landscapes become more complex and change frequencies increase.
Competitive advantages
Trust builds with stakeholders when consistent adherence to regulations demonstrates integrity and ethical practices. This reputation becomes an asset during business development activities and partnership negotiations, maintaining positive market positioning.
Rapid demonstration of compliance posture to prospects and partners creates significant competitive advantages, particularly in industries where regulatory compliance influences purchasing decisions. Organizations with demonstrable continuous compliance capabilities often enjoy preferred vendor status with risk-conscious customers.
Market differentiation is a positive factor in sectors where regulatory adherence carries value. Compliance credentials provide advantages that traditional audit-first approaches cannot match.
Real-world results
Organizations implementing ComOps have demonstrated substantial efficiency improvements through documented case studies.

Organizations using integrated approaches demonstrate substantially better security outcomes. In 2024, 60% of organizations managing IT risk ad-hoc or when a negative event happens experienced a data breach, compared to only 35% using an integrated, mostly manual tool and 41% using an integrated, automated tool. The data reveals a consistent three-year pattern where organizations with reactive or siloed risk management approaches report higher breach rates than those using integrated, automated tools.
Unified risk and compliance operations provide superior protection because they:
These results demonstrate that ComOps transformation delivers quantifiable improvements in both operational efficiency and risk management effectiveness.
Building your business case
A systematic analysis of current costs, projected benefits, and risk reduction opportunities forms the foundation for developing compelling business cases. This financial foundation becomes essential for securing organizational support and resources necessary for successful transformation.
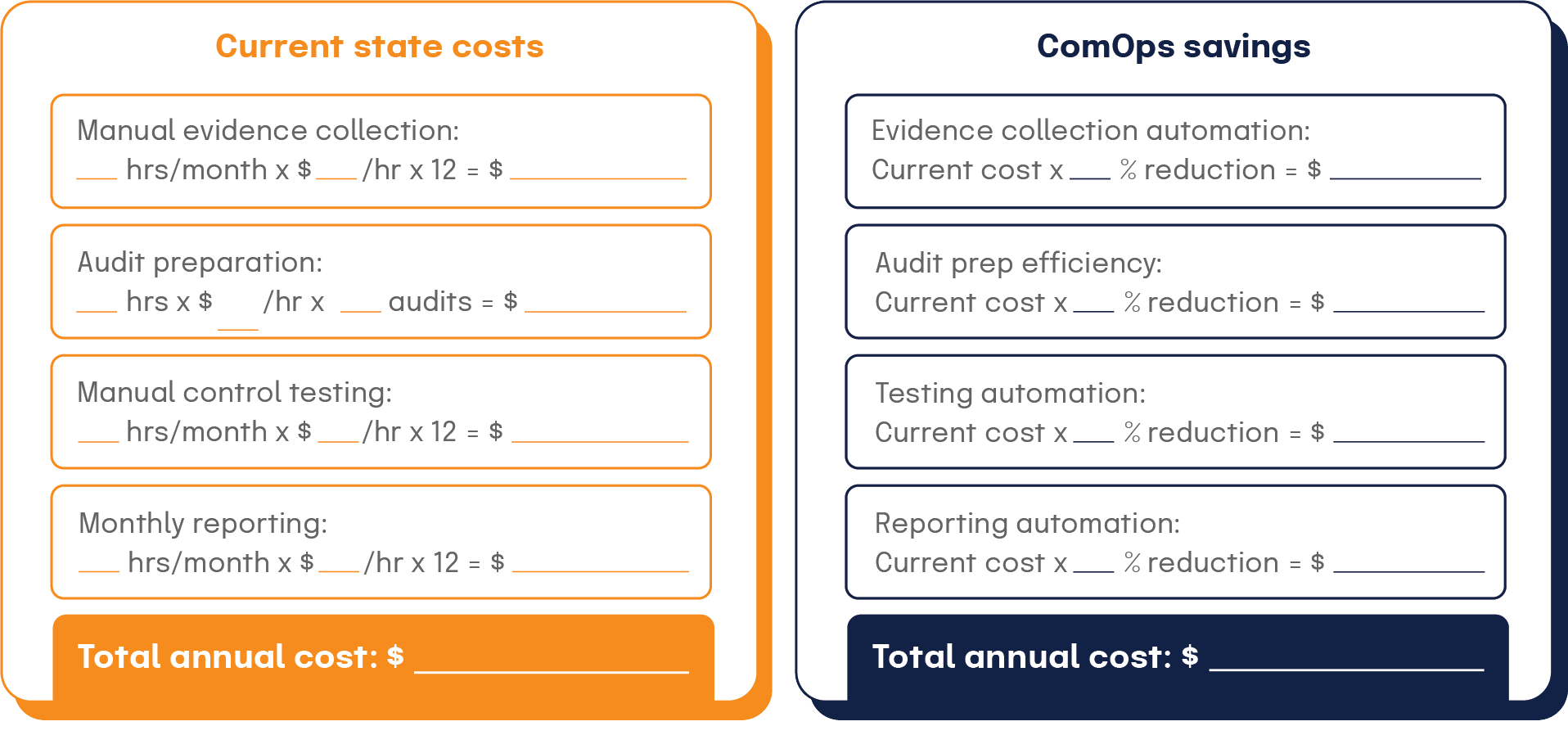
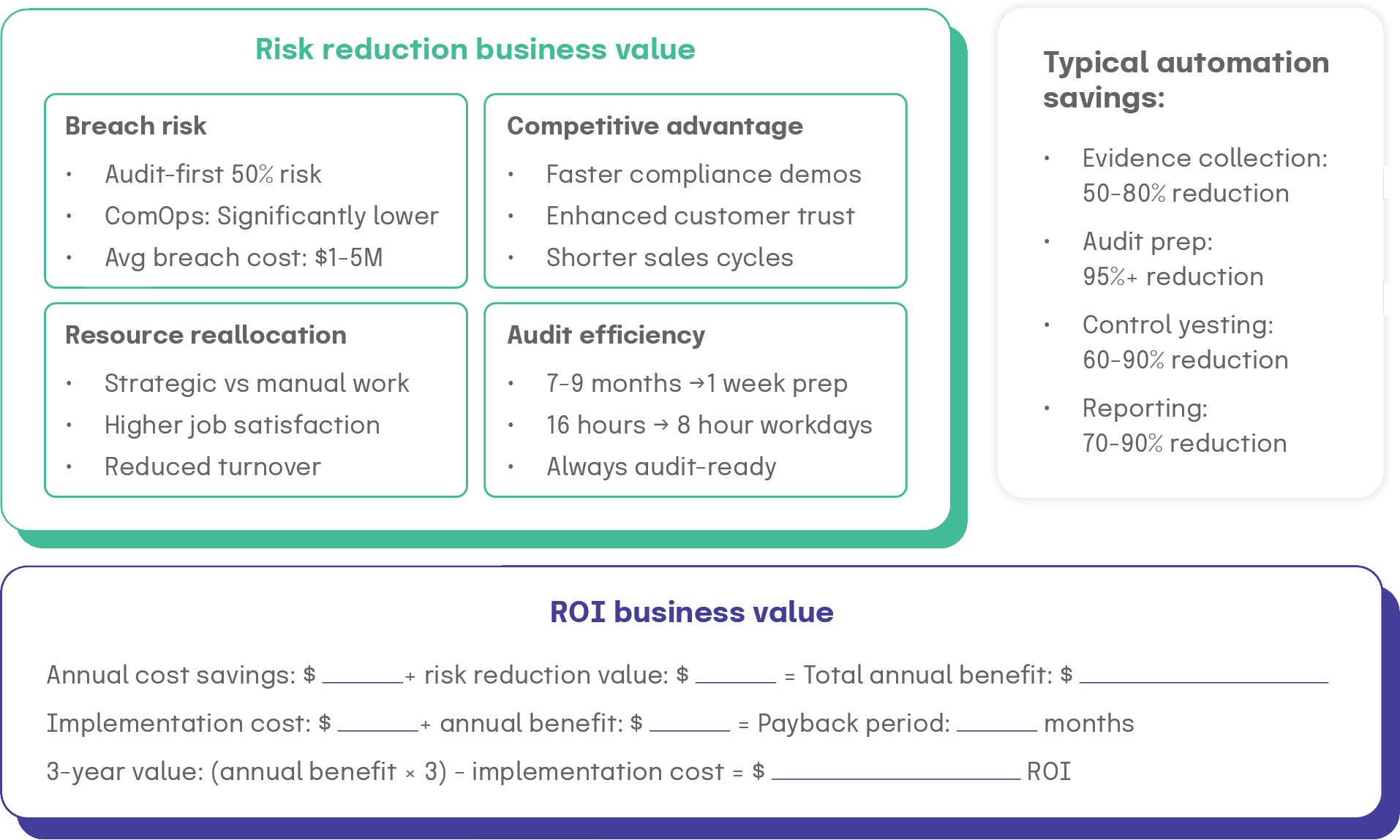
Automation Cost Savings Exercise

A structured approach enables organizations to calculate potential cost savings from automation:
Current state analysis
Automation impact calculations
Annual cost savings calculation
Risk reduction and resource reallocation workshop

After you’ve completed the business case calculator, consider running a half-day workshop to gain organizational buy-in for the transformation from audit-first to ComOps.
Suggested workshop structure
