GDPR Security Compliance: What Every Company Needs to Know
Navigating the labyrinth of GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliance can be daunting, but it’s essential if you want to protect your organization, safeguard personal data, and avoid costly penalties. If GDPR compliance makes you feel overwhelmed, you’re not alone. It’s one of the most comprehensive privacy regulations in the world, and understanding it all can be challenging. The good news is that GDPR compliance builds trust with your customers and helps ensure your business thrives in an increasingly data-driven world. This guide will help you cut through the noise and provide a clear, actionable roadmap to achieving GDPR security compliance. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of what GDPR entails, how it impacts your organization, and the steps you need to take to achieve compliance.
What is GDPR?
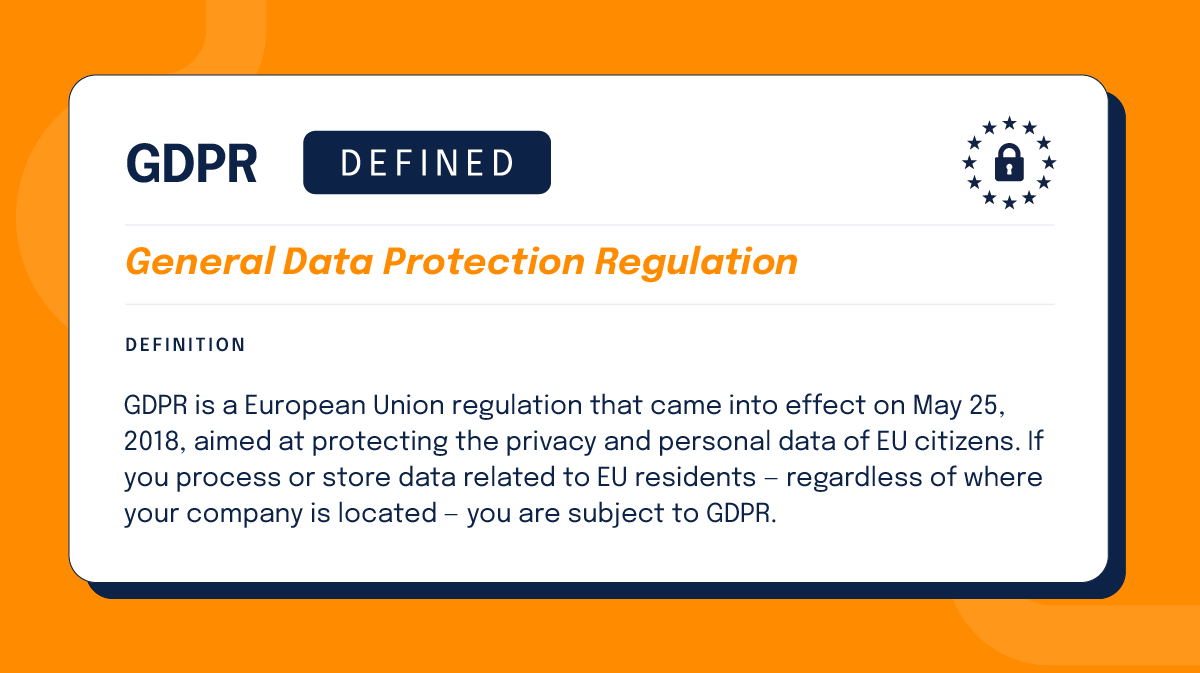
GDPR is a European Union regulation that came into effect on May 25, 2018, aimed at protecting the privacy and personal data of EU citizens. If you process or store data related to EU residents — regardless of where your company is located — you are subject to GDPR.
Want to take a deep dive into GDPR? Read the guide ->
The stakes are high. Non-compliance can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of your global annual revenue, whichever is higher. Beyond financial penalties, failing to comply with GDPR can damage your reputation, erode customer trust, and leave you vulnerable to cyberattacks.
GDPR has a two-tier fine structure that imposes penalties based on the severity of violations. Tier 1 fines can reach up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher, for less severe infractions such as record-keeping failures or insufficient security measures. Tier 2 fines, for more serious breaches like violating core privacy principles or mishandling user consent, can go up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
But GDPR isn’t just about avoiding fines. It’s about demonstrating a commitment to privacy and security—values that are increasingly important to customers, partners, and regulators.
How the EU AI Act and GDPR work together
The EU AI Act is a comprehensive regulatory framework that classifies AI systems by risk level and establishes rules to ensure their safety, transparency, and compliance with fundamental rights, particularly for high-risk applications that impact individuals and society. It entered into force on August 1, 2024, with its provisions set to be gradually implemented over the following 6 to 36 months.
The EU AI Act and GDPR complement each other by regulating AI systems that process personal data, ensuring both ethical development and legal compliance. While GDPR enforces privacy, fairness, and transparency, the AI Act introduces risk-based security and governance requirements.
To comply with GDPR’s principles of lawfulness, fairness, and transparency, organizations must:
To comply with GDPR’s principles of lawfulness, fairness, and transparency, organizations must:
- Establish a legal basis for AI-driven data processing
- Conduct bias audits to prevent discrimination in AI decisions
- Implement explainability measures so individuals understand AI-driven outcomes and can challenge them under GDPR’s Article 22
GDPR violations remain under the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) and national DPAs, while AI Act violations will be enforced by new AI regulatory bodies. In cross-border cases, regulators will collaborate, similar to GDPR’s one-stop-shop mechanism.
