Fintech Compliance and How to Maintain It

Fintech compliance requires vigilance, proactive measures, and a deep understanding of regulations. Overall, regulation seeks to protect consumers, ensure financial stability, and prevent financial crimes — but it can be extremely complex. Every fintech company knows it must navigate a vast web of rules to operate legally and ethically.
This article delves into the essentials of fintech compliance. With so many moving parts, we broke them down into key areas, each with their own requirements. Not all the areas covered below have formal regulations, but all of them do have a significant impact on the integrity of a fintech institution. If you need more info, source links are included at the end of each section.
Later, we’ll look at the key challenges and best practices associated with fintech compliance. Lastly, we’ll explore how you can maintain your compliance in the most effective way possible. Let’s dive in.
Key areas of fintech compliance

1. Anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF)
Regulations
Fintech companies are required to adhere to AML and CTF regulations established by international bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). The goal is to prevent illegal activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing.
Requirements
- Know your customer (KYC): Fintech companies must implement procedures to verify the identities of their customers by collecting and verifying personal information.
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuous monitoring of transactions is necessary to detect and report suspicious activities.
- Record keeping: Companies must maintain detailed records of transactions and customer information for regulatory review and audits.
Sources
Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
2. Data privacy and security
Regulations
Compliance with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S. is crucial for fintech companies.
Requirements
- Secure data handling: Companies must ensure that personal and financial data are handled, stored, and processed securely, using encryption and other security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Cybersecurity measures: Institutions must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and establish procedures for responding to security incidents. This also includes notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities in the event of a breach.
- Regular security audits: Companies must conduct regular security audits and risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Sources

3. The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC)
Regulations
Fintech companies operating in the financial sector must comply with the guidelines and standards set forth by the FFIEC. The FFIEC aims to ensure the safety, soundness, and consumer protection within the financial system through rigorous oversight and examination.
Requirements
- Risk Management: Fintech companies must develop and implement robust risk management frameworks to identify, measure, monitor, and control risks, including cybersecurity threats and operational risks.
- Consumer Protection: Adherence to consumer protection laws and regulations is critical, ensuring transparency, fairness, and the safeguarding of consumer data and funds.
- Examinations and Reporting: Regular examinations by FFIEC member agencies are conducted to assess compliance with regulatory standards. Fintech companies must be prepared to provide documentation and reporting that demonstrates their adherence to FFIEC guidelines.
Sources

4. Consumer protection
Regulations
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) enforces laws like the Truth in Lending Act (TILA) and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) to ensure fair treatment and transparency in financial transactions. Consumer protection laws are designed to safeguard users from fraud, unfair practices, and misinformation.
Requirements
- Transparency: Fintech companies must provide clear and transparent communication regarding fees, terms, and conditions of their services, ensuring that customers understand the costs and risks.
- Dispute resolution: Companies should have mechanisms in place for resolving customer complaints efficiently and fairly, setting up customer service channels and processes for addressing disputes.
- Fair treatment: All customers must be ensured of fair treatment in all interactions, maintaining a high standard of customer service and support.
Sources
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
Truth in Lending Act (TILA)

5. Regulatory reporting and licensing
Regulations
Fintech companies must adhere to the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and obtain the appropriate licenses from regulatory bodies like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK or the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) in the US, ensuring accurate and timely reporting of financial activities.
Requirements
- Regular reporting: Companies must regularly report their financial health, compliance status, and other relevant metrics to regulatory bodies. This includes submitting periodic reports and disclosures as required by regulators.
- Adherence to regulations: Fintech companies must comply with local and international financial regulations, obtaining and maintaining the necessary licenses and registrations to operate legally in various jurisdictions.
Sources

6. Payment services and electronic money
Regulations
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is an information security standard designed to help organizations who handle credit card transactions maintain a secure environment. In the EU, compliance with the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) is crucial for fintech companies.
Requirements
- Strong customer authentication (SCA): Companies must implement strong customer authentication to ensure secure payments, using multi-factor authentication methods to verify the identity of customers during transactions.
- Transaction security: Fintech companies should manage transaction limits to prevent fraud and ensure the security of their payment systems. This includes monitoring for suspicious activities and implementing security measures to protect against unauthorized access.
Sources