Session 1: Current state risk assessment (60 minutes)
Session 2: Risk reduction opportunities (90 minutes)
Session 3: Resource reallocation analysis (90 minutes)
Session 4: Business case development (60 minutes)
This approach produces a quantified and broadly agreed-upon business justification while building organizational alignment around transformation objectives. With a solid financial foundation established, organizations can then examine the methodology that will drive their transformation success.
Hyperproof’s ComOps methodology
Before getting into the details of transformation planning, understanding the foundational principles that make compliance operations effective becomes essential. These principles provide the conceptual framework that guides successful implementation decisions.
Control-centric operations
Controls should serve as the organizational hub for all compliance-related activities. This principle centers Hyperproof’s ComOps methodology. Rather than treating controls as isolated checklist items, this approach positions them as living components that connect requirements, evidence, risks, issues, and work items into a consolidated compliance ecosystem.

Key philosophy shifts include moving from periodic compliance checking to continuous compliance monitoring. The question changes from “Are we compliant?” to “How do we know our controls are working?” Isolated controls become an interconnected compliance ecosystem, while point-in-time assessments transform into ongoing effectiveness validation.
Control health emerges as a central concept in this approach. Organizations monitor whether controls operate effectively, have current supporting evidence, and address their intended risks, not simply whether controls exist on paper.
Automation principles
Automation serves as a means to reduce manual administrative work and improve compliance accuracy and timeliness. This does not mean removing human judgment from compliance decisions. Instead, it eliminates repetitive manual tasks that consume resources without adding strategic value.
Automated collection systems gather evidence continuously, confirming currency and freeing compliance staff for analysis and improvement activities. Common evidence types for automation include access control reports, configuration snapshots, policy documentation, and audit logs.
Automated tests verify that collected evidence meets expected formats, contains required information, and demonstrates control operation. Hyperproof can generate tasks, route them to appropriate personnel, and escalate issues when deadlines approach.