Both laws emphasize security, but GDPR (Article 32) mandates encryption and access controls, while the AI Act adds:
- Cybersecurity protections against adversarial AI attacks
- Continuous monitoring of AI models
- Risk assessments for AI vulnerabilities
Impact on cross-border data transfers
AI systems processing personal data across jurisdictions must comply with GDPR’s transfer mechanisms (e.g., SCCs, adequacy agreements) and AI-specific risk assessments to ensure governance remains strong, even outside the EU. Take, for example, the unlawful processing of biometric data. Both regulations classify biometric data as highly sensitive. GDPR strictly limits its use, requiring explicit consent or a legal basis, while the AI Act further restricts biometric identification in public spaces, especially for law enforcement. Organizations processing biometric data across jurisdictions must ensure compliance with both frameworks to avoid severe penalties and protect individuals’ fundamental rights.
Separate vs. unified assessments
While companies may need GDPR’s Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) and an AI Act Conformity Assessment, integrating AI Act compliance into existing GDPR frameworks can reduce duplication. Aligning privacy, security, and risk management efforts ensures efficient, future-proof compliance.
By understanding how the EU AI Act and GDPR intersect, organizations can build AI systems that are secure, transparent, and ethically sound while staying ahead of evolving regulations.
The core principles of GDPR
At the heart of GDPR are seven key principles that guide how personal data should be handled:
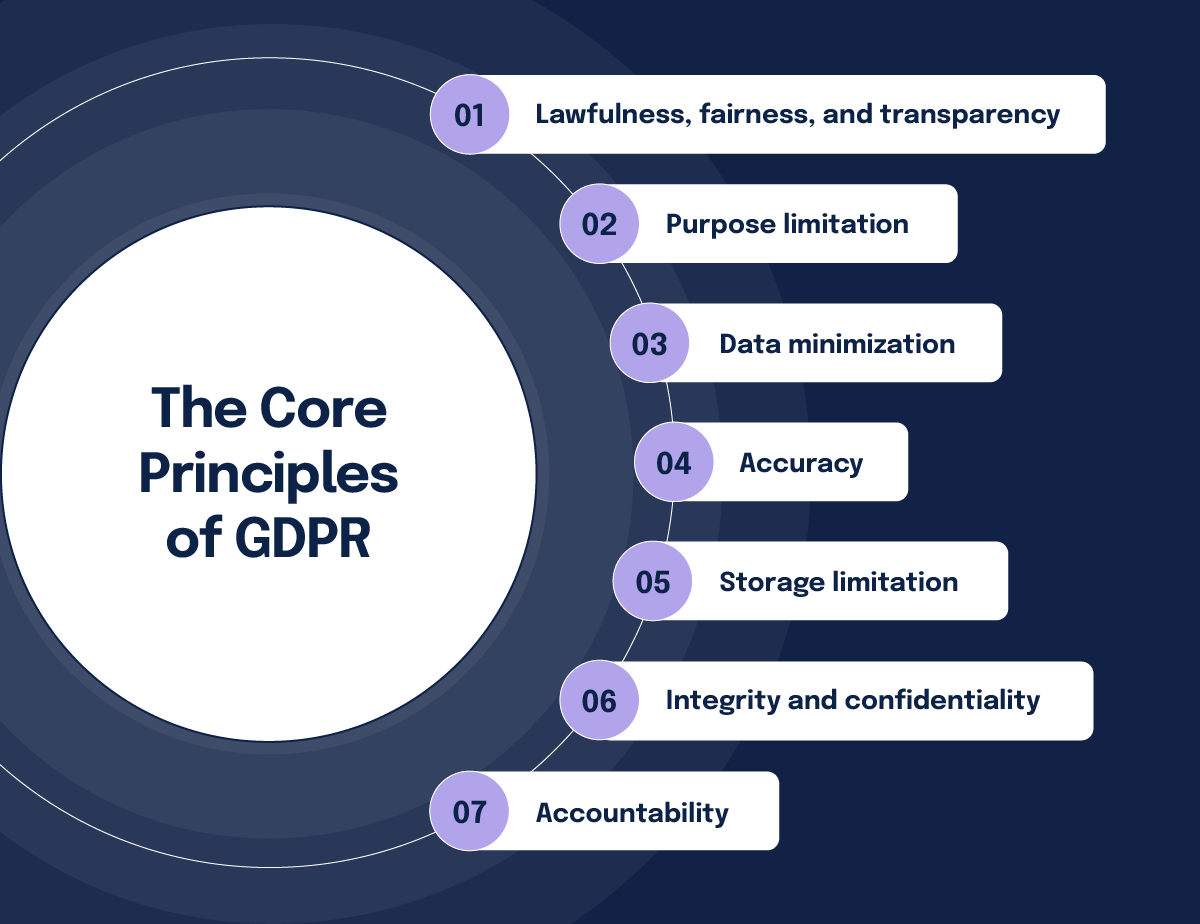
1. Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency
You must process personal data legally, fairly, and in a way that’s transparent to the individual.