7. Regulatory technology (RegTech) integration
Regulations
The World Economic Forum defines RegTech as “the application of new technological solutions that assist highly regulated industry stakeholders, including regulators, in setting, effectuating, and meeting regulatory governance, reporting, compliance, and risk management obligations.” Integrating these technologies is increasingly essential for enhancing compliance.
Requirements
- Automated compliance: Fintech companies should leverage RegTech solutions to automate compliance tasks such as monitoring, reporting, and risk management. This helps them stay ahead of regulatory changes and ensures timely compliance with evolving regulations.
- Efficiency and accuracy: Automating compliance processes improves efficiency and reduces the risk of human errors. By automating tedious compliance work, companies can focus on their core business activities.
Sources

8. Cross-border transactions and international regulations
Regulations
The SWIFT network and Basel Framework set standards for secure and efficient cross-border transactions, requiring banks and fintechs to comply with international AML/CTF regulations to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing globally.
Requirements
- Multi-jurisdictional compliance: Fintech companies must comply with tax laws, foreign exchange regulations, and AML standards in each country where they operate. This means understanding and adhering to the specific regulations of each jurisdiction.
- Adaptable compliance programs: Companies must ensure that their compliance programs are adaptable to different regulatory environments and capable of managing cross-border transactions effectively.
Sources

9. Ethical AI and algorithmic transparency
Regulations
Emerging guidelines and standards, like the NIST AI RMF, NIST CSF, and ISO 42001, address the ethical use of AI in financial services.
Requirements
- Algorithmic transparency: Fintech companies must ensure that their AI algorithms are transparent, fair, and free from biases. Regular audits and assessments are also essential to ethical operation.
- Bias mitigation: Companies should implement measures to detect and mitigate biases in their AI algorithms, ensuring fair treatment of all customers.
Sources

10. Ethical standards and corporate governance
Regulations
The OECD Principles of Corporate Governance provide a framework for ethical standards, ensuring that fintech companies maintain transparency, accountability, and integrity in their operations and decision-making processes.
Requirements
- Codes of conduct: Fintech companies must establish clear codes of conduct and ensure transparency in their operations. They should implement strong governance structures to oversee compliance and ethical behavior.
- Employee understanding: Companies should ensure that their employees understand and adhere to ethical standards and governance principles. This fosters a culture of integrity and accountability.
Sources

11. Third-party risk management
Regulations
The Federal Reserve’s SR 13-19 guidance emphasizes the need for robust third-party risk management practices. This standard requires financial institutions to assess and monitor the risks posed by their vendors and service providers.
Requirements
- Due diligence: Fintech companies must conduct due diligence on third-party vendors to ensure they comply with relevant regulations and adhere to the company’s standards, regularly monitoring their compliance status.
- Clear contracts: Companies should establish clear contractual agreements with vendors to define compliance expectations and responsibilities. Adequate measures should be implemented to manage third-party risks effectively.
Sources
12. Fraud prevention and detection
Regulations
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) require financial institutions to implement strong internal controls and information security measures to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Technology tools are increasingly important for fraud prevention and detection.
Requirements
- Multi-factor authentication: Implementing multi-factor authentication is crucial for securing transactions and preventing unauthorized access.
- Advanced technologies: Fintech companies can use advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect suspicious activities and prevent fraud.
- Regular audits: Companies should conduct regular audits to identify and mitigate fraud risks, establishing procedures for responding to and investigating suspected fraud cases.
Sources