Framework mapping
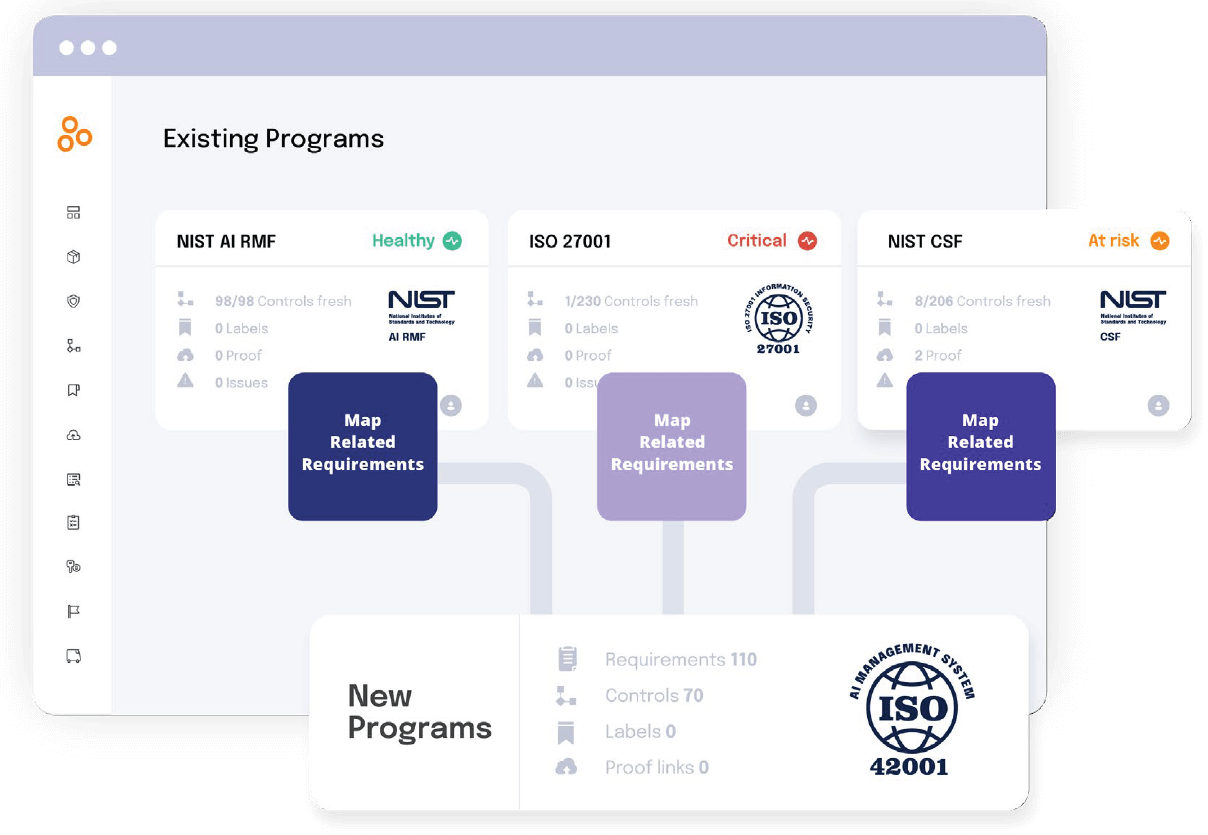
Hyperproof’s crosswalk functionality allows organizations to consolidate redundant controls across multiple compliance frameworks. This reduces administrative overhead while maintaining comprehensive coverage of regulatory requirements.
Smart Content features provide pre-built mappings for ISO 27001, FedRAMP, and the Hyperproof Common Controls Framework (CCF). These mappings automatically create appropriate labels and risks linked to controls, establishing comprehensive compliance foundations with minimal manual configuration effort.
Jumpstart capabilities enable organizations to reuse existing controls when implementing additional frameworks rather than creating entirely new control sets. Custom program creation supports internal compliance requirements, industry-specific regulations not covered by standard framework libraries, and custom requirement structures with up to four hierarchical levels.
Hyperproof’s jumpstart feature delivers significant business value by accelerating compliance program implementation through the reuse of existing organizational controls and requirements across multiple frameworks, helping organizations get “from Point A to Point B as quickly as possible” while maximizing their previous compliance investments. This capability eliminates redundant work and provides quantified progress visibility with estimated percentages showing how much existing work can be leveraged for new framework implementations, ultimately reducing time-to-compliance and operational costs.
Planning your transformation
With a solid understanding of ComOps principles, organizations can develop comprehensive transformation plans that address both technical requirements and organizational change management needs. Successful implementation requires coordination across multiple organizational functions, each contributing particular expertise and responsibilities to the transformation process.
Building your team
Compliance managers
Compliance managers provide strategic direction and regulatory requirement coverage. They function as primary stakeholders for program design decisions and define success metrics and transformation objectives.
Hyperproof administrators
Technical configuration falls to Hyperproof administrators, who handle system setup and user access management. They configure automation workflows that bridge technical capabilities and business requirements while managing integration activities.
Control owners
Control owners from operational departments contribute domain expertise about control implementation and evidence generation. They verify that automated collection systems align with actual operational procedures and identify automation opportunities that compliance teams might overlook.
Security team members
Security team members bring technical expertise for system integration and access control configuration. They verify that automated collection systems maintain appropriate security controls and provide buy-in that often determines when automation initiatives succeed.
IT staff
Information technology staff support integration activities, network configuration, and system access provisioning. They identify potential technical constraints early in the process and verify that transformation activities align with broader IT initiatives.
Assessing your current state
A structured evaluation of existing Hyperproof implementation and organizational compliance practices provides the foundation for planning transformation activities.
Managing the security-compliance relationship
Effective security-compliance collaboration requires addressing traditional friction points and establishing clear roles and responsibilities for automated processes.
Evidence collection requirements must align with security operational procedures. Security concerns about system access and data handling require addressing, while automation opportunities that compliance teams might overlook need identification.
Balancing compliance visibility requirements with security operational needs requires establishing clear agreements about system administration responsibilities. Credential management and evidence quality standards need definition.
Classification standards for collected evidence need to be defined, along with appropriate access controls for sensitive data. Compliance team access to necessary evidence must be maintained throughout.