2. Purpose limitation
Data should only be collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
3. Data minimization
Collect only the data you need to achieve your stated purposes.
4. Accuracy
Keep personal data accurate and up to date.
5. Storage limitation
Do not keep personal data longer than necessary.
6. Integrity and confidentiality
Use appropriate security measures to protect personal data.
7. Accountability
Be able to demonstrate compliance with all of the above principles.
Understanding the core principles of GDPR goes beyond just satisfying a regulatory requirement—it’s an opportunity to reimagine how your organization handles personal data. By embracing concepts like transparency, data minimization, and accountability, you can position your business as a leader in privacy-first operations.
These principles not only safeguard individual rights but also foster loyalty among your customers and partners. In an era where data integrity and ethical handling are at the forefront of consumer and regulatory expectations, organizations that embrace these values build trust if promoted as part of a broader privacy strategy.
How GDPR impacts your security practices
GDPR places a strong emphasis on data security. Article 32 explicitly requires you to implement technical and organizational measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk. This includes:
Encryption and pseudonymization
By encrypting or pseudonymizing personal data, you can make it much harder for unauthorized parties to misuse it.
Access controls
Limit access to personal data to only those who need it for their job responsibilities.
Incident response plans
Have a plan in place to quickly detect, respond to, and report data breaches.
Regular security and GDPR vulnerability assessments
Conduct periodic security audits and GDPR vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate risks to personal data, making sure your technical and organizational measures stay aligned with GDPR’s Article 32 requirements.
What is a GDPR vulnerability assessment?
A GDPR vulnerability assessment is a focused security review that identifies technical and organizational weaknesses in systems that process personal data, so you can meet GDPR’s Article 32 requirement for “a level of security appropriate to the risk.” A typical GDPR vulnerability assessment looks for security flaws, misconfigurations, and access control gaps that could expose personal data, then maps those issues to GDPR obligations and remediation actions.
- Scan applications and infrastructure for vulnerabilities that could expose personal data
- Review access controls, encryption, and logging around systems that store or process EU personal data
- Check configurations of cloud services, databases, and endpoints against GDPR security expectations
- Prioritize remediation based on the potential impact on data subjects’ rights and freedoms
GDPR elevates security from a technical concern to a core business priority, emphasizing that protecting personal data is fundamental to operational integrity. Its requirements push you to evaluate your current security posture and adopt measures that proactively address risks.
From implementing encryption to refining incident response strategies, GDPR ensures that security becomes a continuous, adaptive process rather than a one-time checklist. This shift not only mitigates compliance risks but also empowers your organization to handle data responsibly in a world where trust and transparency are key to sustained success.
Key steps to achieving GDPR compliance

1. Audit your data
Start by identifying what personal data you collect, where it’s stored, how it’s processed, and who has access to it. This audit is crucial for understanding your current state and identifying gaps in compliance.
2. Update your privacy policies
Your privacy policies should clearly explain how you collect, use, and protect personal data. They must be written in plain language to ensure transparency.
3. Obtain proper consent
Under GDPR, consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. Ensure your consent mechanisms meet these criteria.
4. Implement strong data security measures
From encryption to secure storage solutions, make sure your data is protected at all times. This also includes training your employees on cybersecurity best practices. As part of these efforts, schedule regular GDPR vulnerability assessments to test your controls in real-world conditions and uncover gaps before attackers or regulators do.
5. Designate a data protection officer (DPO)
If required, appoint a DPO to oversee your GDPR compliance efforts and serve as a point of contact for data protection authorities. A DPO is mandatory when an organization systematically monitors individuals on a large scale or processes large amounts of sensitive personal data. For example, a healthcare provider that processes large volumes of patient health records would be required to appoint a DPO.
6. Develop a breach response plan
GDPR requires you to report data breaches within 72 hours. A well-prepared incident response plan can make the difference between compliance and costly fines.
7. Document everything
GDPR’s accountability principle means you need to keep detailed records of your data processing activities, risk assessments, and compliance measures.
To comply with GDPR’s consent requirements, organizations must ensure consent is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous (Article 7). A well-designed consent mechanism includes clearly defined choices, such as separate checkboxes for different data processing purposes (e.g., marketing emails vs. data sharing with third parties). Pre-ticked boxes are not allowed, and users must actively opt-in. Consent requests should be concise, easy to understand, and separate from other terms and conditions to ensure transparency. Additionally, organizations must provide an easy way to withdraw consent at any time, such as a visible “unsubscribe” link in emails or a preference management dashboard. For websites and apps, users should be able to accept, reject, or customize tracking preferences, rather than using deceptive techniques that pressure users into consenting. Regular audits and timestamped consent records also help organizations demonstrate compliance and accountability under GDPR.
Achieving GDPR compliance requires more than ticking boxes—it’s about embedding privacy and security into the very fabric of your organization. The process begins with a comprehensive data audit, which serves as the foundation for identifying vulnerabilities and areas of improvement. From there, effective compliance demands cross-functional collaboration, involving IT, legal, and business leaders to align operational practices with regulatory requirements.