13. Blockchain and cryptocurrency regulations
Regulations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides guidelines on virtual asset service providers (VASPs), mandating AML/CTF compliance for cryptocurrency exchanges and other blockchain-related activities. Furthermore, PCI DSS should be considered for any cryptocurrency project as it covers general security controls to help protect IT systems while providing coverage for cryptography security controls as well.
Requirements
- ICO regulations: Fintech companies must comply with regulations related to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), understanding and adhering to the specific regulatory requirements for each type of digital asset activity.
- Cryptocurrency exchange compliance: Companies must ensure compliance with regulations governing cryptocurrency exchanges, implementing measures to ensure the security and integrity of their operations.
- Digital asset custody: Fintech companies should understand and comply with regulations for digital asset custody, ensuring proper management and protection of digital assets.
Sources
14. Compliance training and awareness
Regulations
Standards, like the FFIEC IT Examination Handbook, highlight the importance of ongoing compliance training and awareness programs to ensure that employees at all levels understand and adhere to regulatory requirements and ethical standards.
Requirements
- Regular training: Fintech companies should provide regular compliance training and workshops for their employees, educating them about relevant regulations, compliance policies, and procedures.
- Culture of compliance: Companies should foster a culture of compliance within the organization, ensuring that all employees understand the importance of adhering to compliance requirements.
Sources

15. Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance
Regulations
The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) provide standards for ESG reporting, guiding financial institutions and fintech companies in disclosing their environmental and social impacts to stakeholders. There is a growing emphasis on ESG factors in the financial industry, including fintech.
Requirements
- ESG policies: Fintech companies must implement policies addressing environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance, establishing ESG metrics and reporting on them to meet regulatory requirements.
- Integration: Companies should integrate ESG considerations into their business operations and decision-making processes.
Sources

16. Disaster recovery and business continuity
Regulations
Preparing for potential disruptions and ensuring business continuity is a key compliance aspect.
Requirements
- Disaster recovery plans: Fintech companies must develop and maintain disaster recovery plans to minimize the impact of disruptions.
- Regular testing: Conducting regular testing of disaster recovery plans ensures their effectiveness.
- System resilience: Ensuring the resilience of critical systems and processes helps to maintain business operations during disruptions.
Sources
Business Continuity Institute (BCI)

17. Customer complaint handling
Regulations
Handling customer complaints efficiently and effectively is part of consumer protection compliance. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) mandates that financial institutions establish effective processes for handling customer complaints, ensuring timely resolution and adherence to consumer protection laws like the Dodd-Frank Act.
Requirements
- Complaint management system: Fintech companies must implement a robust system for managing customer complaints, ensuring that complaints are resolved in a timely manner.
- Timely resolution: Companies should ensure that customer complaints are addressed and resolved promptly.
- Data analysis: Analyzing complaint data helps to identify and address systemic issues, ensuring continuous improvement in services and compliance practices.
Sources