Cultural transformation strategy
Some fundamental changes in organizational mindset and daily practices need to extend beyond technical system implementation. The transition from reactive audit preparation to proactive compliance operations requires this broader cultural transformation.
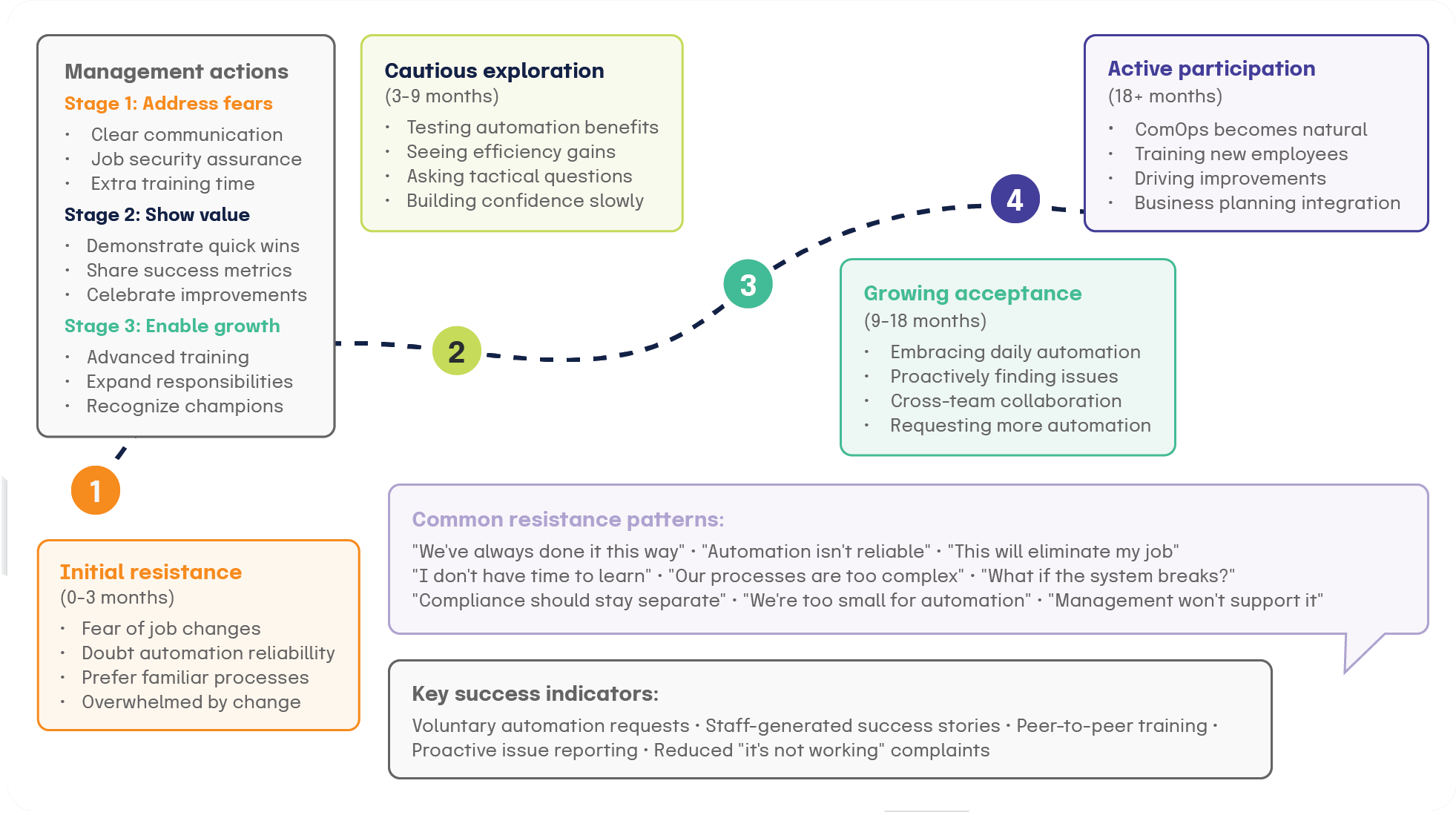
Understanding resistance patterns
Midsized organizations commonly experience staff worries about learning new systems overwhelming their limited capacity. Fear that automation will eliminate jobs or fundamentally change responsibilities creates resistance. Operational teams resist compliance team involvement in their systems, while doubt about automation reliability follows experiences with system failures.
Larger enterprises face different resistance patterns. Functions resist sharing data or coordinating processes. Multiple concurrent transformation initiatives can contribute to change fatigue. Concerns about shifting influence and decision-making authority emerge, while overwhelming scope across multiple business units creates implementation challenges.
Resistance management strategies
Dedicated training time during transition periods helps address capacity concerns. Temporary additional support while teams adapt to new processes demonstrates commitment to success. Showing how automation reduces rather than increases workload over time builds confidence.
Explaining how automation strengthens human capabilities rather than replacing them addresses job security fears. Career development opportunities arising from strategic compliance focus become visible, while examples of enhanced job satisfaction from reduced repetitive tasks provide motivation.