Experts recommend treating GDPR as an ongoing commitment rather than a one-time project, integrating practices like data minimization and regular security assessments into your workflows. By approaching compliance strategically and proactively, you not only mitigate risks but also position your organization to adapt seamlessly to future regulatory changes.
GDPR and Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is required under GDPR when data processing is likely to pose a high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms, such as when handling sensitive personal data, conducting systematic monitoring, or using automated decision-making with legal effects. DPIAs help organizations identify and mitigate risks by evaluating data processing activities, security measures, and potential privacy impacts before implementation. For example, a company deploying AI-driven employee monitoring or biometric authentication must conduct a DPIA to assess compliance risks and implement safeguards to protect personal data. While a DPIA focuses on privacy and legal risks to individuals’ rights and freedoms, a GDPR vulnerability assessment focuses on uncovering technical and organizational security weaknesses that could lead to data breaches or non-compliance.
Data Subject Requests (DSRs) under GDPR
For GDPR compliance, it’s also critical to be aware of Data Subject Requests (DSRs), also known as Data Subject Rights (DSRs) requests. DSRs empower individuals to exercise their rights over their personal data. Organizations that process personal data must have procedures in place to handle these requests promptly and transparently, typically within one month (extendable by two months for complex cases).
DSRs give individuals control over their personal data. For example, individuals can request access (Article 15) to their data, rectification (Article 16) of inaccuracies, or erasure (Article 17) if data is no longer needed or was processed unlawfully. The Right to Object (Article 21) allows individuals to stop data processing for marketing or other purposes. Organizations must handle these requests promptly to maintain compliance and build trust in their data practices. You can find the entire list of DSRs with detailed explanations here.
Common GDPR challenges and how to overcome them
Achieving compliance isn’t always straightforward. Here are some common challenges you may face and strategies to address them:
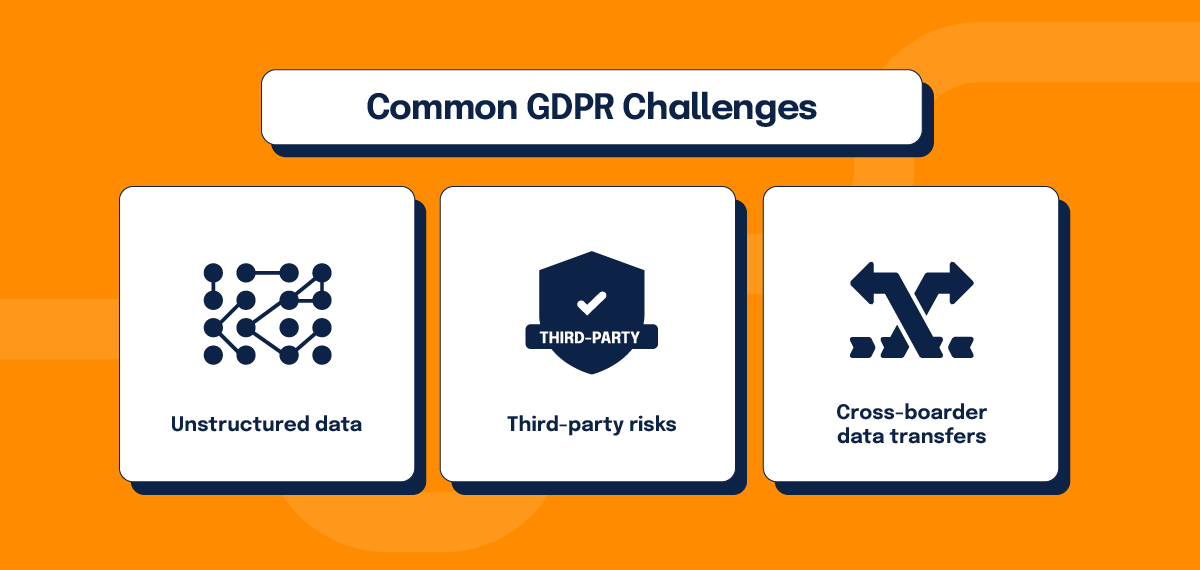
1. Unstructured data
Personal data often resides in emails, documents, and other unstructured formats, making it harder to identify and manage. Using automated tools to classify and monitor data can help.
2. Third-party risks
If you work with vendors who process personal data on your behalf, their non-compliance can become your problem. Conduct thorough third-party due diligence and require GDPR-compliant contracts.
3. Cross-border data transfers
Transferring data outside the EU requires additional safeguards. Ensure you use approved mechanisms like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs). After Schrems II invalidated the EU-U.S. Privacy Shield, organizations transferring personal data outside the EU must use SCCs or BCRs along with Transfer Impact Assessments (TIAs) to evaluate data protection risks. For example, a European financial firm using a U.S.-based cloud provider must implement SCCs and assess U.S. surveillance risks under FISA 702. If risks exist, supplementary safeguards like end-to-end encryption ensure GDPR compliance by keeping data inaccessible, even if requested by authorities.