18. Regulatory sandboxes
Regulations
Regulatory sandboxes allow fintech companies to test innovative products and services in a controlled environment.
Requirements
- Sandbox participation: Fintech companies should engage with regulatory bodies to participate in sandbox programs, ensuring compliance with sandbox rules.
- Compliance with rules: Companies must ensure they adhere to the rules and guidelines set by the sandbox program.
- Refining practices: Using the sandbox environment to refine compliance practices before a full-scale launch helps in addressing potential regulatory issues early.
Sources
Financial Conduct Authority Sandbox
Fintech compliance challenges, best practices, and how Hyperproof can help
Maintaining compliance in the fast-paced fintech industry requires a strategic blend of best practices and robust technology. Hyperproof’s platform supports these efforts by enhancing key compliance areas, ensuring fintech companies remain agile and resilient in the face of regulatory challenges. Let’s look at some key challenges, best practices, and how Hyperproof can help you maintain fintech compliance.
Continuous monitoring and program updates
Challenges
One of the biggest challenges fintech companies face is the constant evolution of regulatory frameworks, such as new laws and amendments that require ongoing vigilance and adaptation. Furthermore, operating in multiple countries means navigating a complex web of different regulatory environments. Each jurisdiction may have unique laws regarding financial operations, data privacy, and consumer protection which complicates compliance efforts even more.
Best practices
Regularly updating compliance programs is crucial to ensure that all policies, procedures, and controls remain aligned with current regulations across all jurisdictions. Compliance monitoring requires tracking regulatory changes and assessing how these changes impact your company’s business. Your compliance efforts should be proactive, where potential issues are identified and addressed before they become significant risks.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof’s platform automates regulatory tracking and provides real-time updates. This reduces manual tasks and human error, enabling you to focus on evaluating the broader impact of regulatory change. A proactive approach ensures that compliance programs are aligned with the latest requirements freeing you to focus on business strategy.
Investment in compliance technology
Challenges
Staying compliant with all applicable regulations can be expensive, and these costs can be particularly burdensome for fintech companies. Modern compliance technology can reduce manual processes and time to scale, which helps fintech companies stay competitive in a changing market. Investing in compliance technology solutions is not just about meeting regulatory requirements — it’s about doing so efficiently and effectively.
Best practices