Timeline expectations
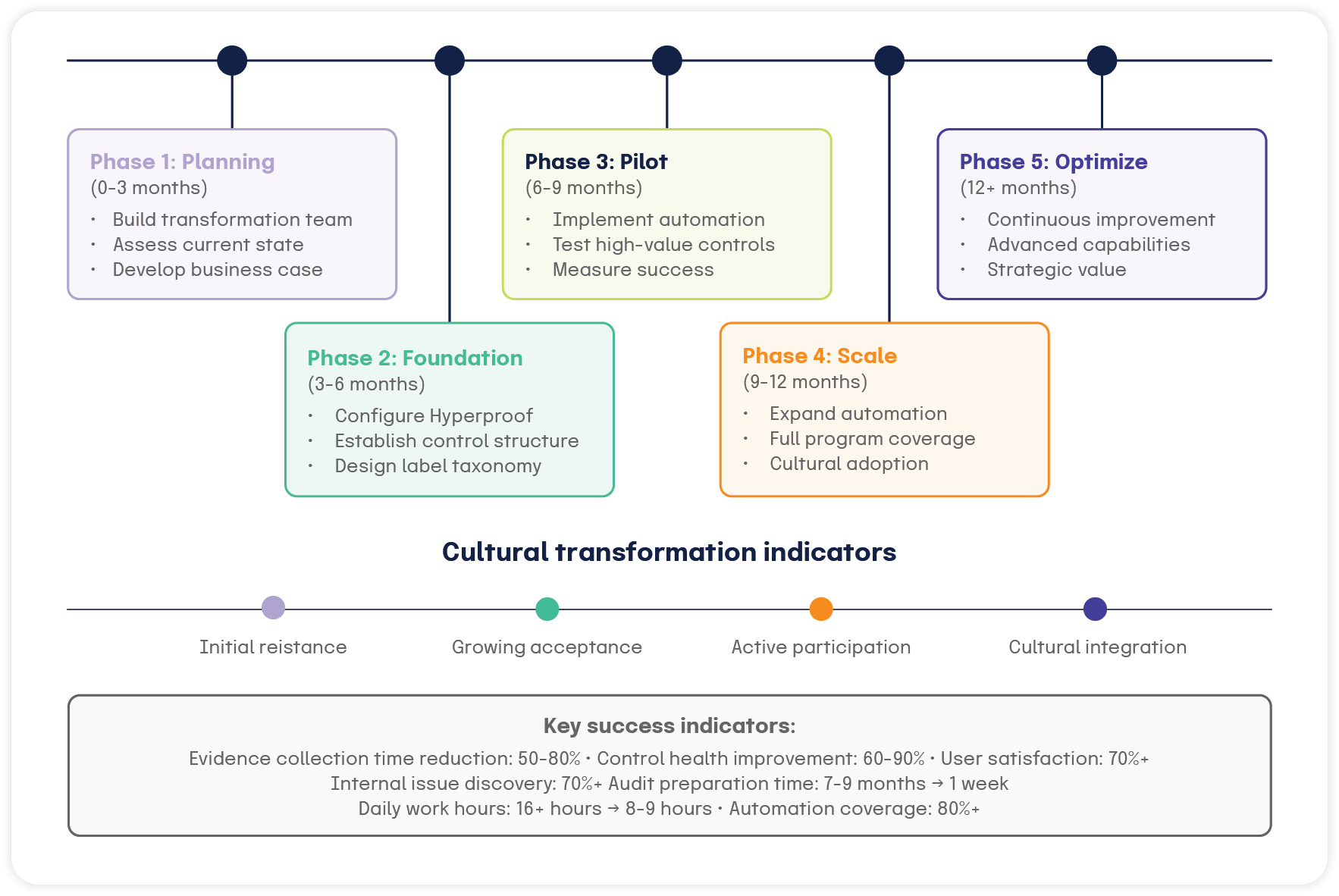
Immediate changes (0-3 months)

Short-term cultural shifts (3-9 months)
Medium-term transformation (9-18 months)
Long-term cultural establishment (18+ months)
Phased implementation approach
Structured approaches to transformation reduce implementation risk and build organizational confidence through demonstrated early successes.
Implementation phases
High-value, low-risk controls provide the best starting points. Controls with frequent evidence collection requirements work well, as do those with clear automation opportunities through available system integrations.
Success metrics need to be defined early. Evidence collection automation percentages, control health improvement metrics, and user satisfaction measures indicate readiness for broader implementation.
Resource allocation requires careful planning. Technical resources for system configuration, change management resources for user training and process adoption, and risk mitigation strategies for potential implementation challenges all need consideration.
Finally, balancing the project timeline is important. Transformation speed must align with organizational change capacity. Overly aggressive timelines may compromise implementation quality, while excessively conservative timelines may lose organizational momentum.
Configuring Hyperproof for ComOps
Technical implementation begins with optimizing Hyperproof to support compliance operations. This foundation enables automation, monitoring, and the control-centric approach that defines successful ComOps programs.
Establishing a control-centric approach
Optimizing program organization and control structures within Hyperproof helps support automated processes and continuous monitoring effectively.
Control optimization involves analyzing existing control language and objectives. Merged controls need verification that they adequately address all original requirements. Hyperproof’s crosswalk feature identifies related requirements across programs, while validation ensures consolidated controls maintain appropriate coverage for each framework.

Owner designation creates responsibility for implementing automation and maintaining ongoing effectiveness. Ownership assignments shift as operational teams assume greater compliance responsibility, while accountability for transformation activities gets confirmed at individual control levels.
Custom fields can be used to capture metadata about automation status, evidence collection methods, and control ownership responsibilities. This enables progress monitoring across transformation activities and identifies controls requiring additional transformation attention.
Hyperproof’s control health calculation
Understanding how Hyperproof calculates control health enables organizations to optimize their configurations for maximum visibility into compliance effectiveness.
Five key factors
Control health statuses
Program health requirements specify that control health calculations only function when a program’s status is set to Operating rather than Defining. Organizations must ensure their programs are in operating status to benefit from automated health monitoring and the control-centric approach that defines ComOps success.
Designing label taxonomy and automation
Labels in Hyperproof function as intelligent organizational structures that automate evidence distribution across multiple controls simultaneously. Unlike traditional folder systems requiring manual file placement, labels automatically associate evidence with relevant controls based on predefined relationships.
Evidence source-based labels might include AWS CloudTrail Logs, GitHub Repository Data, and Active Directory Reports. Control domain-based labels could encompass Access Management, Change Control, and Incident Response. Regulatory framework-based labels might feature SOC 2® Evidence, ISO 27001 Documentation, and NIST Controls.