Navigating GDPR compliance often means addressing challenges that go beyond technical fixes, requiring a balance between operational efficiency and regulatory rigor. Unstructured data, for example, demands innovative solutions like AI-powered tools to uncover hidden personal information scattered across systems. Vendor management poses another challenge, where building strong third-party oversight programs ensures their practices align with your compliance efforts. Cross-border data transfers often test your ability to implement legal safeguards, making mechanisms like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) critical.
Overcoming these obstacles requires a mindset shift: rather than viewing compliance as a burden, treat it as an opportunity to enhance your data governance and foster a culture of privacy across your organization.
The benefits of GDPR compliance
While achieving GDPR compliance requires effort, the benefits can far outweigh the costs:
Enhanced customer trust
Demonstrating a commitment to privacy can strengthen your relationships with customers and differentiate your brand.
Improved data management
GDPR forces you to streamline your data processes, leading to greater efficiency and reduced risk.
Competitive advantage
Compliance can be a selling point, especially when dealing with privacy-conscious clients or partners.
Reduced risks
By adhering to GDPR, you minimize the likelihood of data breaches and regulatory fines.
Data breaches are minimized under GDPR by requiring organizations to implement robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular risk assessments. Additionally, GDPR mandates data minimization and pseudonymization, reducing the amount of sensitive data exposed in the event of a breach, while strict breach notification requirements ensure rapid response and mitigation.
GDPR compliance goes beyond regulatory obligations. It’s a strategic investment in building resilience, fostering trust, and positioning your organization as a leader in a privacy-driven future.
The role of technology in GDPR compliance
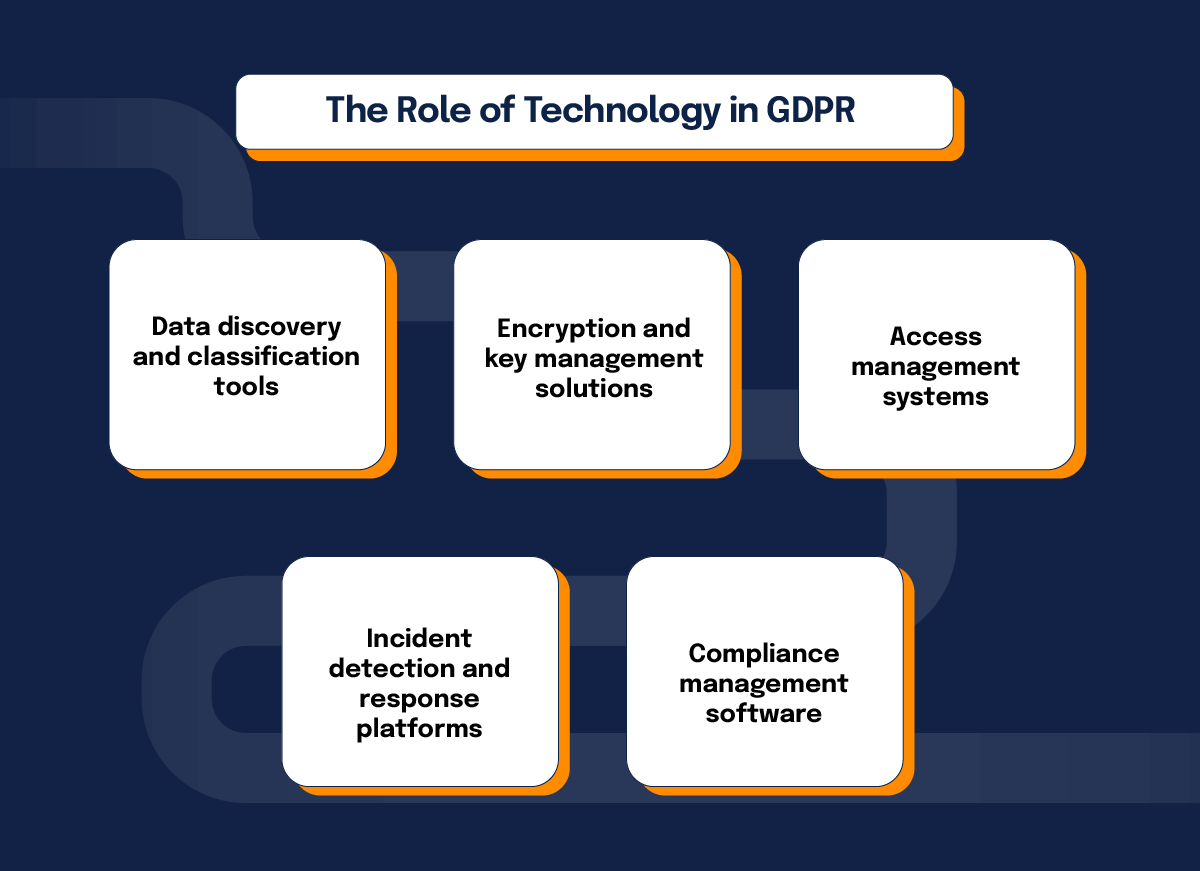
Data discovery and classification tools
These tools automatically scan your systems to identify where personal data resides and classify it based on sensitivity or type. This capability helps you maintain visibility over your data and ensures you’re applying the appropriate protection measures.