Choosing the right compliance technology enables you to automate complex compliance tasks, get real-time insights, and reduce your team’s manual tasks, which can be error-prone and inefficient. Additionally, advanced analytics can help avoid compliance risks and costly penalties and identify patterns that might be missed by traditional methods.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof is an integrated compliance management platform that streamlines processes and provides predictive insights. By centralizing compliance activities, the platform ensures consistency and reduces the risk of breaches, making your compliance operations more efficient.
Fostering a culture of compliance
Challenges
A robust compliance program is underpinned by a strong culture of compliance across the organization — but it can be hard to get there. Culture must be built from the top down, with executives leading by example and demonstrating a commitment to ethical business practices and employees understanding exactly why compliance is important.
Best practices
All employees, regardless of their role, should be enabled to understand the importance of compliance. Regular training sessions and continuous reinforcement of these values are essential. Also, fostering an environment where employees feel empowered to speak up about potential compliance issues without fear of retaliation is crucial for maintaining integrity within the organization. Additionally, collecting evidence for audits, conducting user access reviews, and working with the IT, compliance operations, and/or risk management teams shouldn’t feel like a chore.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof supports a compliance-centric culture by integrating with the tools people throughout your organization already use, like ServiceNow, Jira, and Asana. With Hyperproof, you can meet your colleagues where they already work and build and maintain a cohesive and uninterrupted work environment so compliance operations is no longer a chore and a hassle.
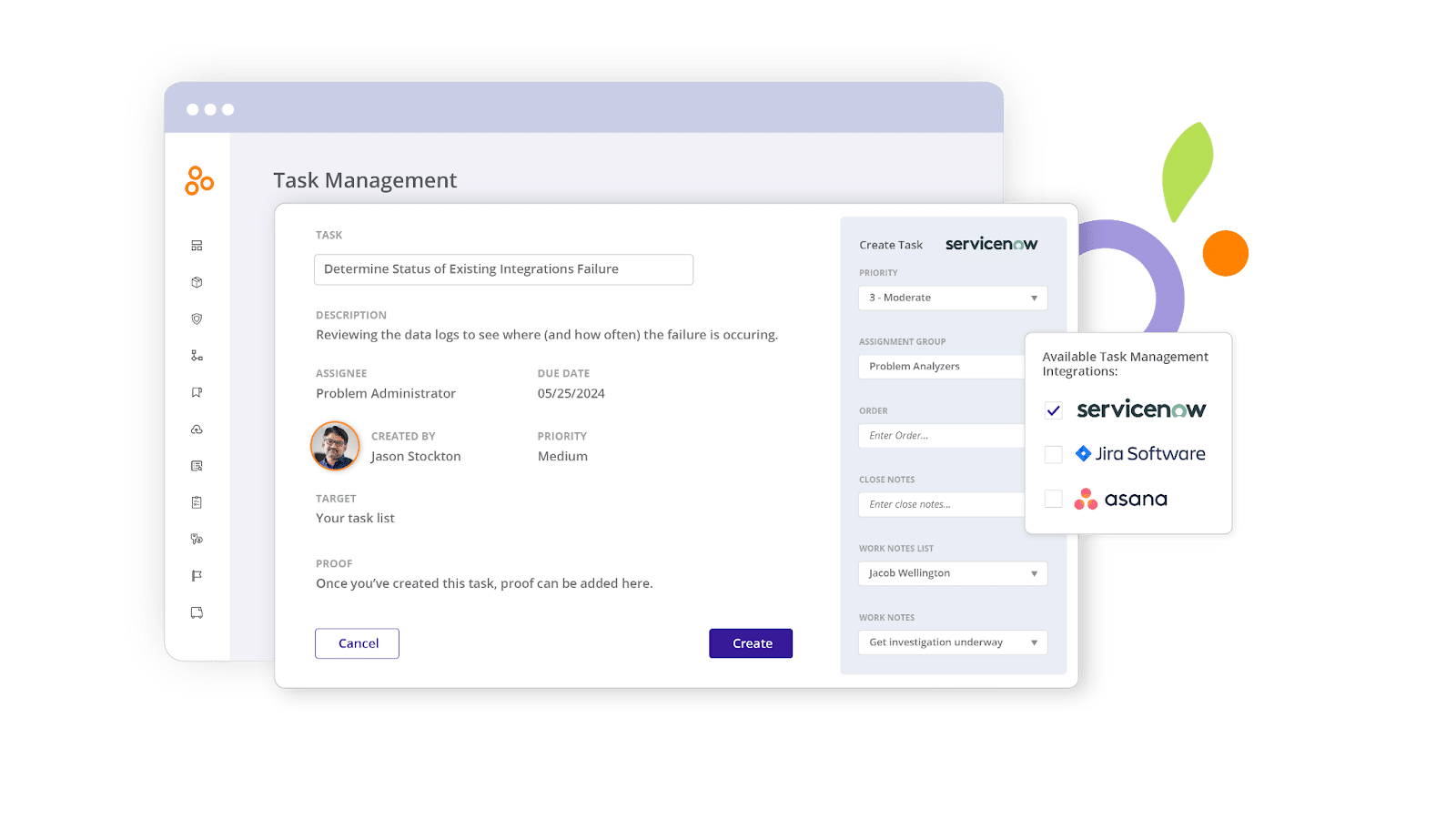
Proactive regulator engagement
Challenges
In fintech, open lines of communication with regulators can be difficult to maintain over the long run. Regulations evolve, staff members change, and people get distracted. Consistent engagement with regulatory bodies is essential to ensure that you can quickly respond to new regulations.
Best practices
Dedicate specific resources to build strong, collaborative relationships with regulators. This gives you clear insight into the regulatory landscape, which helps you navigate compliance requirements more effectively. Regular communication—combining ongoing dialogue with compliance technology—ensures your company’s commitment to compliance and fosters a more cooperative regulatory environment.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof facilitates proactive engagement by providing tools for regular communication with auditors. The platform is continuously updated to account for the latest regulatory changes, ensuring your compliance work is up-to-date. Hyperproof helps you demonstrate your company’s commitment to compliance and build strong relationships with regulatory bodies.