Automation capabilities emerge when new evidence arrives via automated collection or manual upload to a label. The platform automatically associates it with all controls linked to that label. Evidence currency monitoring occurs across entire evidence categories rather than tracking individual pieces of evidence. Tests configured at the label level automatically apply to all evidence collected under that label, confirming consistent validation across multiple control implementations.
Implementing automation
With Hyperproof properly configured for control-centric operations, organizations can deploy automation capabilities that transform reactive compliance into continuous monitoring. This implementation phase requires careful coordination between technical configuration and operational process changes.
Automated evidence collection
Direct connections between Hyperproof and external systems that generate compliance-relevant data can eliminate manual gathering entirely.
Implementation requires collaboration between compliance teams and system administrators. Security team provisioning of appropriate access permissions becomes necessary, along with firewall rules or IP address allowlist configuration for connection setup.
Evidence currency requirements must balance with system performance considerations. Daily collection supports user access reports for timely access reviews (Note: Access Reviews is an additional module available for purchase). Monthly or quarterly collection works well for stable policy documents.
Evidence versioning strategies
The new file approach creates separate evidence items for each collection cycle, maintaining historical records of changes over time. Alternatively, the versioning approach updates existing evidence items with new versions, maintaining change history while keeping single evidence items per collection source.
Configuring continuous monitoring and testing
Hyperproof’s freshness tracking and automated testing capabilities allow organizations to monitor control effectiveness continuously rather than relying on periodic manual assessments.
Freshness policies should align with business change rates and regulatory expectations. Daily or weekly freshness validation works for rapidly changing environments, while monthly or quarterly freshness requirements suit stable environments.
Evidence type characteristics and organizational change management capabilities need consideration. Shorter expiration periods provide more current evidence but may create an administrative burden. Longer periods reduce administrative overhead but may compromise evidence currency.
Automated testing implementation
Control-level tests apply only to evidence associated with particular controls. Label-level tests apply to all evidence collected under particular labels, potentially validating multiple controls simultaneously.
Test types supported
Test scheduling options
Establishing automated workflows
Repeating tasks and automated workflows reduce manual compliance activities by systematically generating work assignments based on predetermined schedules or triggering events.
Calendar schedules support periodic activities like access reviews through daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, semiannual, or annual recurring tasks. Event-driven repeating tasks respond to new employee onboarding triggers, system configuration change responses, and control health status changes.
Task management features distribute work based on control ownership, functional expertise, or workload balancing. Individual assignment or group assignment scenarios receive support, while escalation procedures for incomplete tasks beyond specified deadlines enable accountability.
Integration capabilities leverage existing workflow tools while benefiting from Hyperproof’s compliance functionality. Task synchronization with external project management systems maintains compliance audit trails across multiple systems.
Pilot programs and scaling
Pilot program implementation provides organizations with controlled environments for testing ComOps methodologies and demonstrating value to stakeholders who may be skeptical about automation benefits.
Running your pilot program
Pilot selection criteria
Controls that demonstrate clear automation benefits work well for pilots, particularly those without risk to important compliance obligations. Controls with frequent evidence collection requirements and available automated collection connections provide high-visibility, high-value demonstration opportunities.
Focus areas might include single compliance frameworks, particular business units, or particular types of evidence collection. Maintaining manageable complexity while providing meaningful results becomes important for stakeholder buy-in.
Success measurement
Quantitative metrics include evidence collection time reduction percentages, control health improvement measurements, audit preparation efficiency gains, and task completion rate improvements.
Qualitative assessments emerge from user satisfaction surveys, stakeholder feedback collection, change champion effectiveness evaluation, and process improvement identification.
Expanding automation across programs
Scaling successful pilot implementations requires the systematic deployment of automation capabilities across broader control populations while maintaining quality and effectiveness standards.
High-impact, low-complexity controls serve as initial expansion targets. Medium-complexity automation scenarios follow as organizational capability grows. Advanced automation implementations become available for mature program stages.
Change management considerations
Clear messaging about automation objectives and benefits addresses concerns about process changes and role modifications. User support throughout expansion phases maintains momentum, while success stories from pilot implementations build confidence.
Technical assistance during system integration becomes important for success. User training programs for expanded automation capabilities build institutional knowledge about automation management. Documentation templates support future implementation cycles.