Encryption and key management solutions
Encryption secures sensitive data both at rest and in transit, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Key management systems ensure that encryption keys are stored and accessed securely, providing an extra layer of protection against data breaches.
Access management systems
Implementing access controls allows you to limit who can view or process personal data based on their role and responsibilities. This reduces the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with GDPR’s principle of data confidentiality.
Incident detection and response platforms
These platforms help you detect potential data breaches or security incidents in real time. With features like automated alerts and detailed forensics, they allow your team to respond swiftly and report breaches within GDPR’s 72-hour window.
Compliance management software
Centralizing compliance-related documentation and processes streamlines your ability to monitor and demonstrate GDPR adherence. These tools often include dashboards, audit trails, and automated reminders to help you stay on top of your compliance requirements.
By leveraging these technologies, you can automate labor-intensive processes, reduce human error, and ensure robust safeguards for personal data.
How Hyperproof can help with GDPR security compliance
Hyperproof simplifies the complexities of GDPR compliance by providing a centralized platform with tools and features designed to streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and ensure accountability. With Hyperproof, your organization can transform GDPR compliance from a complex challenge into a manageable, efficient, and collaborative process — empowering you to protect personal data, meet regulatory requirements, and enhance trust with stakeholders. Here’s how we can help:
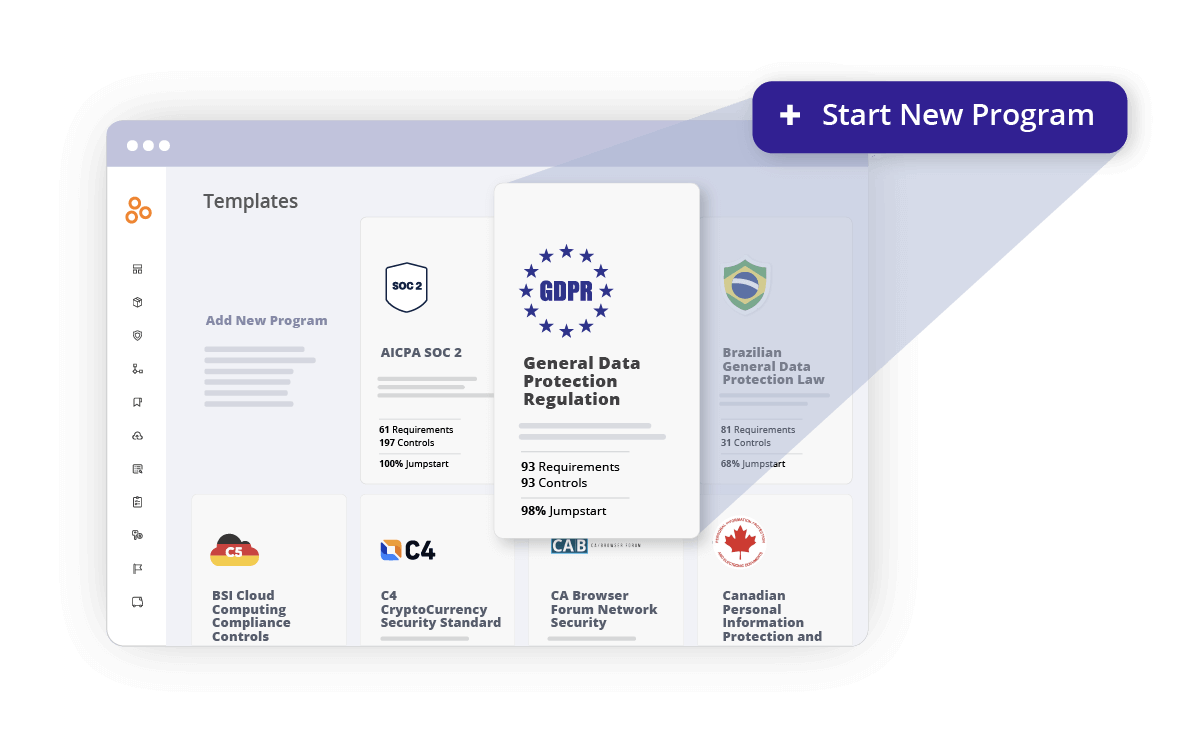
Leverage an out-of-the-box GDPR program template
With pre-populated controls, Hyperproof makes it easy to visualize what it takes to achieve GDPR compliance and understand what is needed of you and your business to meet requirements.