Continuous improvement and stakeholder collaboration
Challenge
Compliance is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Regular reviews of your compliance programs are essential to identify emerging risks and areas for enhancement. Additionally, compliance cannot be achieved in isolation—it requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including internal teams, customers, partners, and regulators.
Best practices
Creating a unified framework for compliance that brings all these stakeholders together is critical for ensuring that your compliance efforts are comprehensive and aligned with broader business objectives.
How Hyperproof can help
Hyperproof supports continuous improvement by enabling regular program reviews and providing data-driven insights. The platform enhances collaboration through centralized data storage and communication tools, ensuring all stakeholders work together towards common compliance goals.
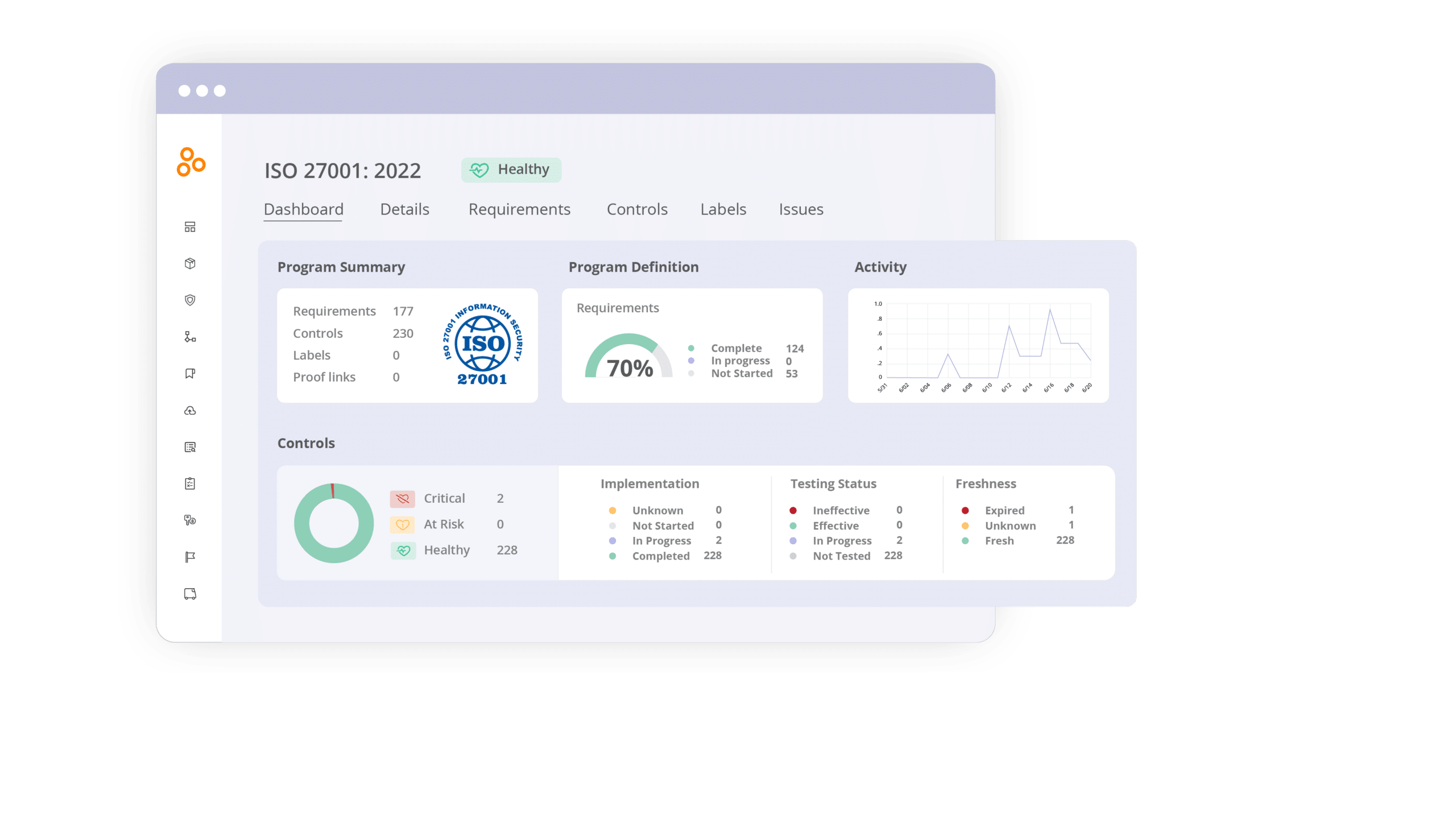
Stay compliant, agile and secure
Fintech entities face a myriad of compliance hurdles. By implementing comprehensive compliance programs and leveraging technology, companies can navigate the regulatory landscape more effectively.
Hyperproof’s solutions provide valuable support in enhancing compliance efforts, mitigating risks, and building trust with regulators, customers, and stakeholders. By addressing key areas of compliance and adopting best practices, fintech companies can maintain robust compliance programs and ensure their long-term success in a complex and dynamic industry.
Additional Resources
For more information on maintaining compliance and leveraging Hyperproof’s solutions, visit:
See Hyperproof in Action
Related Resources
Ready to see
Hyperproof in action?