Measuring success and optimization
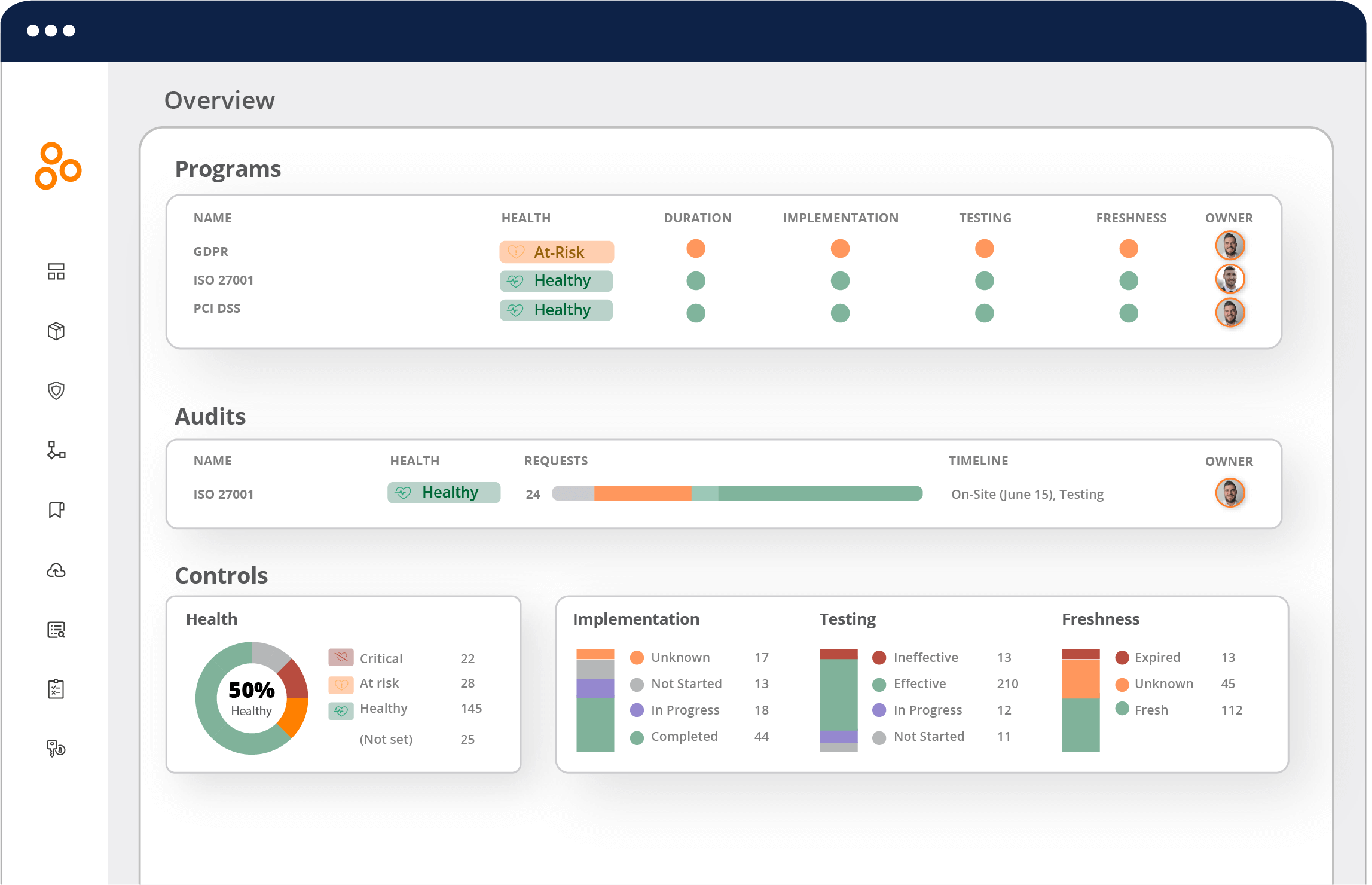
Hyperproof’s dashboards and reporting capabilities provide comprehensive visibility into transformation progress through metrics that reflect both operational efficiency improvements and compliance posture improvements.
KPI tracking in Hyperproof
Hyperproof’s dashboards reveal transformation success through several key indicators. Control health trends show whether your compliance posture is actually improving over time, not just whether you can pass an audit on a given day. When evidence freshness percentages climb, this signals that automated collection systems are working effectively.
The real proof of automation success lies in coverage rates. How many controls have you successfully automated versus those still requiring manual intervention? Meanwhile, manual task volume should decrease dramatically as automation takes hold. One organization saw their evidence collection time drop by 80% within six months of implementation.
User satisfaction tells a different story than pure efficiency metrics. Teams working 16-hour days during audit preparation often report significant stress reduction when moving to normal eight-hour workdays year-round. Training adoption rates reveal whether staff embrace continuous compliance education or resist it. Dashboard usage frequency shows whether teams actually rely on real-time data for decision-making or continue old habits of quarterly scrambles.
Quality can’t be sacrificed for speed. Error rates must be monitored to ensure efficiency improvements don’t compromise accuracy. System performance becomes visible through collection success rates, connection health, and automated test reliability. When AWS Hypersyncs fail repeatedly or GitHub integrations become unstable, these metrics expose problems before they impact audits.
Cultural transformation measurement
The most telling metric of ComOps success is how many issues your team discovers proactively versus how many external auditors find first. Organizations still operating in audit-first mode typically discover fewer than 50% of compliance issues internally. Mature ComOps programs often achieve 70% or higher internal discovery rates.
Voluntary automation requests represent perhaps the strongest indicator of cultural acceptance. When operational teams begin asking compliance for help automating their own processes, the transformation has succeeded. This marks the shift from “compliance is bothering us again” to “compliance helps us work better.”
Staff sentiment surveys can also capture the effects of transformation. Consider running quarterly focus groups with different stakeholder groups to gain deeper insight into the transformation experience than simple satisfaction scores. Leadership observation is similarly important: do executives model continuous compliance behaviors or revert to audit-first thinking when pressure mounts?
Success stories emerge organically when transformation works. Staff-generated examples of transformation benefits carry more weight than management presentations. Change champions develop naturally, and their effectiveness in peer influence becomes measurable through adoption rates and feedback quality.
Continuous improvement cycles

ComOps is never finished. Organizations must adapt continuously to changing requirements, regulatory updates, and operational improvements, which means regular optimization becomes a core competency rather than a periodic activity.
Automation effectiveness requires ongoing assessment. Which controls show the highest automation success? Where do coverage gaps remain? User feedback often reveals automation opportunities that technical analysis misses. A security team might suggest automating configuration snapshots that compliance teams never considered valuable evidence.
The accuracy question matters immensely: does automated monitoring actually reflect real control performance? Sometimes automated tests pass while actual controls fail in ways the tests don’t detect. Test accuracy improvements and expanded monitoring scope require continuous attention. Real-world control operation must align with automated validation; when it doesn’t, problems could remain hidden until auditors arrive.
Configuration changes follow regulatory updates. When NIST releases framework revisions or new privacy laws take effect, Hyperproof programs need adjustment. Smart organizations establish procedures for evaluating framework updates before they become mandatory. Systematic implementation of necessary configuration changes prevents last-minute scrambles when new requirements take effect.