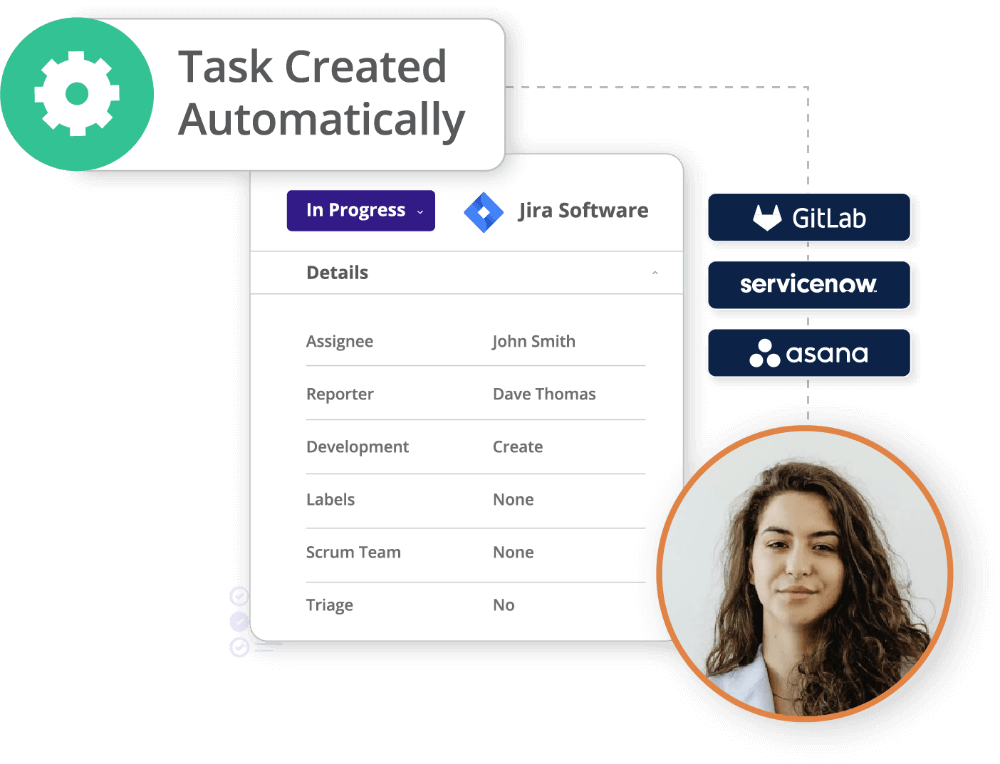
Ensure tasks for GDPR requirements are completed
Automate task assignments to ensure GDPR requirements are met and review workflows to maximize output so you never have to worry about delays.
Seamlessly collect evidence to satisfy GDPR requirements
Streamline processes by automating evidence collection and review workflows via Hyperproof.

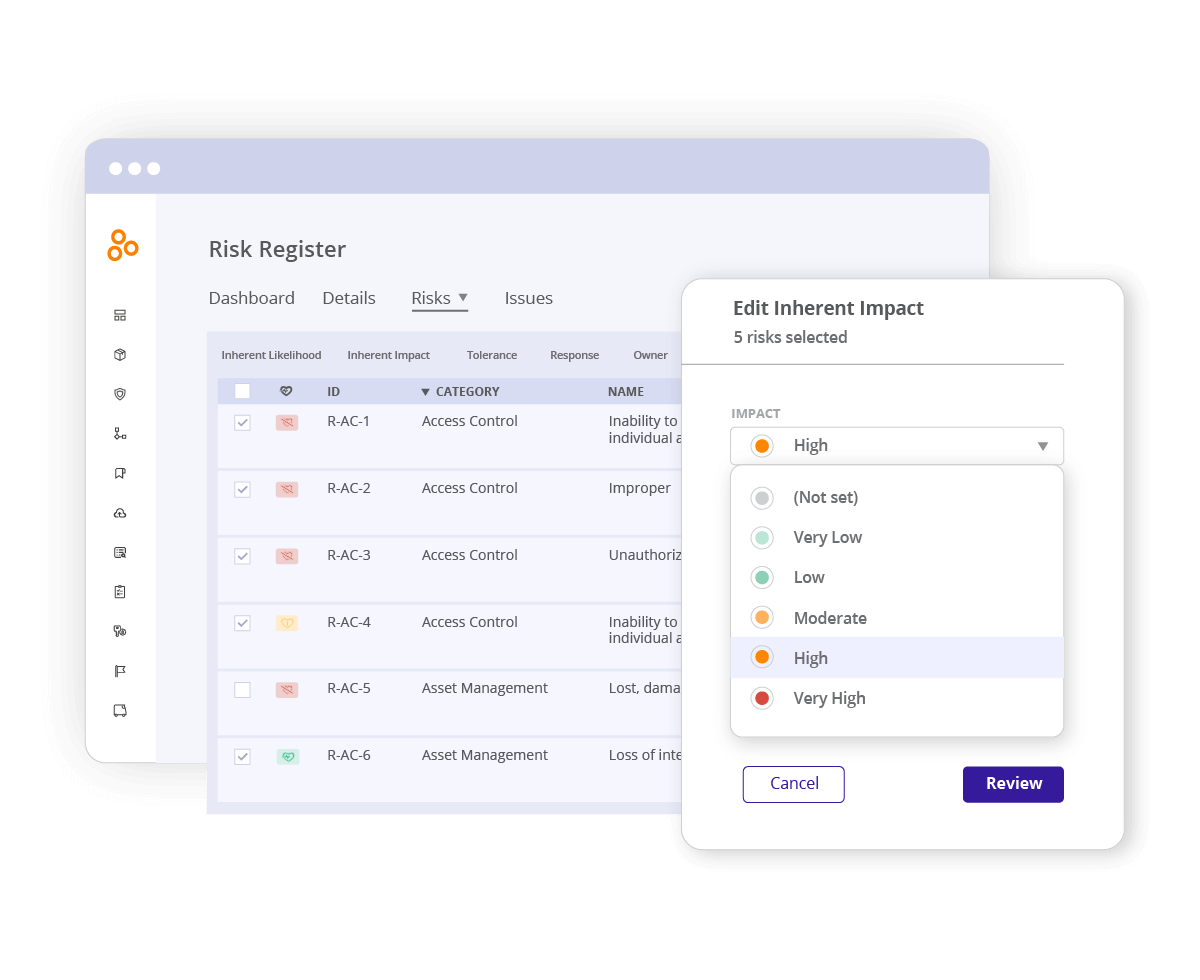
Easily assess and manage privacy risks
Conduct privacy risk assessments and track risks in a central risk register where you can connect your controls to risks and track remediation work.
Reuse your GDPR work to satisfy other frameworks
Use Hyperproof’s Jumpstart feature to map your existing GDPR controls across multiple frameworks like NIST Privacy Framework and CCPA so you can quickly add new frameworks.
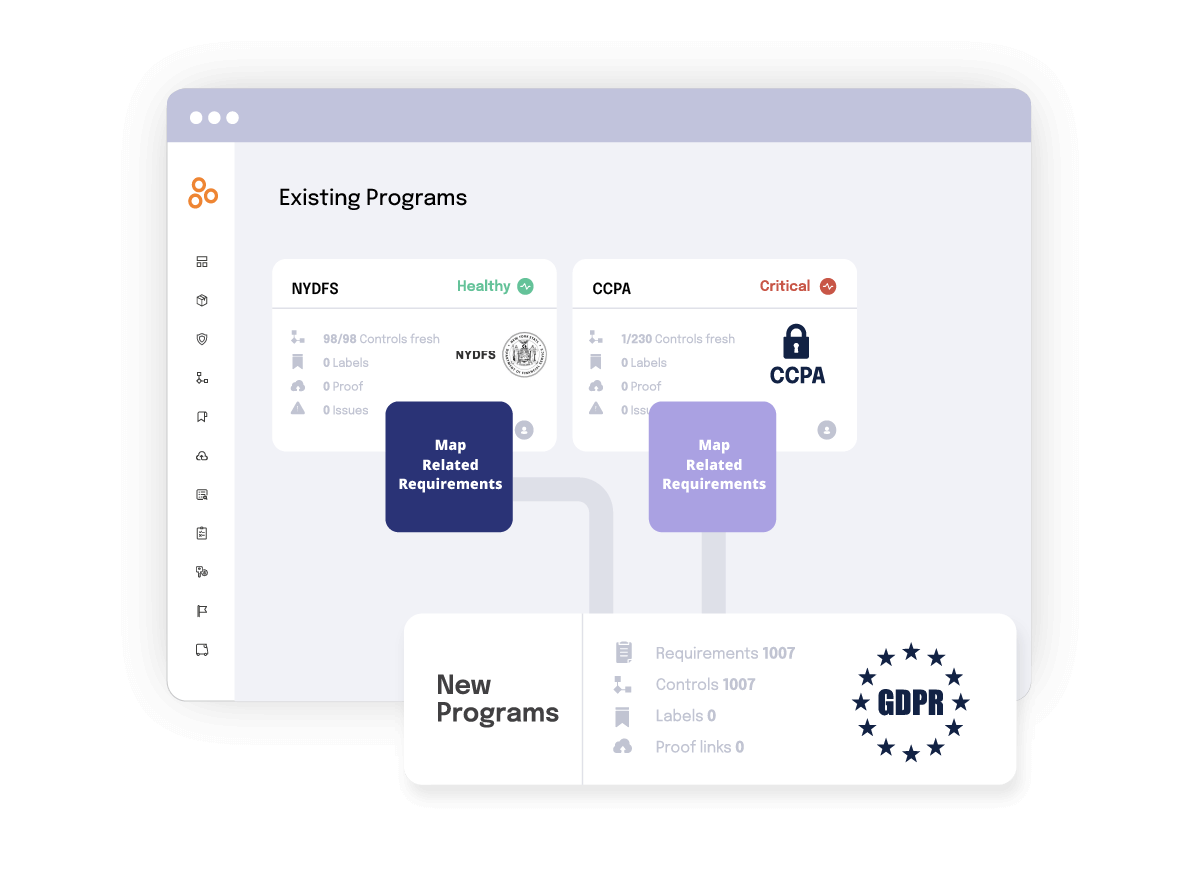
Preparing for the future of data privacy
GDPR is just the beginning. With privacy regulations emerging in other regions, including the U.S. (e.g., CCPA), staying ahead of the curve is critical. By embedding privacy and security into your organization’s DNA, you can future-proof your operations against evolving regulatory landscapes.
Achieving GDPR compliance isn’t a one-time task. It’s an ongoing commitment to protecting the personal data of your customers and employees. By understanding the principles of GDPR, implementing robust security measures, and leveraging technology, you can not only comply with the regulation but also turn it into a competitive advantage.
Take the first step by evaluating your current practices, uncovering gaps, and charting a clear roadmap for improvement. Acting now positions you to not only meet regulatory demands with confidence but also to build lasting trust in a world where privacy is paramount.
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?