Advanced capabilities
Organizations that have successfully implemented core ComOps automation and demonstrated consistent value can leverage advanced Hyperproof features. These sophisticated compliance management capabilities extend beyond basic automation and become available when organizations have established stable, continuous monitoring processes.
External auditor collaboration capabilities
Limited-access roles for external auditors transform the traditional audit experience. Auditors can view only the Proof and Audits tabs while reviewing evidence, only when the request status is set to Submitted to auditor.
Status changes to Needs revision or Approved remain within the auditor’s capabilities. Communication via Activity Feeds occurs with organization control over visibility. Import and export audit request functions provide workflow flexibility.
This capability eliminates traditional back-and-forth document exchange while providing auditors with direct access to current evidence. Appropriate security controls maintain data protection throughout the process.
Risk register integration
Note: The Risk Register is an additional module available for purchase.

Risk management becomes dynamic when integrated with compliance operations. Rather than static spreadsheets updated quarterly, risk assessments change in real time as control health fluctuates.
The math is straightforward but powerful. Inherent risk starts with likelihood multiplied by impact: what could happen if you had no controls in place? Residual risk tells a different story; it adjusts that calculation based on how well your controls actually work.
Here’s where control health makes the difference. A properly functioning firewall provides full mitigation value, so if you calculated it reduces a risk by 40%, you get that full 40%. But when control health drops to at-risk, you only receive half that mitigation. When controls become critical, they provide zero mitigation despite appearing on your control list.
This connection between control performance and risk assessment eliminates a common organizational misstep. Many risk registers assume controls work perfectly when calculating residual risk. Reality often differs significantly.
Advanced mitigation capabilities
Sophisticated organizations separate likelihood mitigation from impact mitigation. Some controls excel at preventing bad things from happening, like multifactor authentication, which reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access. Other controls minimize damage when bad things happen anyway, like backup systems, reducing the impact of ransomware attacks.
Large organizations often need multiple risk registers, which is a feature Hyperproof supports. Business risks differ fundamentally from system risks. Different business units face different threats. Product lines may require separate risk management. International operations introduce country-specific regulatory and operational risks that don’t apply elsewhere.
The real power comes through automation. When automated control testing detects that your backup system failed last night, the linked risk assessments update immediately. You don’t wait for next quarter’s risk review to discover that your ransomware impact mitigation disappeared. This dynamic risk posture visibility transforms risk management from periodic reporting into continuous business intelligence.
Self-service reporting and analytics

Hyperproof has sophisticated business intelligence and reporting capabilities. The platform has reports and dashboards that help answer questions from stakeholders, updated in real-time to understand your compliance, risk, and audit-readiness posture and action items. Export custom reports or receive reports via email.
These advanced capabilities position mature ComOps programs to deliver strategic value that extends beyond traditional compliance management into enterprise risk management and business intelligence.
Sustaining your transformation

The journey from audit-first operations to continuous compliance represents more than a technology upgrade. It constitutes a fundamental shift in how organizations approach compliance management, and sustaining this transformation requires ongoing attention to governance, continuous improvement, and adaptation to changing requirements.
Long-term success factors
Organizations that successfully maintain ComOps programs typically establish governance structures that support ongoing optimization while preserving transformation benefits. Regular review cycles for automation effectiveness, systematic stakeholder feedback collection, and strategic planning for compliance capability expansion become routine.
New opportunities for efficiency improvement and risk reduction require identification. Building on transformation foundations for additional automation initiatives delivers incremental benefits while maintaining operational stability. Capabilities expand as organizational maturity and confidence grow.

Understanding of ComOps principles across compliance and operational teams needs periodic refreshers until it’s a cultural standard. For example, these transformation benefits must be preserved as personnel changes occur. Continued innovation through cross-functional collaboration enables adaptation to shifting organizational priorities over time.
Future considerations
The regulatory landscape will continue changing, requiring organizations to adapt their ComOps implementations to address new requirements while maintaining existing capabilities. Organizations with mature ComOps programs are better positioned to accommodate regulatory changes efficiently compared to those operating with traditional audit-first approaches.
Legal protections provide additional incentive for framework-based ComOps programs. Multiple states, including Ohio, Utah, and Connecticut, have enacted cyber safe harbor laws providing affirmative tort defenses for organizations using publicly available cybersecurity frameworks like NIST 800-171, NIST CSF, CIS Critical Security Controls, and ISO 27001.
Sustaining success
Success in sustaining ComOps transformation depends on maintaining an organizational commitment to continuous improvement. Treating transformation as an ongoing process rather than a one-time project becomes essential.
Proactive risk management maintains early detection and intervention capabilities. Stakeholder engagement preserves cross-functional collaboration and communication. Technology optimization adapts configurations to changing requirements and opportunities.
Organizations that embrace these principles are more likely to realize long-term benefits and maintain competitive advantages in their compliance capabilities.
Business advantages of ComOps
|
Benefit area |
Audit-first approach |
ComOps approach |
|---|---|---|
|
Risk management |
Reactive; risks identified late |
Proactive; risks detected early |
|
Operational efficiency |
Manual processes; resource-heavy |
Automated; streamlined operations |
|
Cost |
High from manual prep/penalties |
Lowered through automation and prevention |
|
Agility |
Slow adaptation |
Quick adaptation to new threats/regulations |
|
Stress management |
Intense periods before audits |
Distributed workload throughout the year |
|
Documentation quality |
Recreated for each audit |
Continuously maintained and current |
ComOps transforms compliance from a periodic checklist activity into an integrated part of daily operations. This shift reduces costs and improves agility while strengthening security posture, enhancing reputation, and ensuring ongoing legal soundness.
Ultimately, continuous compliance operations supports sustainable business growth without regulatory setbacks. Organizations that successfully navigate this transformation will be well-positioned for sustained competitive advantage in an increasingly complex regulatory environment.
Download the PDF












